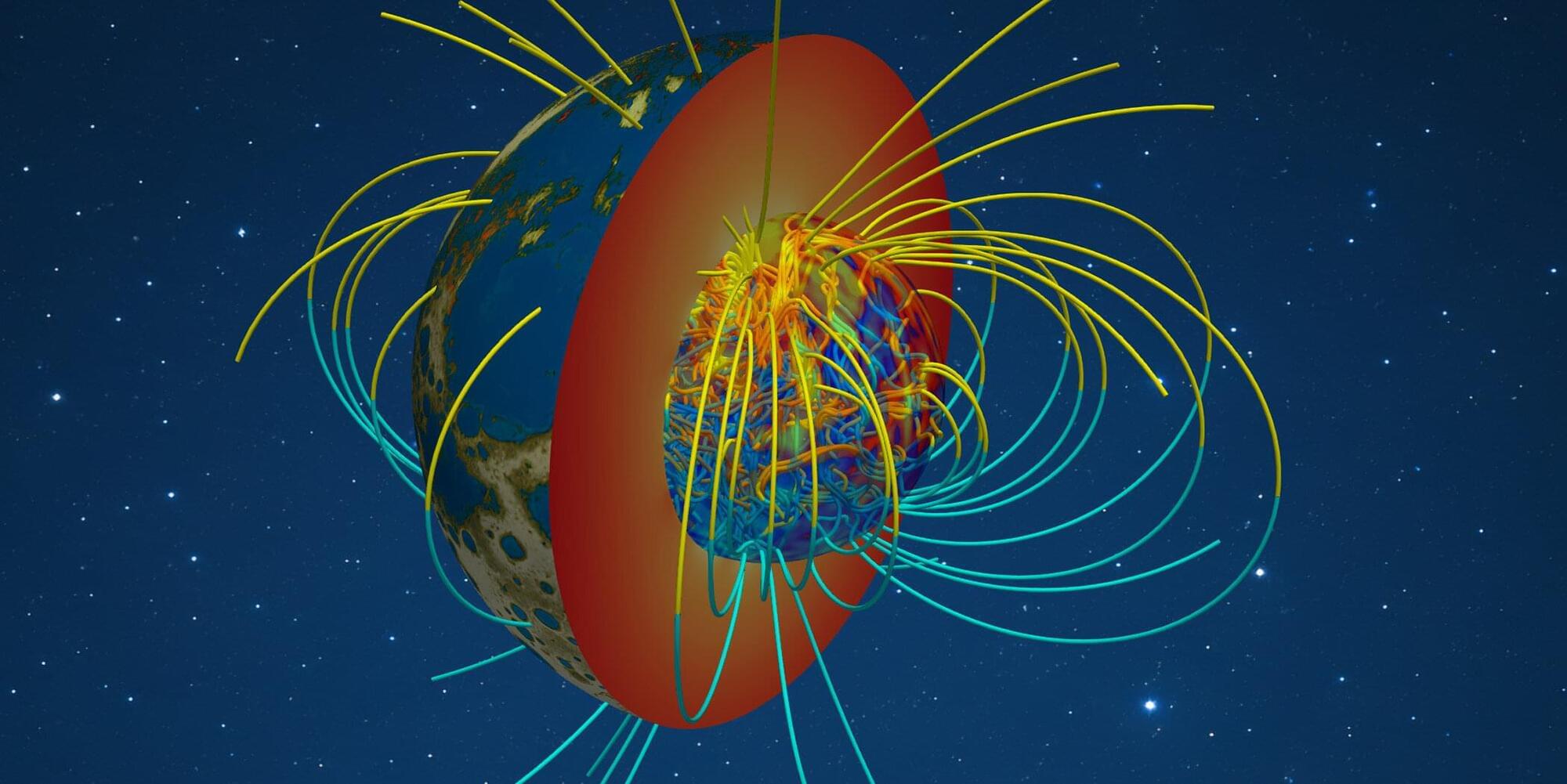
Earth is fortunate in having a magnetic field: it protects the planet and its life from harmful cosmic radiation. Other planets in our solar system—such as Mars—are constantly bombarded by charged particles that make life difficult.

