Researchers detail new AI and phishing kits that steal credentials, bypass MFA, and scale attacks across major services.




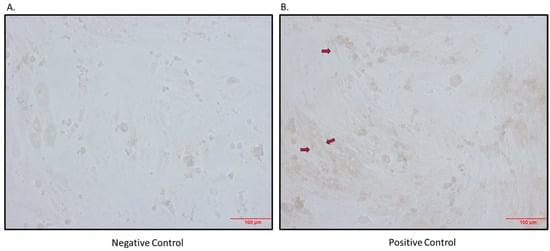
The hyperactivation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is linked to obesity, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes, which are characterized by elevated norepinephrine (NE) levels. Previous research has shown increased sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) protein levels in kidneys of hypertensive rodents, prompting investigation into the expression of SGLT1 in various tissues, such as skeletal muscle. This study aimed to assess (i) whether skeletal muscle cells and tissue express SGLT1 and SGLT2 proteins; (ii) if NE increases SGLT1 levels in skeletal muscle cells, and (iii) whether the skeletal muscle of neurogenically hypertensive mice exhibits increased SGLT1 expression. We found that (i) skeletal muscle cells and tissue are a novel source of the SGLT2 protein and that (ii) NE significantly elevated SGLT1 levels in skeletal muscle cells. As SGLT2 inhibition (SGLT2i) with Empagliflozin increased SGLT1 levels, in vivo studies with the dual inhibitor SGLT1/2i, Sotagliflozin were warranted. The treatment of neurogenically hypertensive mice using Sotagliflozin significantly reduced blood pressure. Our findings suggest that SNS activity upregulates the therapeutic target, SGLT1, in skeletal muscle, potentially worsening cardiometabolic control. As clinical trial data suggest cardiorenal benefits from SGLT2i, future studies should aim to utilize SGLT1i by itself, which may offer a therapeutic strategy for conditions with heightened SNS activity, such as hypertension, diabetes, and obesity.
This case-control study found that adults with schizophrenia had significantly greater frontal cortex serotonin release than healthy controls, and greater release correlated with more severe negative symptoms.
