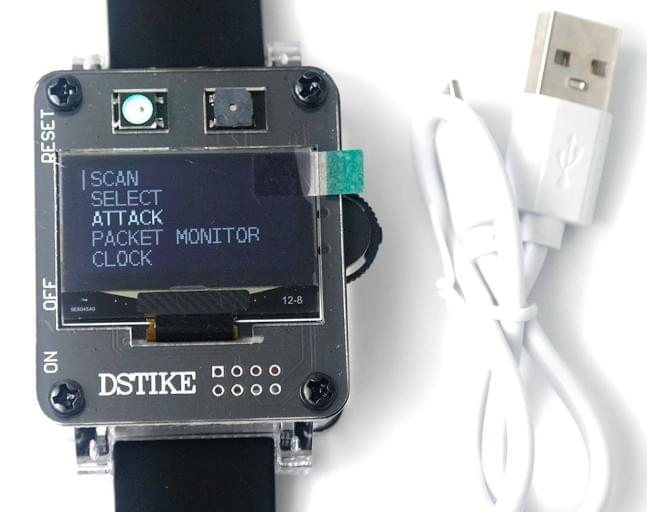
Wearable tech has seen an explosion of creativity and applications in the last decade; especially with circuit components getting smaller and cheaper, and batteries getting better and better. Whereas taking phone calls on your wrist was impressive just a few years ago, now, you can experiment with deauthentication attacks on WiFi networks just from this watch: the DSTIKE Deauther Watch SE.
Based on the ESP8266 WiFi microcontroller, this watch is the latest generation of a project to give you a wearable interface for pen testing local WiFi networks. The watch only works on 2.4GHz networks, due to the restrictions of the ESP8266. It comes pre-flashed with the latest ESP8266 Deauther firmware, which is an open-source project! The watch supports four main functions: a deauther attack, which disconnects all local 2.4GHz networks; deauther beacon, used for creating fake networks; deauther probe, to confuse any nearby WiFi trackers; and packet monitoring, which lets you display local WiFi traffic. As you can see, there’s a lot to appreciate in this slick and discreet package.
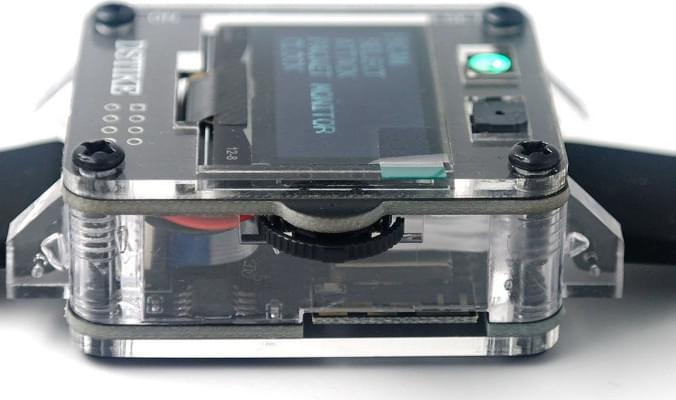

This watch (and its prior iterations) are made and sold by Travis Lin. Much like the seller emphasizes on the product page, this device is meant for educational purposes, and should be only tested on devices and networks you own. But if this has your curiosity piqued, put on your red hat and check out the wearable devices and other security goodies they have for sale!