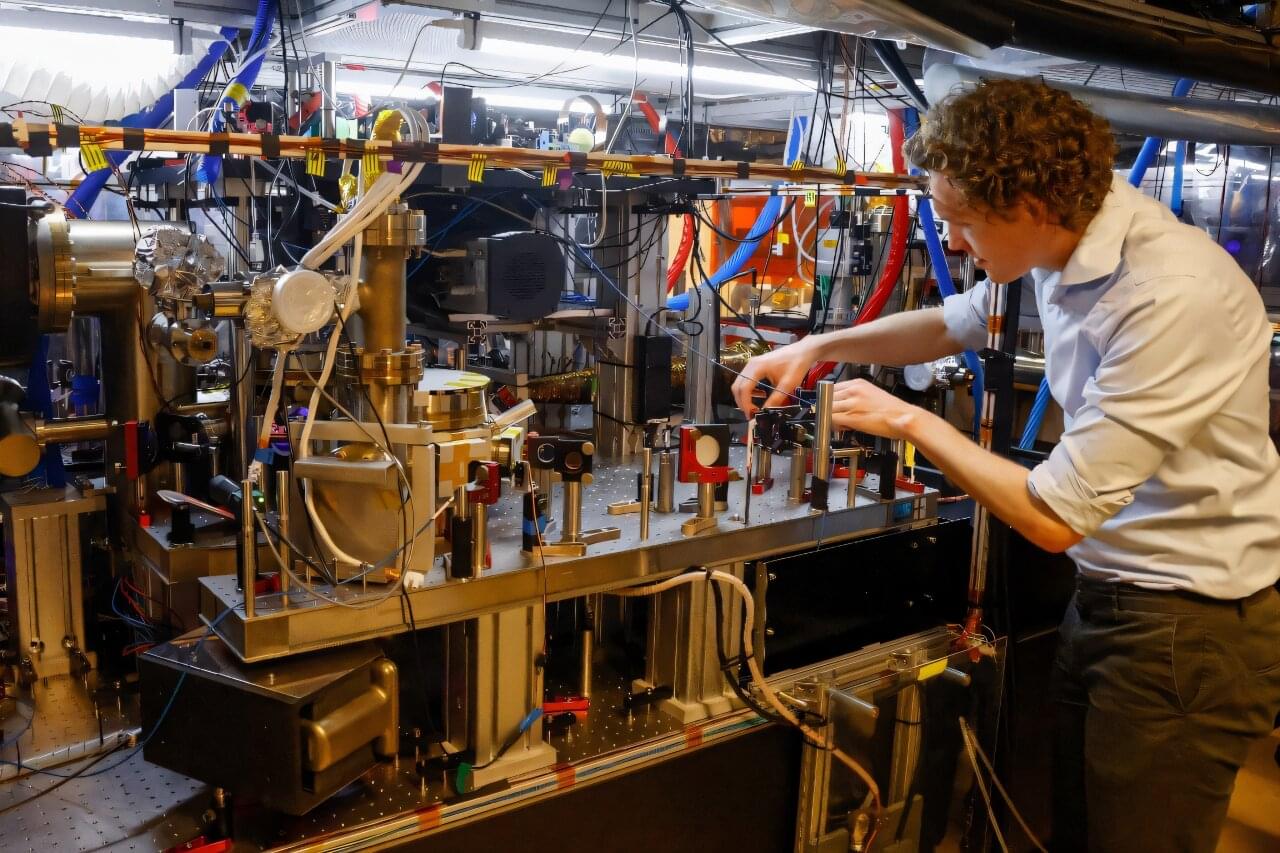
The theory of quantum mechanics has transformed daily life since being proposed a century ago, yet how it works remains a mystery—and physicists are deeply divided about what is actually going on, a survey in the journal Nature said Wednesday.
“Shut up and calculate!” is a famous quote in quantum physics that illustrates the frustration of scientists struggling to unravel one of the world’s great paradoxes.
For the last century, equations based on quantum mechanics have consistently and accurately described the behavior of extremely small objects.

Artificial intelligence and high-performance computing are driving up the demand for massive sources of energy. But neuromorphic computing, which aims to mimic the structure and function of the human brain, could present a new paradigm for energy-efficient computing.
To this end, researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) created a droplet-based platform that uses ions to perform simple neuromorphic computations. Using its ability to retain short-term memory, the team trained the droplet system to recognize handwritten digits and play tic-tac-toe. The work was published in Science Advances.