Question Is serotonin release altered in vivo in schizophrenia, and is it associated with negative symptom severity?
Findings In this case-control neuroimaging study that included 54 adults, frontal cortex serotonin release was significantly greater in the 26 people with DSM-5 schizophrenia compared with 28 matched healthy controls. In schizophrenia, greater frontal cortex serotonin release was associated with more severe baseline negative symptoms.
Meaning Findings suggest that serotonergic dysfunction in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia was associated with negative symptoms, identifying the regulation of serotonergic neurotransmission as a potential target to treat negative symptoms.
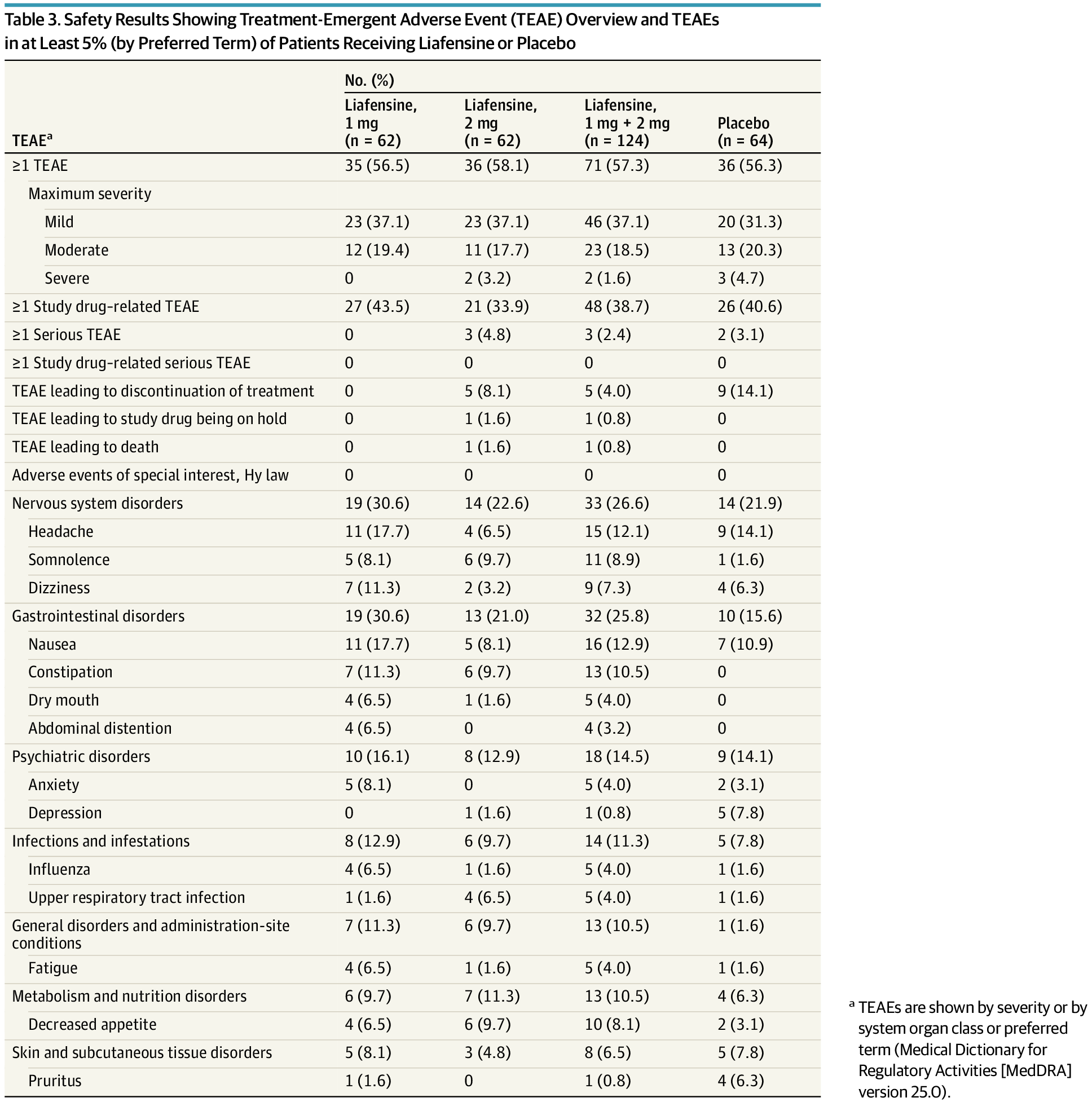
Liafensine was efficacious and well tolerated in ANK3-positive patients with treatment-resistant depression, with clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvements over placebo, highlighting ANK3 as a predictive genetic biomarker for liafensine.
Question Does the newly discovered ANK3 pharmacogenomic biomarker predict the response of patients with treatment-resistant depression (TRD) to liafensine, a triple reuptake inhibitor, despite failure in a non–biomarker-selected TRD patient population in prior phase 2b trials?
Findings In this randomized clinical trial including 189 ANK3-positive patients with TRD, liafensine demonstrated a 4.4-point Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale improvement over placebo, a clinically meaningful and statistically significant difference.
Meaning This represents a first successful genetic biomarker-guided clinical trial in psychiatry, advancing a new treatment for TRD and providing a new path for developing precision medicines in the field.
