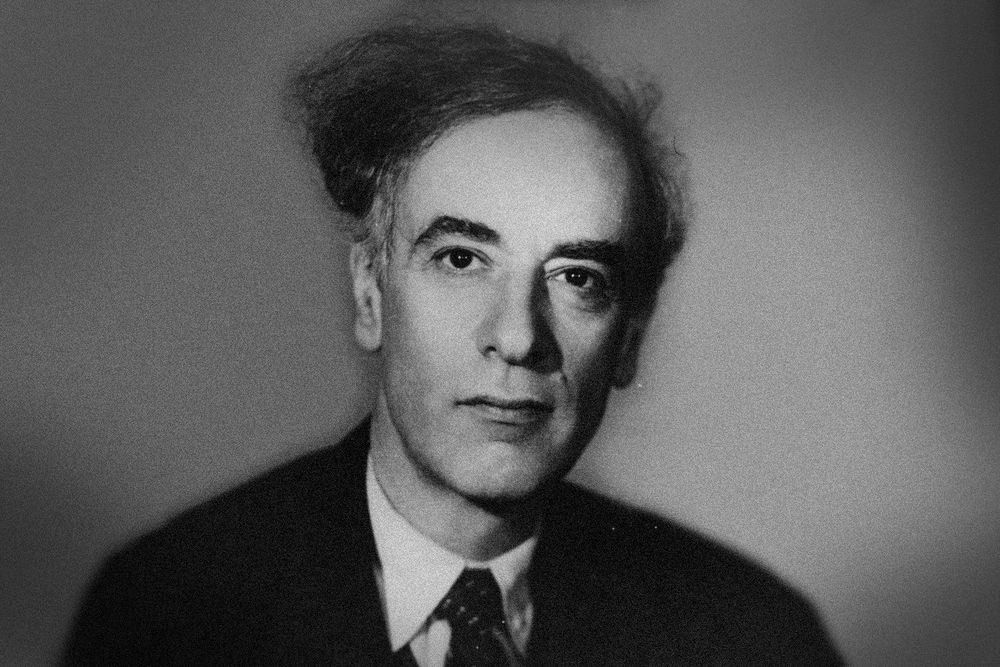A plastic cleanup project could destroy this beautiful, little-known world.
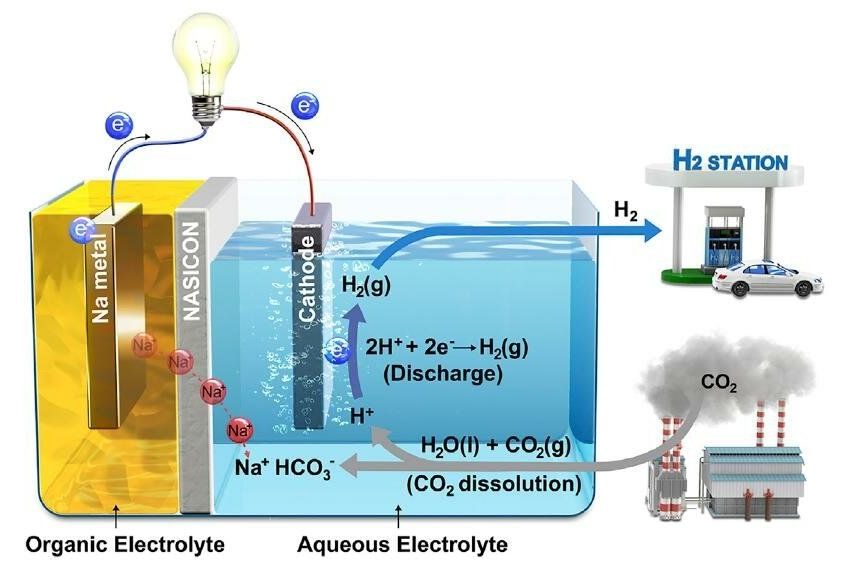
MAJOR BREAKTHROUGH: A recent study affiliated with UNIST has developed a system that produces electricity and hydrogen (H2) while eliminating carbon dioxide (CO2), the main contributor of global warming. This breakthrough has been led by Professor Guntae Kim in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST in collaboration with Professor Jaephil Cho in the Department of Energy Engineering and Professor Meilin Liu in the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Georgia Institute of Technology.