The authors were inspired by the human brain, which computes with ions instead of electrons. Ions move through fluids, and moving them may require less energy than moving electrons in solid-state devices.
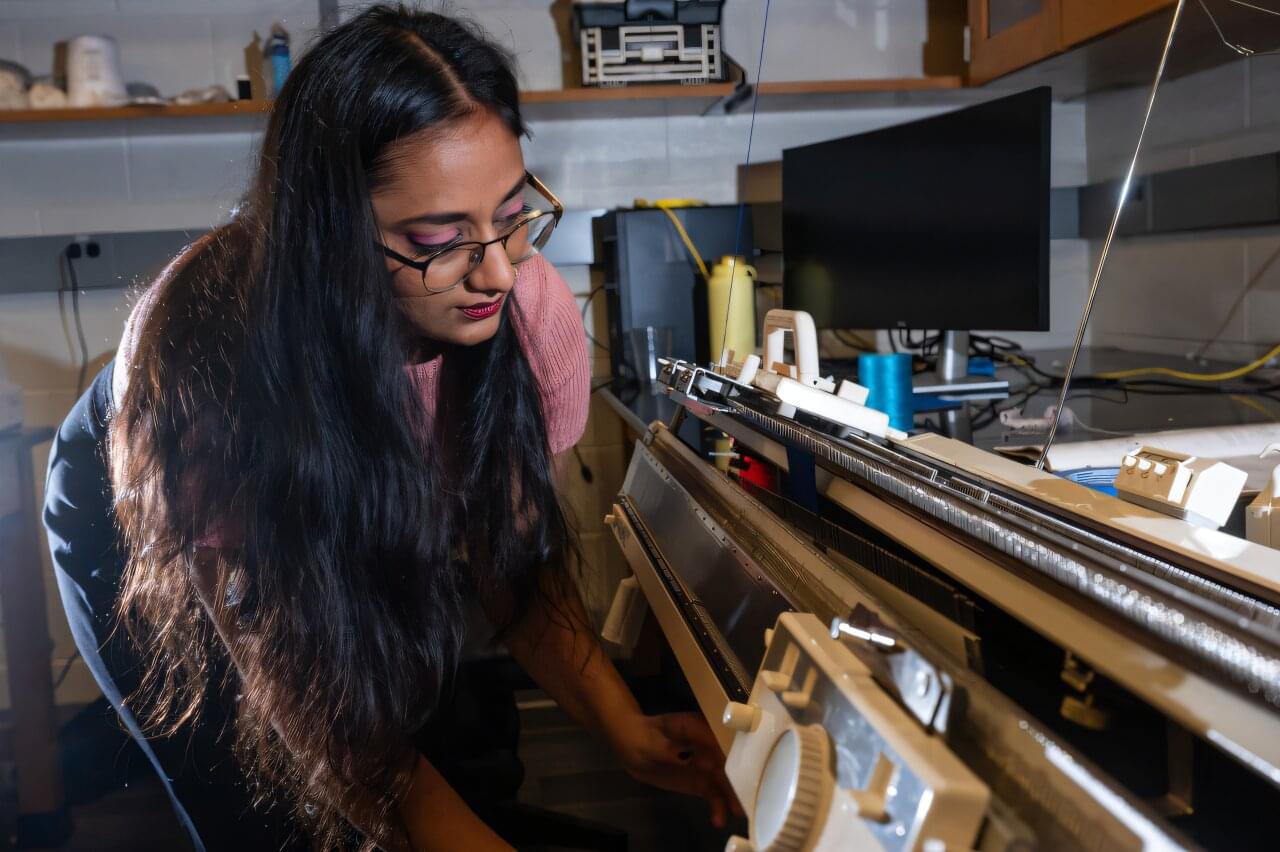

School of Physics Associate Professor Elisabetta Matsumoto is unearthing the secrets of the centuries-old practice of knitting through experiments, models, and simulations. Her goal? Leveraging knitting for breakthroughs in advanced manufacturing—including more sustainable textiles, wearable electronics, and soft robotics.
Matsumoto, who is also a principal investigator at the International Institute for Sustainability with Knotted Chiral Meta Matter (WPI-SKCM2) at Hiroshima University, is the corresponding author on a new study exploring the physics of ‘jamming’—a phenomenon when soft or stretchy materials become rigid under low stress but soften under higher tension.
