Sep 14, 2016
In Search of the Next Circuit Building Method – ORNL has Ideas
Posted by Karen Hurst in category: materials
Awesome @ my friends at ORNL! Luv it and expect much success too.
No one knows what the next, best way to build electronic circuits will be. That said there’s no shortage of efforts to invent something beyond current lithography. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, perhaps not surprisingly, is in the thick of the race and two recent studies from ORNL researchers showcase promising but very different approaches.
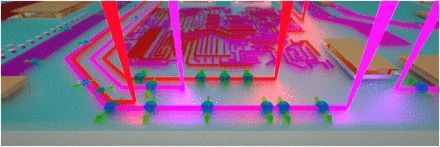
One method suggests phase change in a single complex oxide material may allow “creating” circuit elements much smaller than in today’s CMOS process while a second study puts STEM (scanning transmission electron microscopy) to work directly writing tiny patterns in metallic “ink,” forming features in liquid that are finer than half the width of a human hair. Articles describing both are posted on the ORNL web site.
Continue reading “In Search of the Next Circuit Building Method – ORNL has Ideas” »