COSPAR’s Planetary Protection Policy ensures scientific investigations related to the origin and distribution of life are not compromised.
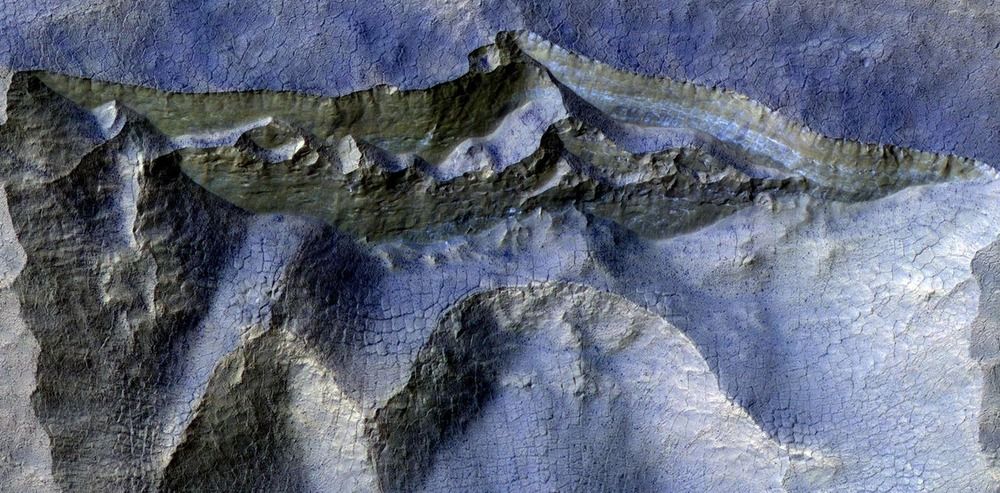
Protecting the Earth from alien life sounds like the latest plot for a blockbuster thriller set in outer space. Whether it’s an invasion or a mysterious alien illness, the extraterrestrial threat to our planet has been well-explored in science fiction. But protecting the Earth from extraterrestrial contamination is not just a concept for our entertainment; as we explore further across our solar system and begin to land on our neighbouring planetary bodies, ensuring that we don’t bring potentially dangerous material home to Earth or indeed carry anything from Earth that may contaminate another planet is a responsibility we must take seriously.
So, who is responsible for ensuring that our space exploration is completed safely? Many nations around the world have their own space agencies, such as NASA and the European Space Agency, who run many different types of missions to explore space. States are responsible for their space activities under the Outer Space Treaty of 1967, including governmental and non-governmental actors. The Outer Space Treaty, among several provisions, regulates in its Article IX against harmful contamination. One of the core activities of the Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) is to develop, maintain, and promote a Policy on Planetary Protection, as the only international reference standard for spacefaring nations and in guiding compliance with Article IX of the Outer Space Treaty.
As we explore further across our solar system, ensuring we don’t bring potentially dangerous material home or indeed carry anything from Earth that may contaminate another planet and compromise scientific investigations is a responsibility we must take seriously.
COSPAR and its role COSPAR is part of the International Science Council, a non-governmental organisation that brings together many different scientific unions and research councils from all over the world. COSPAR was formed to promote international scientific research in space and provide a forum for the discussion of challenges to scientific exploration. COSPAR has a panel that regularly reviews the most up-to-date scientific research and advises COSPAR on new adaptations to planetary protection, for which policy updates and implementation guidelines are required.