In this work, the research team presented a hybrid Na-CO2 system that can continuously produce electrical energy and hydrogen through efficient CO2 conversion with stable operation for over 1,000 hours from spontaneous CO2 dissolution in aqueous solution.
“Carbon capture, utilization, and sequestration (CCUS) technologies have recently received a great deal of attention for providing a pathway in dealing with global climate change,” says Professor Kim. “The key to that technology is the easy conversion of chemically stable CO2 molecules to other materials.” He adds, “Our new system has solved this problem with CO2 dissolution mechanism.”
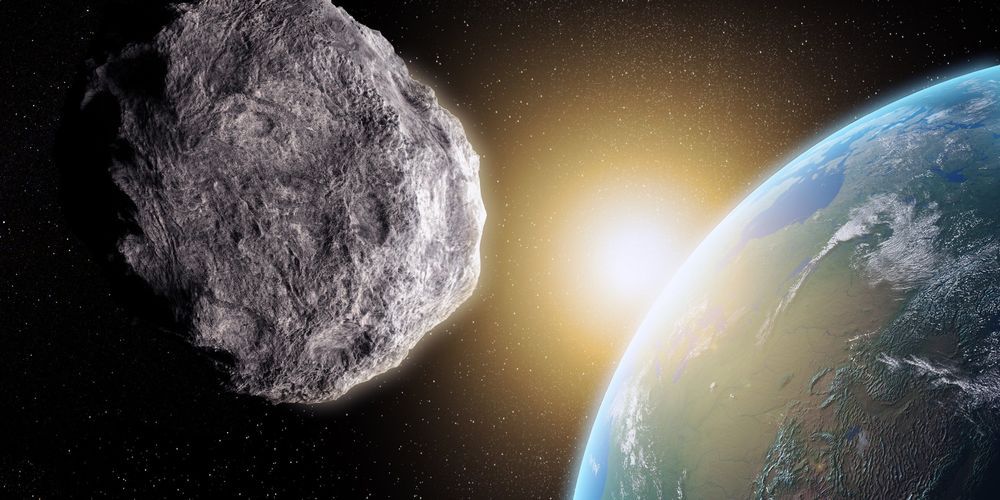
- If an asteroid were to head towards Earth in the foreseeable future, we would be quite defenceless.
- To change that, NASA has approved a mission to throw a “small” asteroid off course in October 2022.
- The aim of the project is to establish whether we can protect our planet from a future asteroid impact.
If an asteroid were to head towards Earth, we would be quite defenceless as we have not successfully developed a method that could reduce the impact of — or entirely avert — a devastating collision.
However, that may be about to change. NASA has approved a project called the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), the aim of which is to throw a “small” asteroid off course in October 2022.
Over the past 100 hundred years, the average human lifespan has increased dramatically, thanks to exponential advancements in science and technology. While living to 80, 90, and even 100 is a possibility, humans have long been in search of the ultimate discovery – immortality.
In order to achieve immortality, scientists have identified four key issues that must be overcome. These include telomere shortening, chronological aging, oxidative stress, and glycation. If these could be drastically reduced or even eliminated, immortality may just be in our reach. However, there are some promising technologies that are prolonging the human lifespan right now, and could eventually lead us to immortality.
It is definitely a creepy a concept to think about, but studies have shown that regular blood transfusions sourced can extend the human lifespan by 10–20 years. Scientists have found that a protein called GDF11 is very common in the blood of young mice, and has been shown to increase skeletal muscle and increase heart strength. This protein has been deemed to have anti-aging properties, making it a promising technology in extending human lifespan.
Who was Lev Landau?
Posted in futurism
Soviet physicist Lev Landau is being honoured with a Google Doodle on what would have been his 111th birthday.
Research at the University of Arkansas on membrane proteins could lead to better development and testing of drugs. Chemistry researchers studied a type of membrane protein that expels drugs from a cell, contributing to drug resistance. They found that the lipid composition of the cell membrane has an effect on the behavior of these proteins, which should be taken into account when testing drugs that target membrane proteins. Their results are available open-access in the journal ACS Central Science.
