Windows 10 users need to avoid Microsoft’s latest update, but it has already been installed by millions…


MEDUSA appears to be a popular name for directed energy weapons. There’s the MEDUSA I wrote about yesterday, a high-energy beam weapon one company hopes could destroy tanks and planes. And then there’s another MEDUSA, a nonlethal microwave weapon that was briefly funded by the Navy that uses “silent audio” (the auditory effect from microwaves). In other words, it makes you hear things in your head:
The main goal of the Phase I project wad to design and build a breadboard prototype of a temporary personnel incapacitation system called MEDUSA (Mob Excess Deterrent Using Silent Audio). This non-lethal weapon is based on the well established microwave auditory effect (MAE). MAE results in a strong sound sensation in the human head when it is irradiated with specifically selected microwave pulses of low energy. Through the combination of pulse parameters and pulse power, it is possible to raise the auditory sensation to the “discomfort” level, deterring personnel from entering a protected perimeter or, if necessary, temporarily incapacitating particular individuals. *
The idea of the “Voice of God” weapon (a weapon that makes you hear voices in your head) has been around for a while, and this small business contract was but one one modest, and likely unrelated, offshoot of other microwave-auditory effect research. The company stated at the end of “phase one” of this research: “An operating frequency was chosen — Hardware requirements were established (commercial magnetron, high-voltage pulse former) — Hardware was designed and built — Power measurements were taken and the required pulse parameters confirmed — Experimental evidence of MAE was observed.”
Branka Marijan of Project Ploughshares has a short video update on The Campaign To Stop Killer Robots.
This week, our Wednesday office update features Program Officer Branka Marijan. Branka just got back from Geneva, where the discussion of Autonomous Weapons continued! Here’s an update on the conversation.


CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. — SpaceX on Saturday fired up the rocket that will ferry the company’s next batch of Starlink satellites into space.
The company conducted a static-fire test on Saturday (Jan. 4) of a Falcon 9 rocket at Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the company said on Twitter. That rocket is expected to send 60 Starlink internet satellites into space no earlier than Monday (Jan. 6), marking the first launch of the year from Florida’s Space Coast.
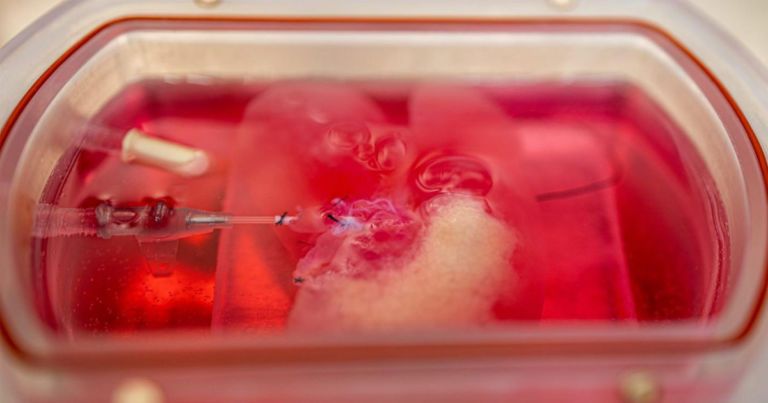
A team of Brazilian researchers have succesfully bioprinted tiny organoids that perform all of the human liver’s functions, Brazilian news service Agência FAPESP reports — functions including building proteins, storing vitamins and secreting bile.
The researchers had to cultivate and reprogram human stem cells, and then 3D print them in layers to form tissue.
While the “mini-livers” perform the functions of a liver, they’re unfortunately still a far cry from an actual full-scale liver.

A 2017 report of the discovery of a particular kind of Majorana fermion — the chiral Majorana fermion, referred to as the “angel particle” — is likely a false alarm, according to new research. Majorana fermions are enigmatic particles that act as their own antiparticle and were first hypothesized to exist in 1937. They are of immense interest to physicists because their unique properties could allow them to be used in the construction of a topological quantum computer.
A team of physicists at Penn State and the University of Wurzburg in Germany led by Cui-Zu Chang, an assistant professor of physics at Penn State studied over three dozen devices similar to the one used to produce the angel particle in the 2017 report. They found that the feature that was claimed to be the manifestation of the angel particle was unlikely to be induced by the existence of the angel particle. A paper describing the research appears on January 3, 2020 in the journal Science.
“When the Italian physicist Ettore Majorana predicted the possibility of a new fundamental particle which is its own antiparticle, little could he have envisioned the long-lasting implications of his imaginative idea.”

Hundreds of thousands of grieving Iranians attend farewell procession dedicated to General Qassem #Soleimani, former head of Iran’s elite Quds Force who was killed in a US drone strike in Iraq earlier this week.