It is contemplated that solving the problem of anxiety in finding an alternativeergy for coping with finite resources and exhaustion of fossil fuel resources would require a great deal of time even when mankind launches full-scale efforts and continues all-out efforts. The of an infinite power capable of supplying a clean, safe, infinite kineticergy for the and prosperity of human society with no need of consumable raw materials would improve the and wouldhance andrich the functionality thereof, would contribute to thehanced prosperity of human society, and wouldable city construction on not only the earth but also other planets.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

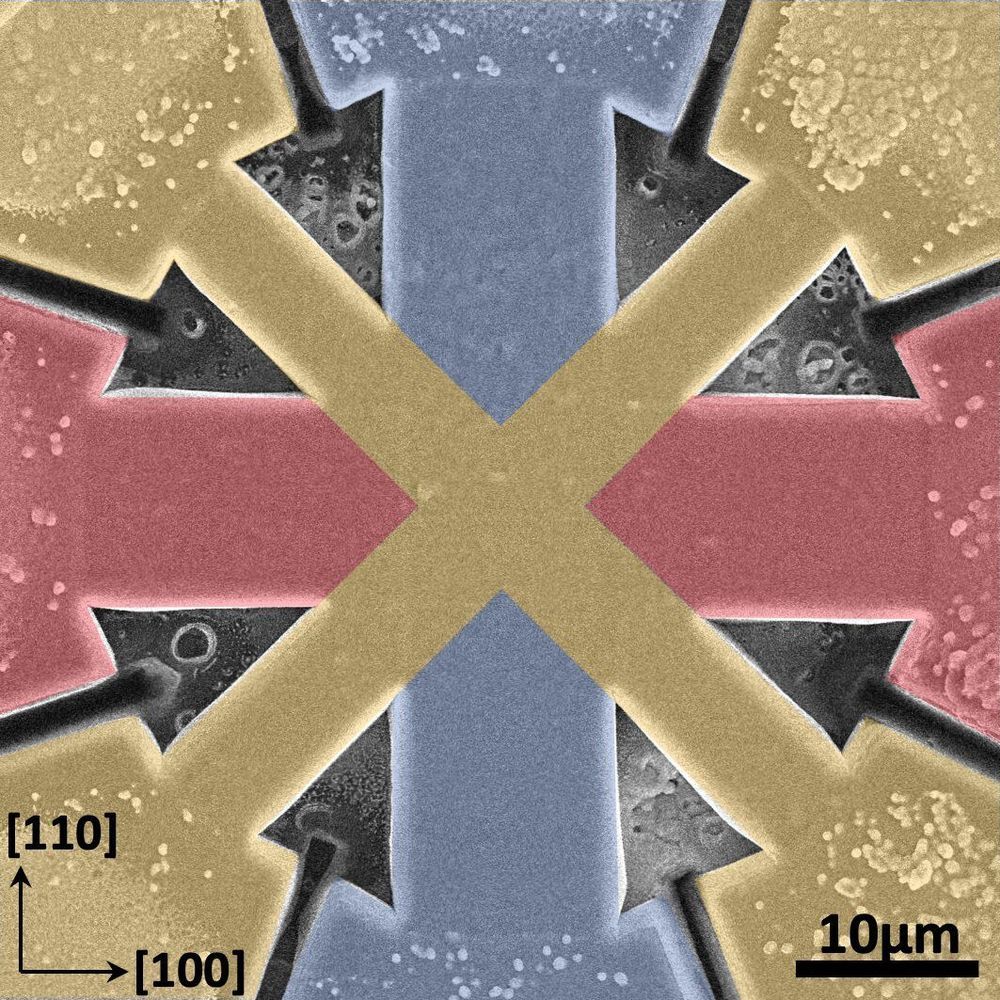
Fine-tuning magnetic spin for faster, smaller memory devices
Unlike the magnetic materials used to make a typical memory device, antiferromagnets won’t stick to your fridge. That’s because the magnetic spins in antiferromagnets are oppositely aligned and cancel each other out.
Scientists have long theorized that antiferromagnets have potential as materials for ultrafast stable memories. But no one could figure out how to manipulate their magnetization to read and write information in a memory device.
Now, a team of researchers at Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley working in the Center for Novel Pathways to Quantum Coherence in Materials, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, have developed an antiferromagnetic switch for computer memory and processing applications. Their findings, published in the journal Nature Materials, have implications for further miniaturizing computing devices and personal electronics without loss of performance.
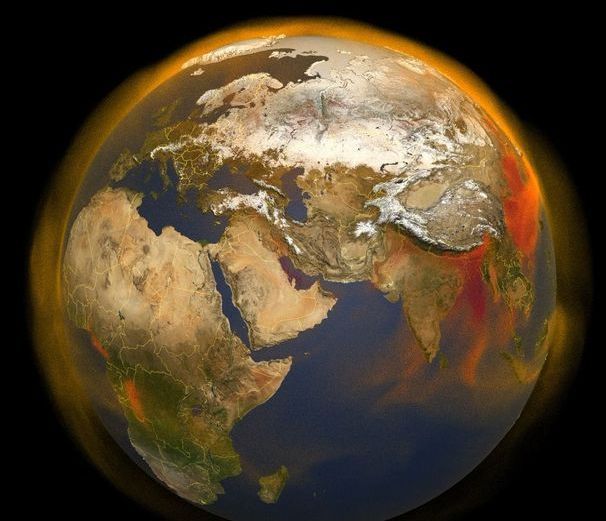