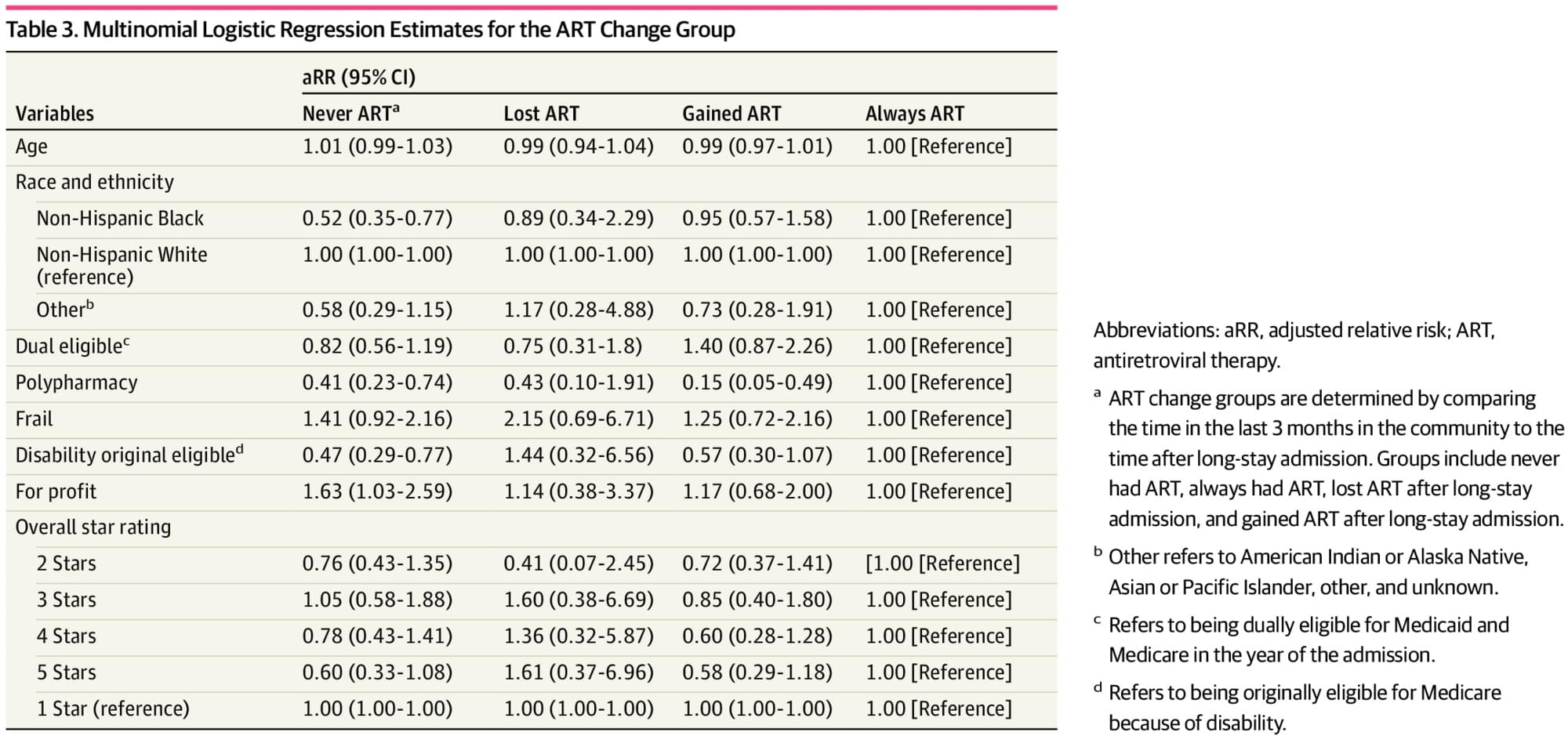
Access to antiretroviral therapy (ART) appears to improve when Medicare beneficiaries with HIV transition to long-term nursing homes, but nursing homes miss opportunities for initiation, as most stays without ART never had ART before admission.
This cohort study aimed to understand changes in ART use for Medicare beneficiaries with HIV transitioning from the community to long NH stays. We found that among a group with a mean age of 61 years, ART use seemed to improve after the transition, that there was no ART use before or after the transition for nearly one-quarter of our sample, and that comorbidities and frailty had no association with ART changes. These findings are contrary to our hypothesis that posited lower ART use after the transition and that lower NH quality rating would be associated with even lower ART use. These findings are critically important to our understanding of NH care for people with HIV because they dispel select concerns that the transition to long-stay NH resident and the transition from Medicare Part A to Part D medication benefits are opportunities for reduced ART use.
Few NHs have experience caring for people with HIV, with many seeing only 1 or 2 individuals in a 3-year span.9 Experience with HIV care correlates with better health outcomes in both the NH setting and the outpatient setting.8 Many community-based studies have found that better adherence to ART is associated with older age,29, 30 and 1 study of NH residents with HIV showed that longer duration of an NH stay was associated with better ART adherence,13 although that same study found that 21% of people with HIV in NHs had no ART. Without following people from the outpatient or community setting into the NH setting, these previous studies were limited in their generalizability because of selection bias; they examined only people with HIV using outpatient services, or only people with HIV using NHs.

Scientists at the University College London (UCL) have developed a novel therapy that helps treat patients with T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). This form of therapy used genome editing tools to modify immune cells and boost immune system response. T-ALL is a rare and aggressive blood cancer that affects specialized immune cells, known as T cells. This immune subset is responsible for identifying and targeting foreign pathogens. Unfortunately, in T-ALL, genetic mutations prevent T cells from maturing and properly functioning.
