Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Neuroscientists Can Now Design False Memories and Plant Them Into Animal Brains
Neuroscientists-can-now-design-false-memories-and-plant-them-into-animal-brains.
Jake Anderson, The Mind Unleashed Waking Times
Scientists have known for some time that specific circuits in the brain react to experiences and encode those same experiences into our minds as memories. These memories are central to our identity and the narrative we construct about ourselves and the world around us.
In past experiments, neuroscientists have been able to partially transfer memories between rodents but they have never wholesale manufactured false memories—until now.

Fisherman found SpaceX Crew Dragon’s parachute compartment door in the ocean
Featured Image Source: David Stokes
SpaceX aims to launch NASA Astronauts to the International Space Station for the first time this year aboard their updated Dragon spacecraft, known as Crew Dragon. The spacecraft successfully conducted the most important safety test last month during an uncrewed In-Flight Abort (IFA) mission which tested the craft’s launch escape system capabilities. During the IFA test, engineers mimicked a real flight to space except that they purposely caused their Falcon 9 rocket to “malfunction” by shutting down its 9 Merlin 1D engines in order to trigger Dragon’s launch escape countdown. Falcon 9 aerodynamically exploded mid-air, as Dragon successfully ignited its 8 SuperDraco engines to escape the danger.
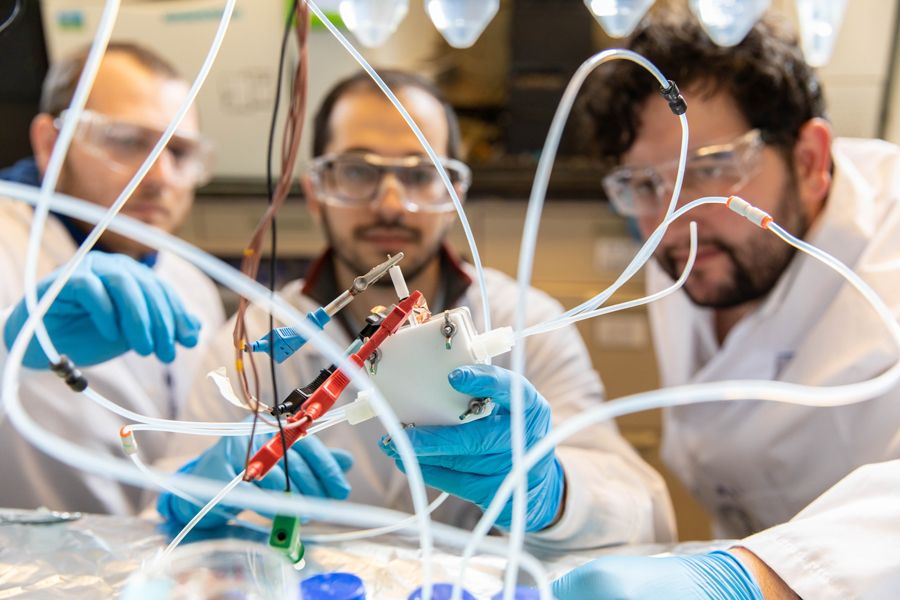

“Reverse fuel cell” converts waste carbon to valuable products at record rates
Fuel cells turn chemicals into electricity. Now, a U of T Engineering team has adapted technology from fuel cells to do the reverse: harness electricity to make valuable chemicals from waste carbon (CO2).
“For decades, talented researchers have been developing systems that convert electricity into hydrogen and back again,” says Professor Ted Sargent (ECE), one of the senior authors of a paper published today in Science. “Our innovation builds on that legacy, but by using carbon-based molecules, we can plug directly into existing hydrocarbon infrastructure.”
In a hydrogen fuel cell, hydrogen and oxygen come together on the surface of a catalyst. The chemical reaction releases electrons, which are captured by specialized materials within the fuel cell and pumped into a circuit.
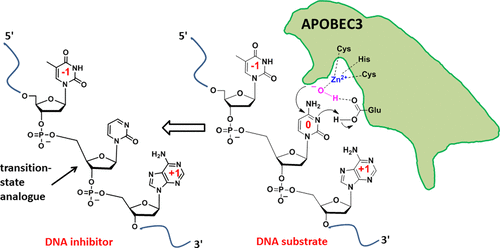
Chemistry in Coronavirus Research: A Free to Read Collection from the American Chemical Society
ACS Publications is providing free access to articles related to the #coronavirus, in support of the on-going coronavirus outbreak relief efforts in #China.
View the Virtual Issue to access all available articles:
In light of the current outbreak of a novel coronavirus (2019–nCoV), ACS Publications would like to share this Virtual Issue that features a collection of articles on coronavirus research. Chemistry has a key role to play in understanding everything from viral structure to pathogenesis, isolation of vaccines and therapies, as well as in the development of materials and techniques used by basic researchers, virologists and clinicians. This Virtual Issue aims to provide a brief overview of the important contributions of chemistry to understanding and controlling the spread of coronaviruses and includes articles from„„, and as well as the preprint server ChemRxiv. We hope the research contained in this Virtual Issue will provide you with important insight into challenges and approaches in virus research.
