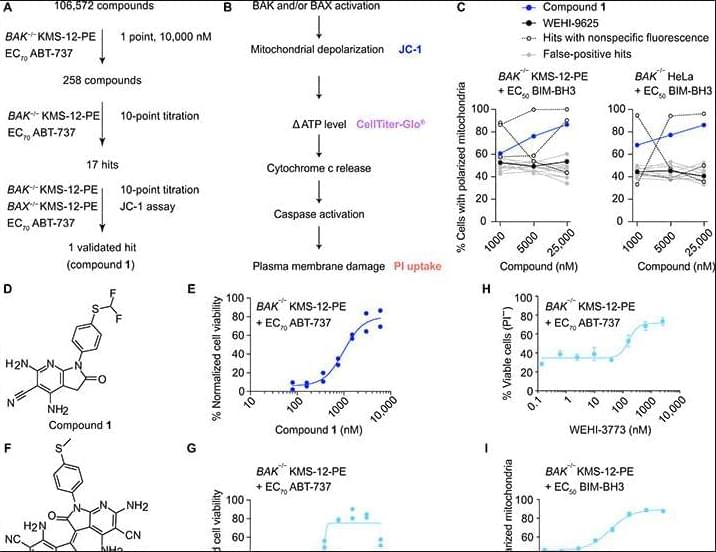
Opposing regulation of BAX and BAK by VDAC2 dictates their role as executioners of apoptosis and their therapeutic targeting.


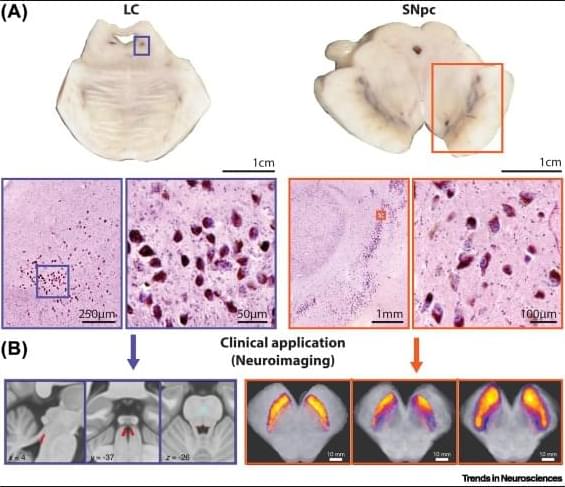
Neuromelanin is a unique pigment made by some human catecholamine neurons. These neurons survive with their neuromelanin content for a lifetime but can also be affected by age-related neurodegenerative conditions, as observed using new neuromelanin imaging techniques. The limited quantities of neuromelanin has made understanding its normal biology difficult, but recent rodent and primate models, as well as omics studies, have confirmed its importance for selective neuronal loss in Parkinson’s disease (PD). We review the development of neuromelanin in dopamine versus noradrenaline neurons and focus on previously overlooked cellular organelles in neuromelanin formation and function. We discuss the role of neuromelanin in stimulating endogenous α-synuclein misfolding in PD which renders neuromelanin granules vulnerable, and can exacerbates other pathogenic processes.