The study, “Pulling Apart the Mechanisms That Lead to Jammed Knitted Fabrics,” is published in Physical Review E, and also includes Georgia Tech Matsumoto Group graduate students Sarah Gonzalez and Alexander Cachine in addition to former postdoctoral fellow Michael Dimitriyev, who is now an assistant professor at Texas A&M University.
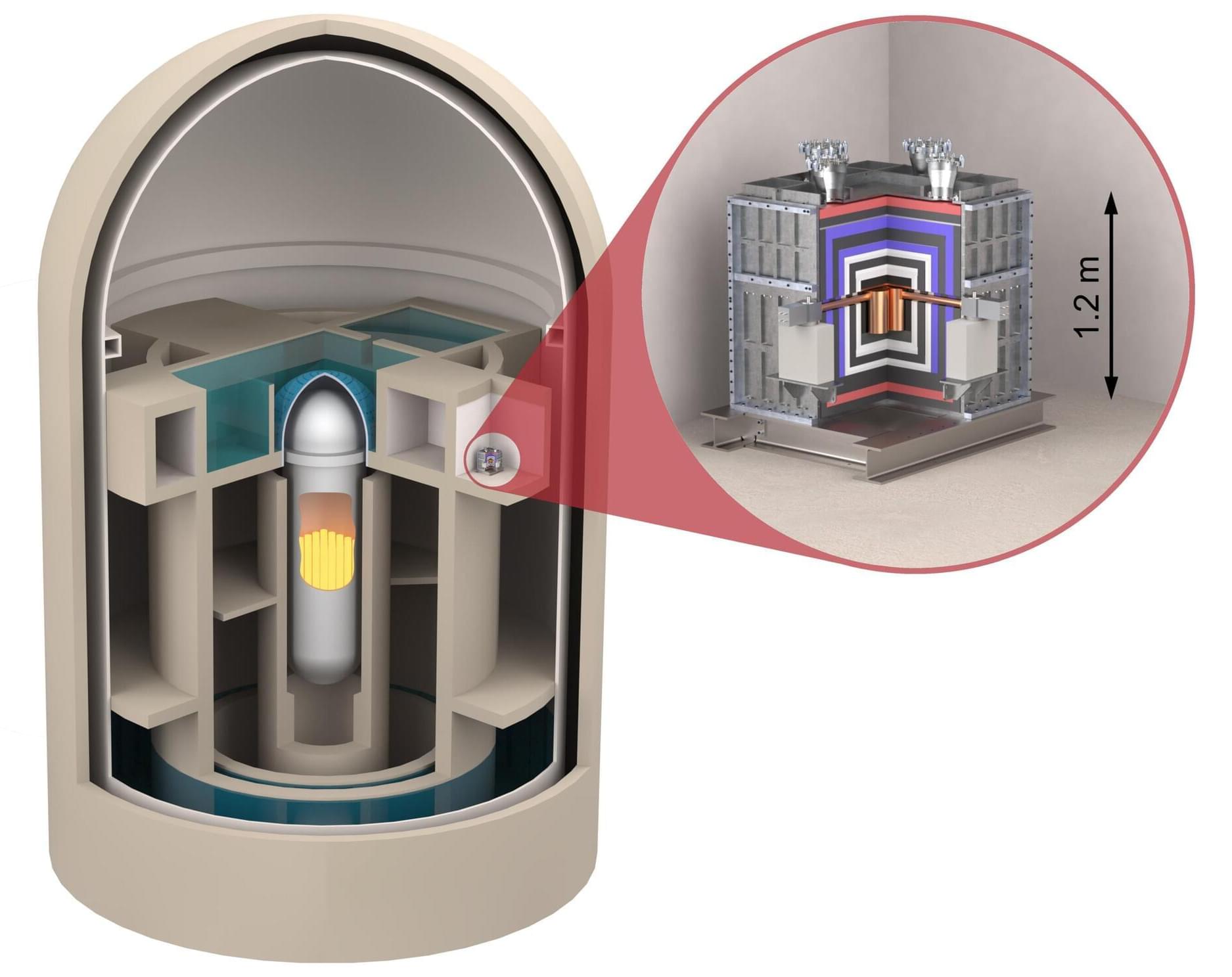
Neutrinos are extremely elusive elementary particles. Day and night, 60 billion of them stream from the sun through every square centimeter of Earth every second, which is transparent to them. After the first theoretical prediction of their existence, decades passed before they were actually detected. These experiments are usually extremely large to account for the very weak interaction of neutrinos with matter.