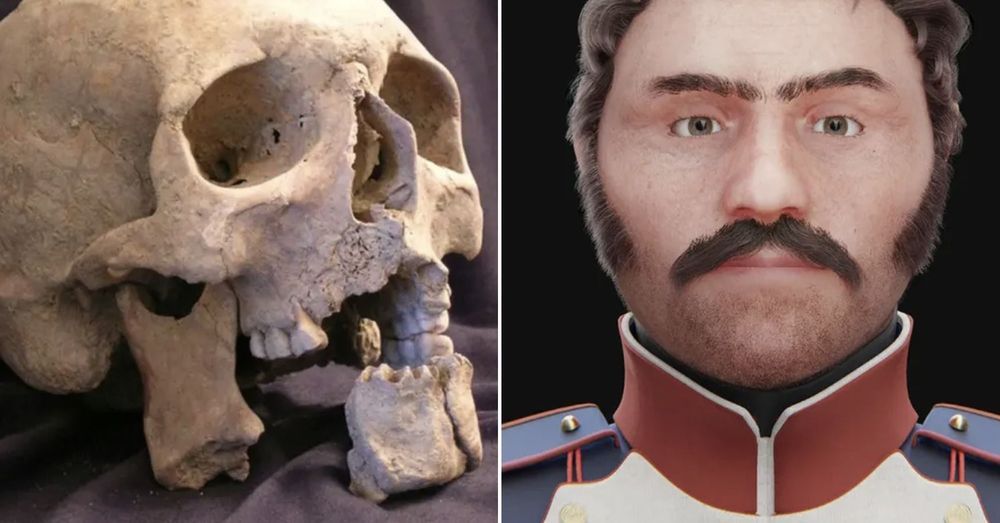
“It is a sad story, but unfortunately it is also the story of hundreds of thousands of young soldiers,” said one archaeologist.
By Dan Vergano
BuzzFeed News Reporter
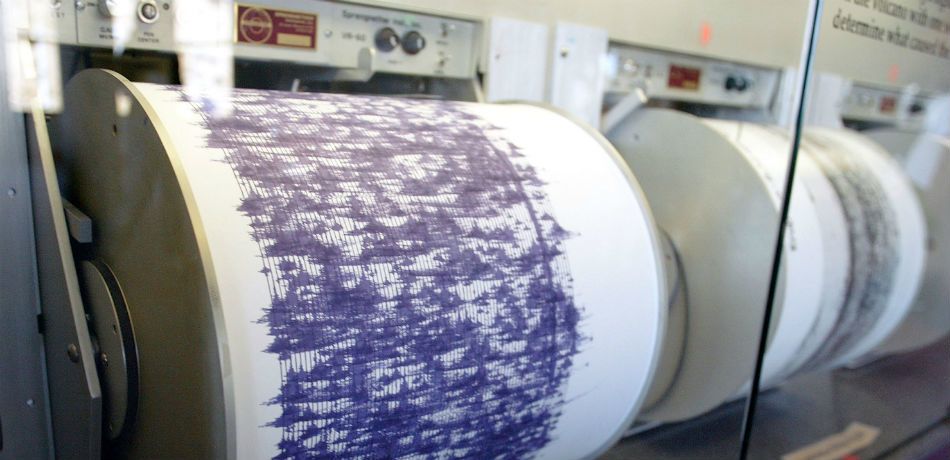
Scientists at Oregon State University have determined why foreshocks are such common indicators of large and deadly earthquakes.
Scientists involved in groundbreaking new research at Oregon State University have determined that major earthquakes are often preceded by “silent slips” and have finally discovered why foreshocks are common indicators of large and deadly earthquakes.
According to Oregon Live, major earthquakes normally follow “shallow mantle creep” and “seismic swarms,” and researchers are much clearer in their understanding now of the “silent slip,” which is what happens when different sections of the Earth’s crust can be observed shifting along the fault line. However, when this occurs, no seismic activity is ever detected, which has been confusing to researchers in the past.