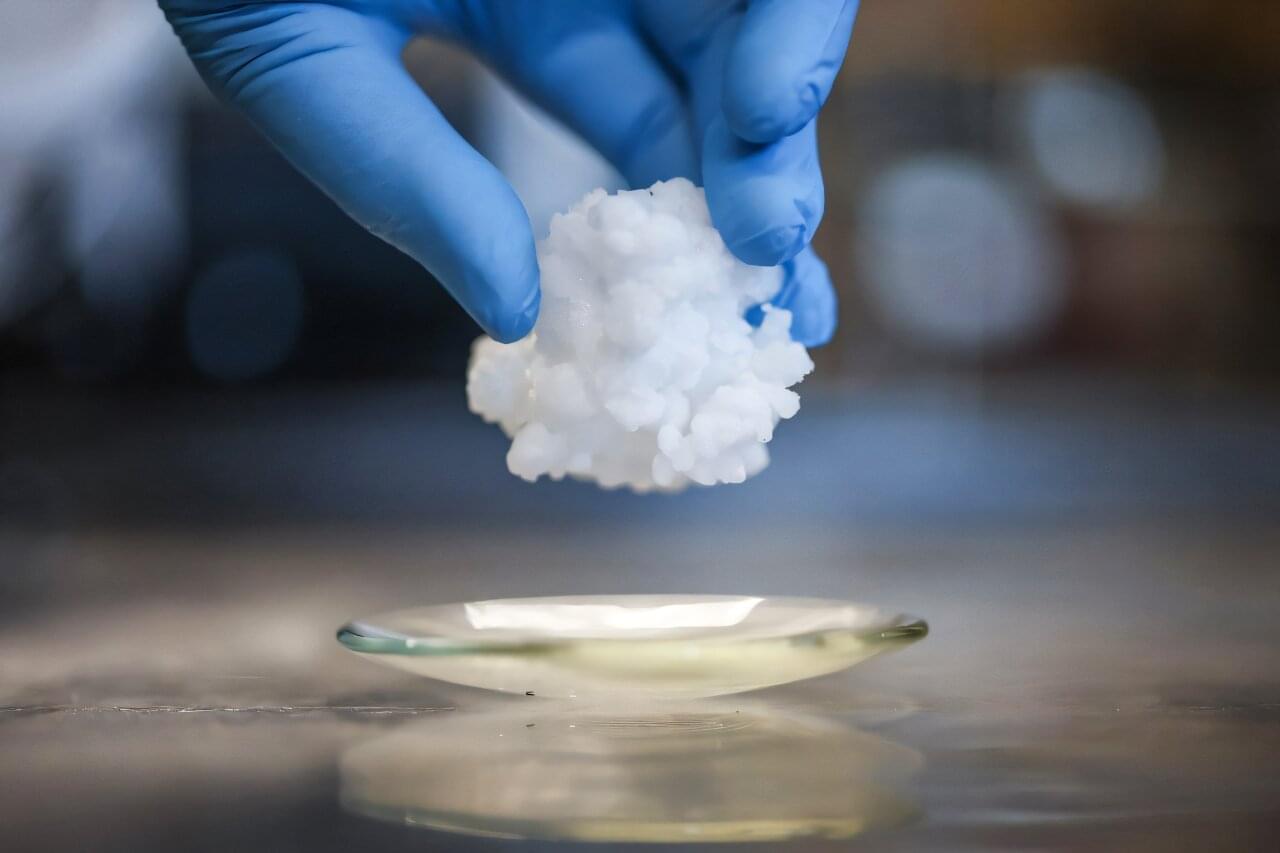

The soft, waxy “solid refrigerant” being investigated in a UK laboratory may not look very exciting, but its unusual properties promise an air-conditioning revolution that could eliminate the need for greenhouse gases.
The substance’s temperature can vary by more than 50 degrees Celsius (90 degrees Fahrenheit) under pressure, and unlike the gases currently used in appliances solid refrigerants, it does not leak.
“They don’t contribute to global warming, but also they are potentially more energy efficient,” Xavier Moya, a professor of materials physics at the University of Cambridge, told AFP.
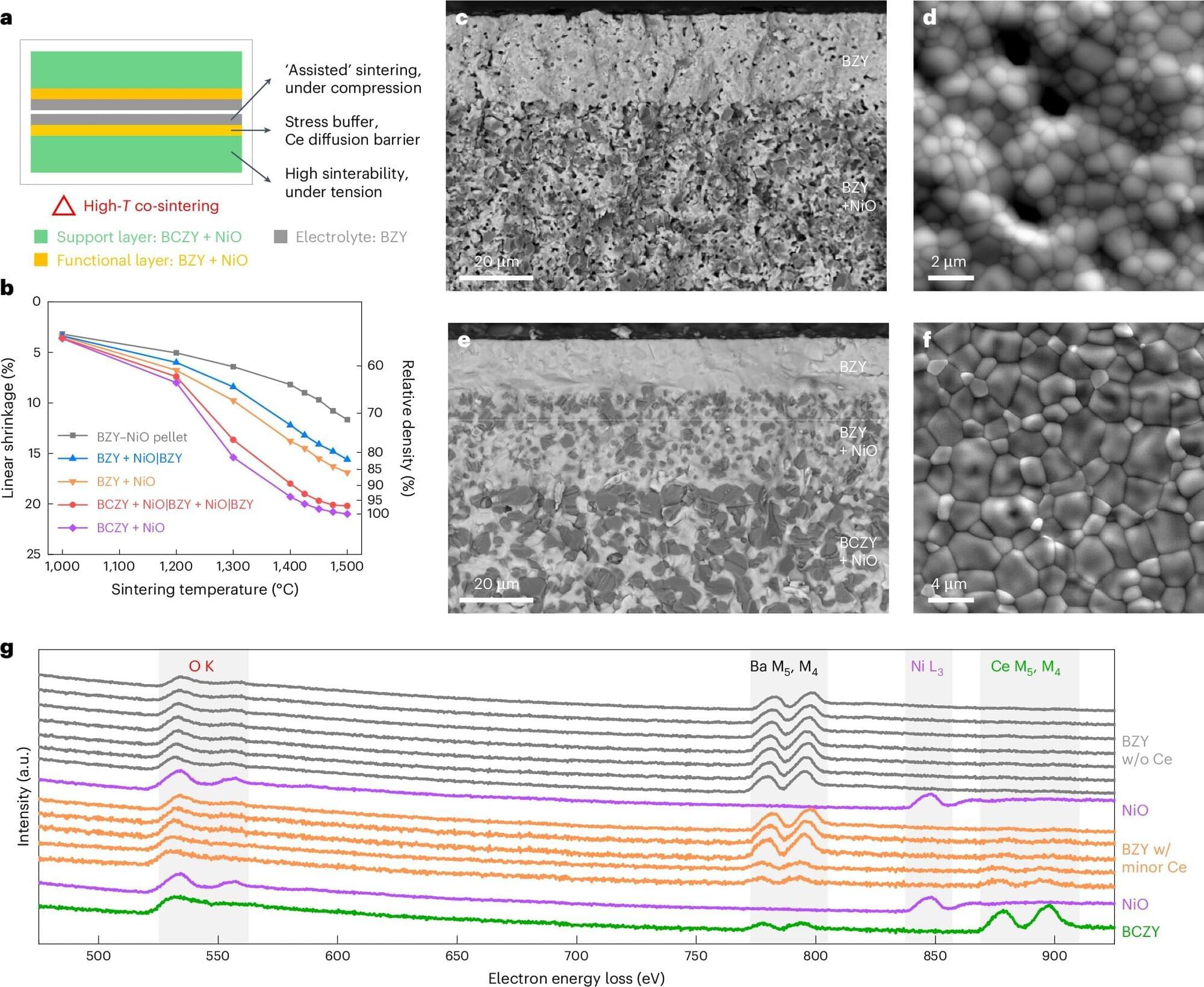
Researchers from the University of Oklahoma have made significant advances in a promising technology for efficient energy conversion and chemical processing. Two recent studies involving protonic ceramic electrochemical cells, called PCECs, address significant challenges in electrochemical manufacturing and efficiency. These innovations are a crucial step toward reliable and affordable solutions for hydrogen production and clean energy storage.
The studies were led by Hanping Ding, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the School of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering at the University of Oklahoma.
PCECs have traditionally struggled to maintain performance under the extreme conditions required for commercial use. In a study featured in Nature Synthesis, Ding and his colleagues reported a new approach that eliminates the need for cerium-based materials, which are prone to breakdown under high steam and heat.
Engineers at RMIT University have invented a small “neuromorphic” device that detects hand movement, stores memories and processes information like a human brain, without the need for an external computer.
The findings are published in the journal Advanced Materials Technologies.
Team leader Professor Sumeet Walia said the innovation marked a step toward enabling instant visual processing in autonomous vehicles, advanced robotics and other next-generation applications for improved human interaction.

