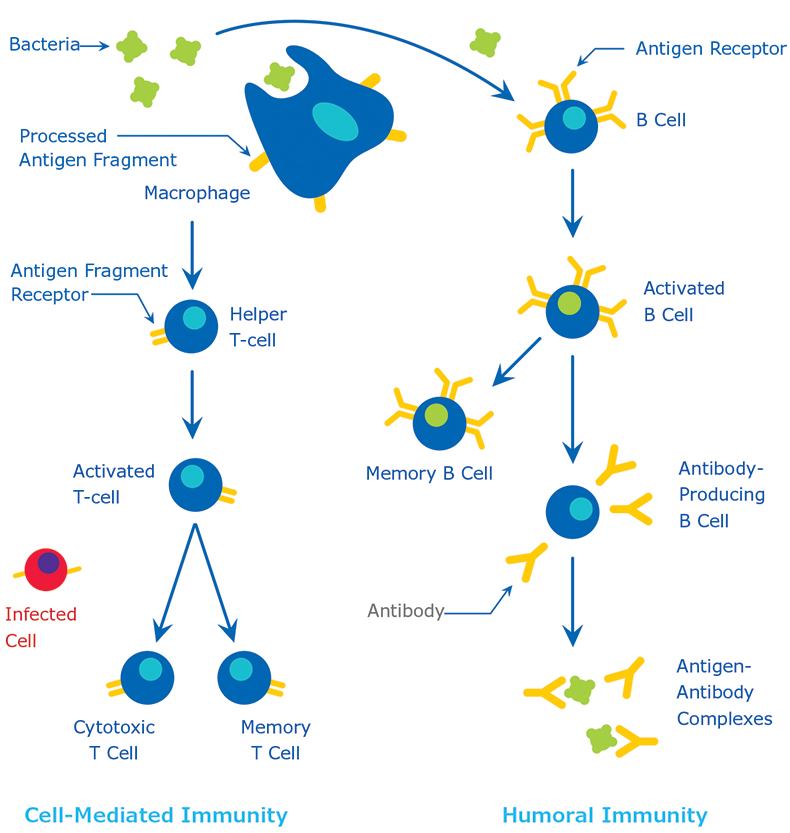
This is my business, but I bet many never heard of this:
There’s diamond under them thar plants. A geologist has discovered a thorny, palmlike plant in Liberia that seems to grow only on top of kimberlite pipes—columns of volcanic rock hundreds of meters across that extend deep into Earth, left by ancient eruptions that exhumed diamonds from the mantle. If the plant is as choosy as it seems to be, diamond hunters in West Africa will have a simple, powerful way of finding diamond-rich deposits. Prospectors are going to “jump on it like crazy,” says Steven Shirey, a geologist specializing in diamond research at the Carnegie Institution for Science in Washington, D.C.
Miners have long known that particular plants can signal ore-bearing rocks. For example, Lychnis alpina, a small pink-flowering plant in Scandinavia, and Haumaniastrum katangense, a white-flowered shrub in central Africa, are both associated with copper. That’s because the plants are especially tolerant to copper that has eroded into soils from the mother lodes.
But the new plant, identified as Pandanus candelabrum, is the first indicator species for diamond-bearing kimberlite, says Stephen Haggerty, a researcher at Florida International University in Miami and the chief exploration officer of Youssef Diamond Mining Company, which owns mining concessions in Liberia. Haggerty suspects that the plant has adapted to kimberlite soils, which are rich in magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus. “It sounds like a very good fertilizer, which it is,” says Haggerty, who has published the discovery in the June-July issue of Economic Geology.