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics (MPIK) in Heidelberg have now succeeded in detecting antineutrinos from the reactor of a nuclear power plant using the CONUS+ experiment, with a detector mass of just 3 kg. The work is published in Nature.
Originally based at the Brokdorf nuclear power plant, the CONUS experiment was relocated to the Leibstadt nuclear power plant (KKL) in Switzerland in the summer of 2023. Improvements to the 1 kg germanium semiconductor detectors, as well as the excellent measurement conditions at KKL, made it possible for the first time to measure what is known as Coherent Elastic Neutrino-Nucleus Scattering (CEvNS).


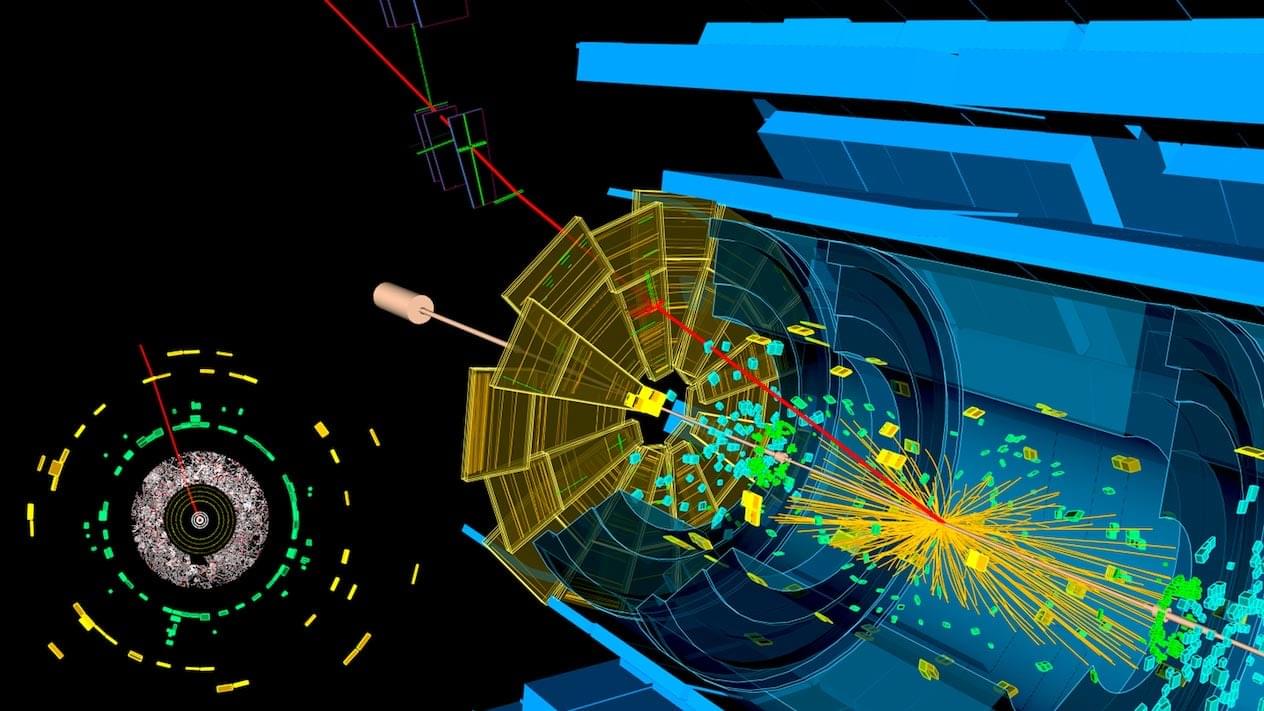
In one of the most extreme environments on Earth—the Large Hadron Collider—normal electronics fail almost instantly. But engineers at Columbia University have created custom microchips that not only survive the collider’s intense radiation but play a pivotal role in unlocking the secrets of the univ