The world’s first gene therapy (BE-CAR7) uses base-editing, which can specifically change a single base in a cell’s DNA. BE-CAR7 was the first therapy to treat T-ALL in both children and adults. In 2022, a 13-year old girl was given BE-CAR7 followed by another eight children and two adults undergoing the same treatment. The following results from these patients were published in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), by Dr. Waseem Qasim and others. Qasim is a Professor of Cell and Gene Therapy in the Department of Infection, Immunity, and Inflammation at the UCL. His work focuses on pediatric oncology with a focus in gene therapy. Qasim’s work has long involved treatment of T-ALL and improving therapies for children with leukemia.
Qasim and his team reported that 82% of patients receiving BE-CAR7 achieved remission, which allowed them to undergo stem cell transplant without disease. Treatment was accompanied by tolerable side effects, including low blood counts, cytokine release syndrome, and rashes. Additionally, 64% of patients remained disease-free even after three years. These remarkable results indicate the strong impact gene therapy has on T-ALL.

A single-dose oral medication called zoliflodacin shows promise as a new treatment for antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea, according to a Phase III trial published in The Lancet.
The study found that one dose of zoliflodacin was as effective as the current standard treatment, which combines two antibiotics: an injection of ceftriaxone followed by an oral dose of azithromycin.
Gonorrhea is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections, affecting over 82 million people globally each year. However, it is increasingly difficult to treat as the bacteria that cause infection develop resistance to current antibiotics. This new medication has the potential to help slow the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and make gonorrhea treatment more accessible worldwide.
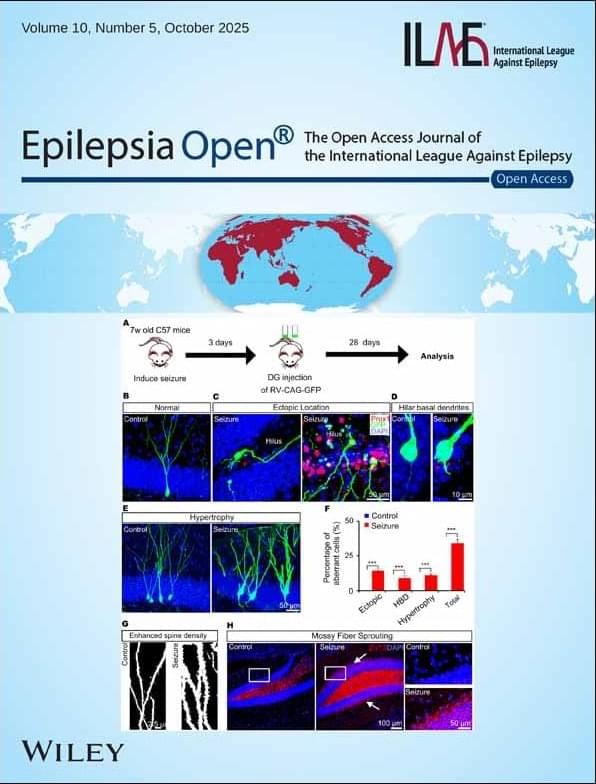
“Ultra-refractory epilepsy (URE) is a newly described form of extremely difficult-to-treat epilepsy. In our study of 62 patients, all had already failed at least six different treatment attempts, including medications, brain surgery, or nerve stimulation. Most patients continued to have frequent seizures despite all available therapies, and only a small minority achieved long-term seizure freedom. These findings show that URE is a severe condition with a major unmet medical need, highlighting the importance of developing new treatment strategies.”
Read this original article from Epilepsia Open Journal at doi.org/10.1002/epi4.70196.
Objective Drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) is defined as the failure of two antiseizure medications (ASMs) to achieve complete seizure control, affecting approximately 30% of epilepsy patients. In some cases, additional ASMs and surgical approaches are also unsuccessful. Ultra-Refractory Epilepsy (URE) is a newly described entity, characterized by the failure of six distinct epilepsy treatment strategies, including ASMs, surgical resection, and neurostimulation techniques. This study aimed to analyze demographic and clinical data of URE patients managed at the Brno Epilepsy Center, a member of the European Reference Network (ERN)—EpiCARE.