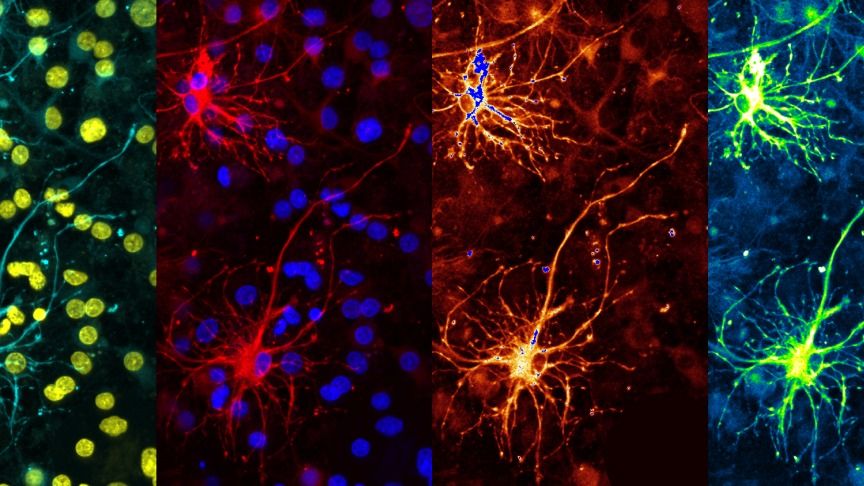
In this Viewpoint, Geoffrey Hinton of Google’s Brain Team discusses the basics of neural networks: their underlying data structures, how they can be trained and combined to process complex health data sets, and future prospects for harnessing their unsupervised learning to clinical challenges.
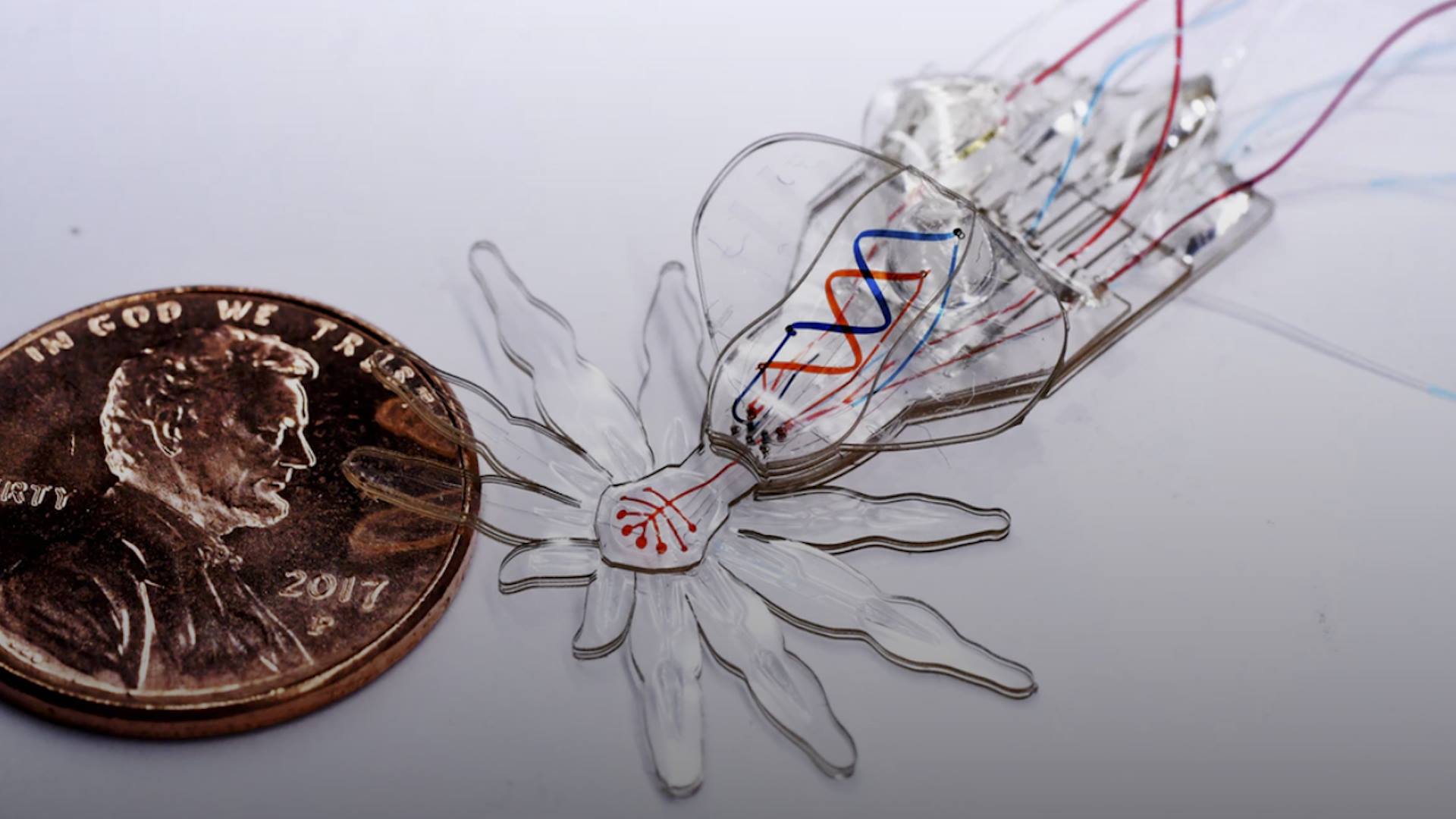
As an immediate application, Neural Lace could potentially help patients suffering from brain injuries and certain illnesses. However, the utimate goal and mission of Neuralink are to successfully merge the human brain with machine, fusing human intelligence with Artificial Intelligence. As a result, this is expected to bring humanity up to a higher level of cognitive reasoning.
Neural Lace: How it works
At some point, Neural Lace is going to enable humans to upload and download information directly from a computer. Just in a similar way how Neo from the Matrix does in order to learn new skills and acquire new information.
Now, another hurricane season is already underway in the Caribbean.
Our research on rainwater harvesting — a low-cost, low-tech way to collect and store rainwater — suggests this technique could be deployed across the Caribbean to improve these communities’ access to water both after storms and in everyday life.
Even before hurricanes Maria and Irma hit last September, some Caribbean islands were unable to provide reliable clean water for drinking and washing to all residents.
An extraordinary new anti-ageing technique could see humans live to 150 years old and allow them to regrow their organs by 2020.
Harvard Professor David Sinclair and researchers from the University of New South Wales developed the new process, which involves reprogramming cells.
Dr Sinclair said the technique could allow people to regenerate organs, and even allow paralysis sufferers to move again, with human trials due within two years.