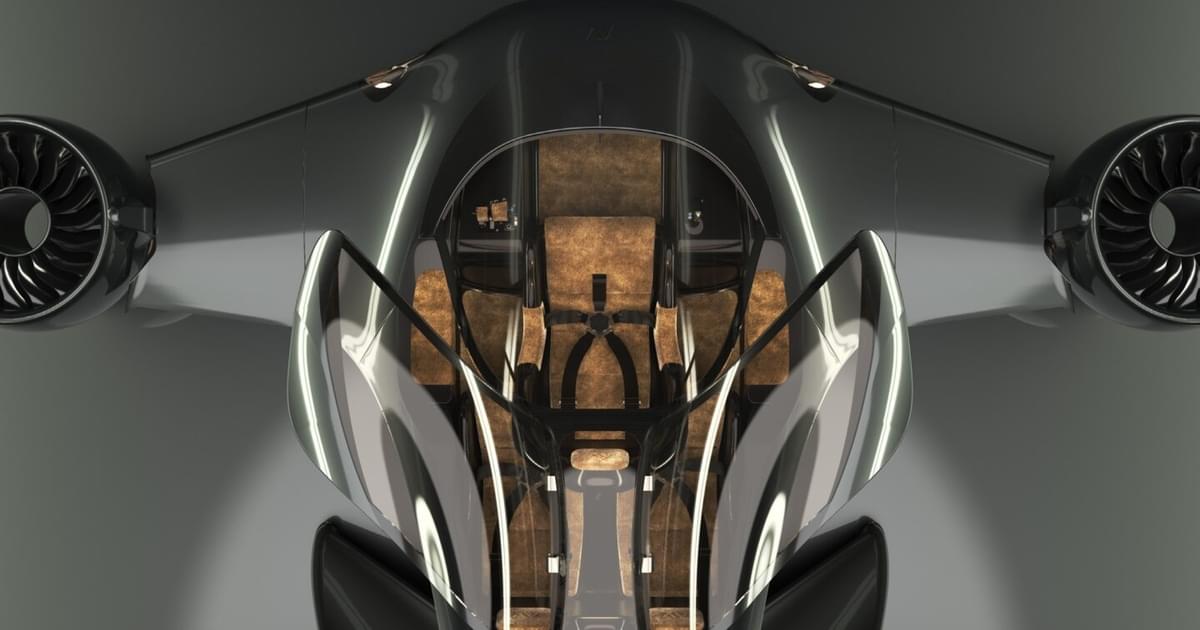
San Mateo, Calif.-based Alef Aeronautics has unveiled the world’s first commercially available flying car, the Alef Model A.
A prototype model made a test flight on 19 February 2025 on a blocked-off road in California. According to Alef’s chief executive officer, Jim Dukhovny, the test was “the first documented verifiable flight of a flying car (an actual car, with vertical takeoff, non-tethered.)”
Much more than just a toy or a concept vehicle from science fiction, the Alef Model A has attracted significant interest and support, proving the validity and potential of its design. Its basic plan is that it can drive on the road like any car, have vertical takeoff and landing capabilities, and fly in a forward motion. The company also announced a goal for the vehicle to be “affordable for most people.”

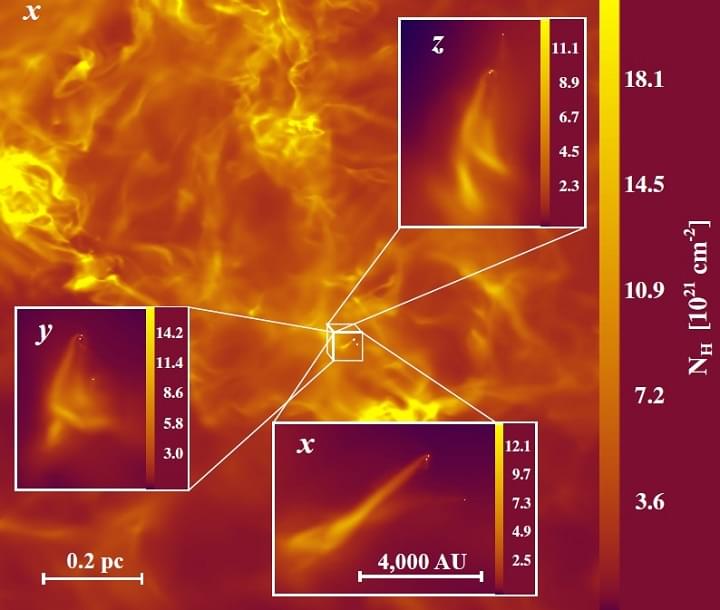
A study led by Paolo Padoan, ICREA research professor at the Institute of Cosmos Sciences of the University of Barcelona (ICCUB), is challenging the understanding of planetary disk formation around young stars.
The paper, published in Nature Astronomy, reveals that the environment plays a crucial role in determining the size and lifetime of these planetary disks, which are the sites of planet formation.
When a star forms, it is surrounded by a spinning disk of gas and dust. Over time, this material eventually forms the planets. Traditionally, scientists believed that once a disk forms, it simply loses too much over time as it feeds the star and the growing planets.