Any comments?
Ultraprecise 3D printing technology is a key enabler for manufacturing precision biomedical and photonic devices. However, the existing printing technology is limited by its low efficiency and high cost. Professor Shih-Chi Chen and his team from the Department of Mechanical and Automation Engineering, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK), collaborated with the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory to develop the Femtosecond Projection Two-photon Lithography (FP-TPL) printing technology.
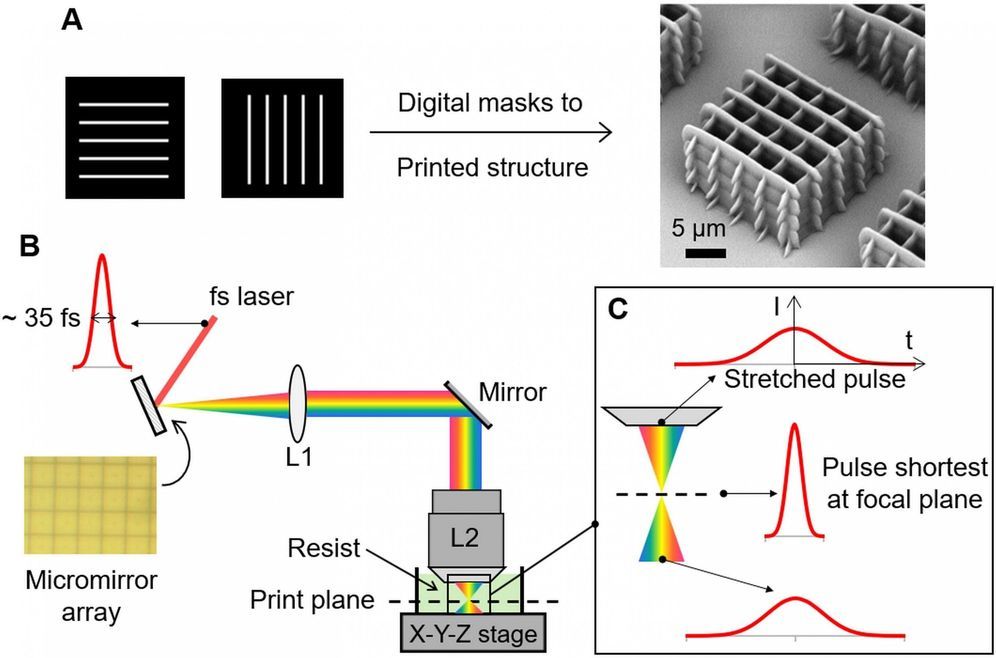
By controlling the laser spectrum via temporal focusing, the laser 3D printing process is performed in a parallel layer-by-layer fashion instead of point-by-point writing. This new technique substantially increases the printing speed by 1,000—10,000 times, and reduces the cost by 98 percent. The achievement has recently been published in Science, affirming its technological breakthrough that leads nanoscale 3D printing into a new era.
The conventional nanoscale 3D printing technology, i.e., two-photon polymerization (TPP), operates in a point-by-point scanning fashion. As such, even a centimeter-sized object can take several days to weeks to fabricate (build rate ~ 0.1 mm3/hour). The process is time-consuming and expensive, which prevents practical and industrial applications. To increase speed, the resolution of the finished product is often sacrificed. Professor Chen and his team have overcome the challenging problem by exploiting the concept of temporal focusing, where a programmable femtosecond light sheet is formed at the focal plane for parallel nanowriting; this is equivalent to simultaneously projecting millions of laser foci at the focal plane, replacing the traditional method of focusing and scanning laser at one point only. In other words, the FP-TPL technology can fabricate a whole plane within the time that the point-scanning system fabricates a point.