New 3D View of Methane Tracks Sources and Movement around the Globe
NASA’s new 3-dimensional portrait of methane concentrations shows the world’s second largest contributor to greenhouse warming, the diversity of sources on the ground, and the behavior of the gas as it moves through the atmosphere. Combining multiple data sets from emissions inventories, including fossil fuel, agricultural, biomass burning and biofuels, and simulations of wetland sources into a high-resolution computer model, researchers now have an additional tool for understanding this complex gas and its role in Earth’s carbon cycle, atmospheric composition, and climate system.
Since the Industrial Revolution, methane concentrations in the atmosphere have more than doubled. After carbon dioxide, methane is the second most influential greenhouse gas, responsible for 20 to 30% of Earth’s rising temperatures to date.
“There’s an urgency in understanding where the sources are coming from so that we can be better prepared to mitigate methane emissions where there are opportunities to do so,” said research scientist Ben Poulter at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
Watch out Silicon Valley: European Union gets into the venture capital game
Frustrated by Europe’s lack of home-grown tech giants, Commission officials hope EIC will help small tech firms grow in Europe, instead of being lured away to Silicon Valley. “The aim here is to close the big gap that exists between Europe and the United States,” says Mark Ferguson, Ireland’s chief scientist and EIC board chair. But one challenge will be backing risky but promising startups without becoming “the financiers of last resort for all the failing companies that aren’t going to do very well,” says Christopher Tucci, a professor of technology management at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne, who advised the Commission while it drafted Horizon Europe.
European Innovation Council buys shares in disruptive technology startups.

🗯️ Photo
FUTURE AFRICA: SUSTAINING THE SOURCE.
Let’s discuss on the theme: COMPLIANCE TO GLOBAL SUSTAINABILITY.
💥Register for this Online/Virtual Reality Conference — https://conference.taffds.org/
Or
Chain Fortunes Limited an affiliate of TAFFD’s.
Chain Fortunes Limited Heritage Bank 6001729202.
Why Germs Thrive on Planes — and How to Stop Them
Here’s how a sneeze travels inside a plane cabin.
Watch Raymond Wang’s full TED Talk here: http://t.ted.com/oa2OEWB
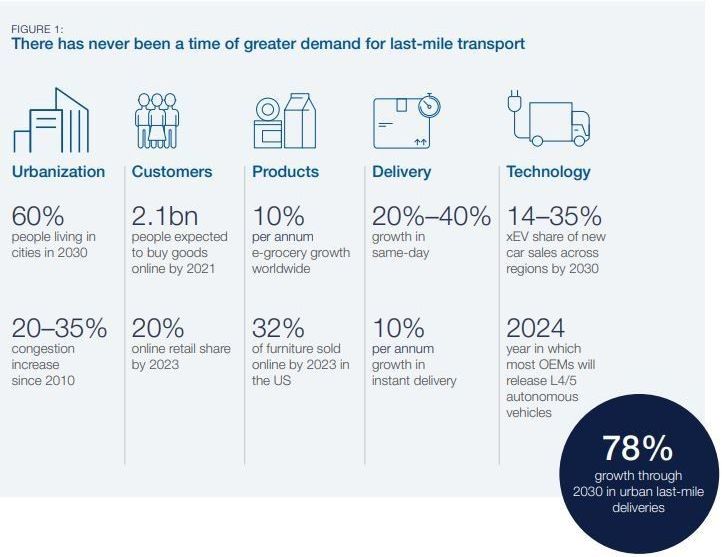
How COVID-19 could open the door for driverless deliveries
The COVID-19 pandemic has put an incredible strain on global supply chains, from medical supplies to household goods, as spikes in demand stress-test logistics infrastructures. There is an opportunity for unmanned delivery vehicles to assist in addressing this demand and help to reduce the risk of spreading infection.
Here’s a look at some of the challenges and opportunities for automated vehicles (AVs) in last-mile deliveries and local logistics.

Melinjo Seed Extracts May Help Improve Diabetes And Obesity
Researchers from Kumamoto University have found that Melinjo seed extracts may help to improve diabetes and obesity by stimulating the production of adiponectin which is a hormone that works to help improve both conditions; individual genotype differences were also discovered that were responsible for variations in its efficacy.
Melinjo fruit contain high levels of antioxidant and antibacterial properties as well as high levels of polyphenols such as resveratrol that has been shown to induce adiponectin and may help to improve lifestyle related diseases such as metabolic syndrome. A type of resveratrol called Gnetin C which is found in MSE has higher antioxidant activity and has been shown to stay in the blood longer than resveratrol, but the exact mechanisms of how they exert their biological activity remains unknown.
Genetic analysis was used to find that differences in the type of DsbA-L gene affects adiponectin activation; meaning that DsbA-L induction may promote adiponectin activation and help to improve lifestyle related diseases. Their recent research has attempted to determine whether MSE enhances the function of DsbA-L; whether MSE promotes adi[onectin activation; and whether MSE has a therapeutic effect on either obesity and diabetes.