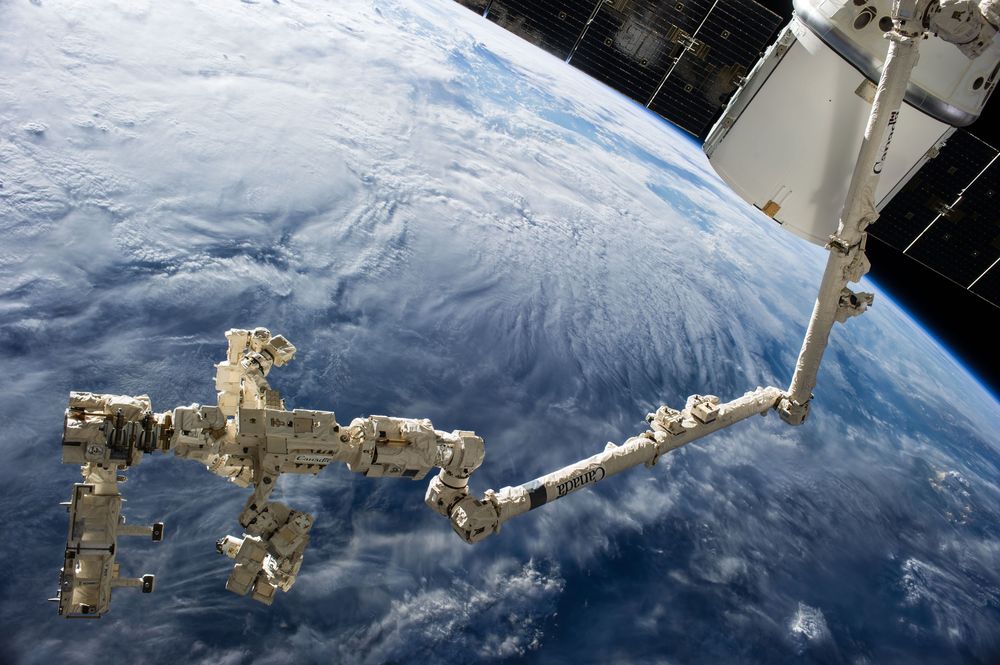
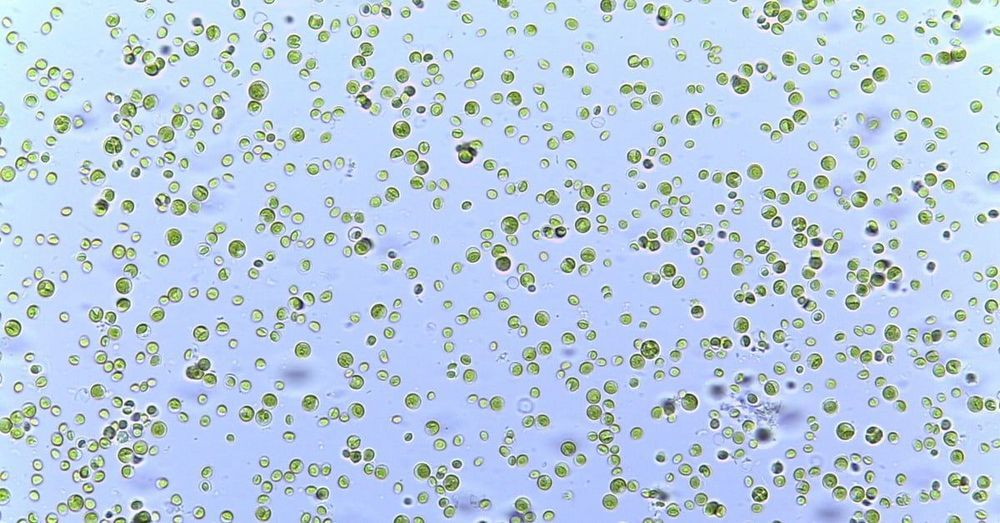
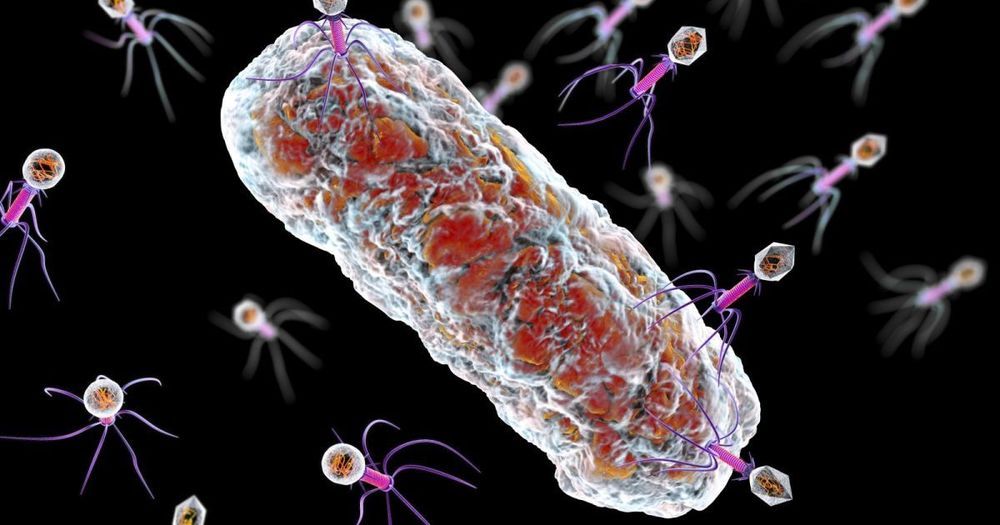
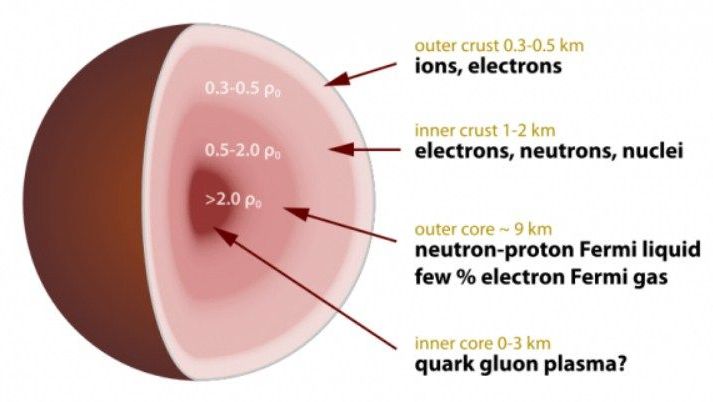
Antonin Tuynman: Where we see complexity, we see high informational content, organised in a complex way which often involves hierarchical levels. The diversity in highly complex systems might at first glance seem a chaotic mixed bag and hodgepodge; it is not. The diversified apparent mishmash is not a sign of apparent chaos, where you’d expect high thermodynamic entropy. It is not the stifling rigidity of a perfect order either. Complexity is an intricate architecture of stacked and intertwined hierarchical levels, with multifarious information exchanges between them. In fact Complexity selects the best of Order and Chaos. This seemingly ordered chaos or chaotic order, brings us the gift of the ability to ever introduce new variations. An ability to regenerate, copy, multiply and spread itself. An ability to induce ever changing patterns to adapt itself to the circumstances. An ability of recursive self-modification. Also knowhttps://www.ecstadelic.net/top-stories/the-entropic-enigma-o…amorphosis #OuroborosCode
The mighty worm Ouroboros had lost trace of its path and didn’t know its whereabouts. Nor did it know where it was going. In fact it didn’t know anything anymore, as it had drunk from the Lethe, Hades’ river flowing though Hypnos’ caves. Drinking from Lethe, forgetfulness and daughter of Eris, Goddess of Strife and Discord, made one lose all memory of past existence.
Disoriented Ouroboros started turning, and by continuing to turn, it finally found a trail of what seemed to be a path. A tasty object lay there, waiting to be eaten, and as Ouroboros bit it, a painful jolt of energy shot through its body awakening all the memories it had forgotten. Abruptly Ouroboros awoke from its dreamtime of daze and stupor and recognized itself as the ever effulgent Consciousness, Creator of Macrocosm and Microcosm.
Read more




 01:20.
01:20.