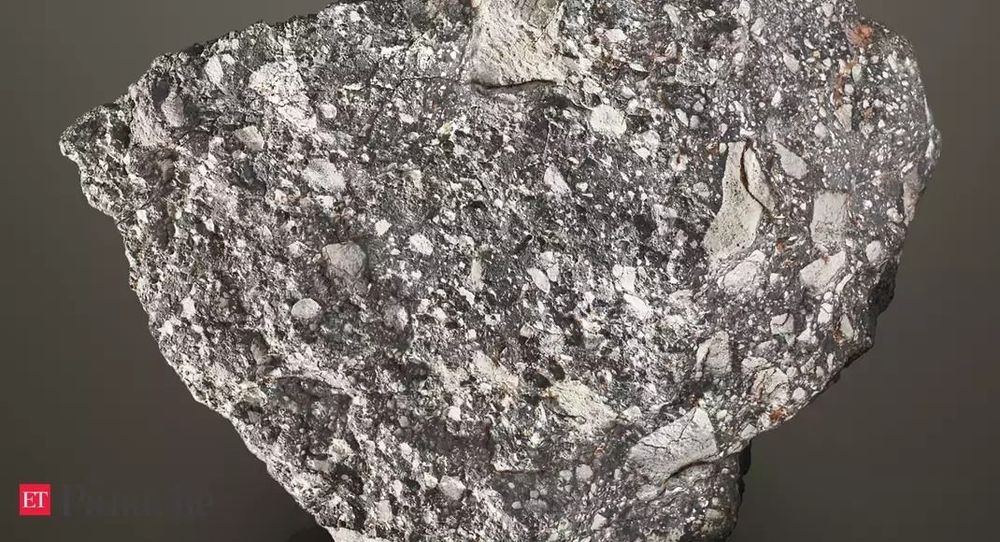
International auction house Christie’s is set to offer one of the largest lunar meteorites in existence for private sale. It is the fifth largest piece of the moon, larger than any moon rock returned by the Apollo programme.
Christie’s presents NWA 12691, a significant lunar rock, among the largest known in existence. Moon rock is among the rarest substances on Earth, with less than 650 kgs of lunar meteorites known to exist. This example is the fifth largest piece of the Moon on Earth, larger than any returned by the Apollo programme. Valued in the region of £2 million, the specimen is available for immediate purchase via Christie’s Private Sales.
Lunar meteorites arrived on Earth after having been blasted off the lunar surface by the collision with an asteroid or comet. All of the Moon’s large craters were created by such impacts. This particular meteorite was part of a large meteorite shower straddling the Western Saharan, Algerian and Mauritanian borders, responsible for nearly half of all known lunar meteorites. Approximately 30 different meteorites were collected, analysed, classified and assigned different NWA numbers in the belief they might be from different events and represent different lunar samples; but it has been determined that they all originate from the same lunar impact event as the current offering. NWA 12691 was found in the Sahara Desert two years ago.