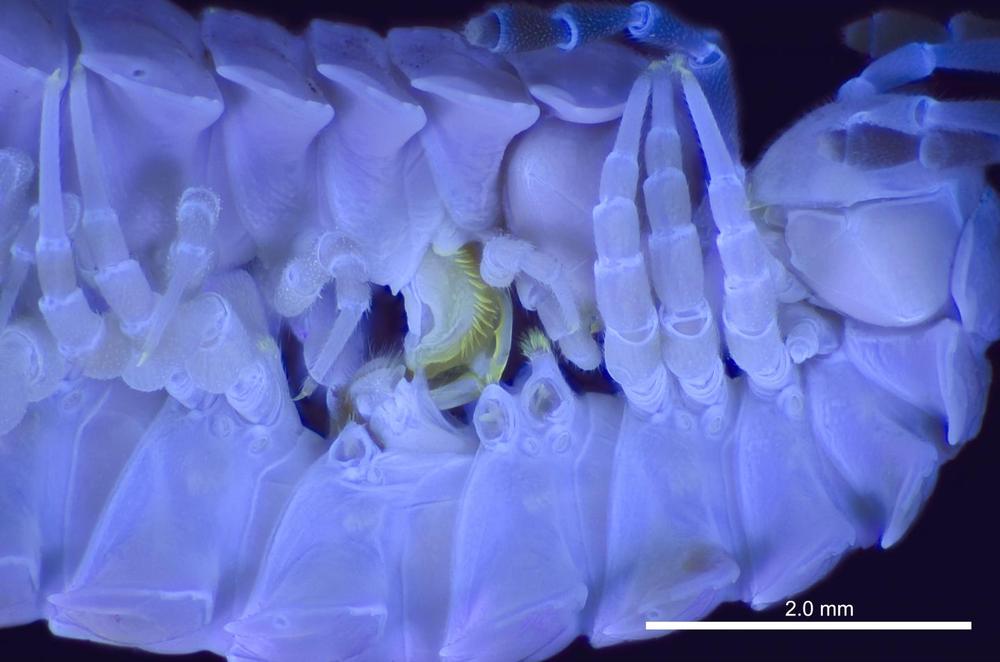
A team of US scientists has just solved a long-standing biological mystery – how exactly do millipedes mate? Using a variety of novel imaging methods, including microscopic ultraviolet photography and micro-CT scanning, the research finally figured out how these tiny creatures get it on.
“This is the first time we’ve been able to understand these millipedes’ mechanism of insertion, how the male and female organs interact with each other,” says Petra Sierwald, from Chicago’s Field Museum and one of the study’s authors. “Before this, we had no idea how he would actually get the sperm into her.”
Millipedes can generally be somewhat shy organisms, so getting them to mate in laboratory conditions hasn’t been easy. The new study focused on a type of small, brown North American millipede called Pseudopolydesmus, known for being more than willing to mate, even in the most exhibitionist situations.