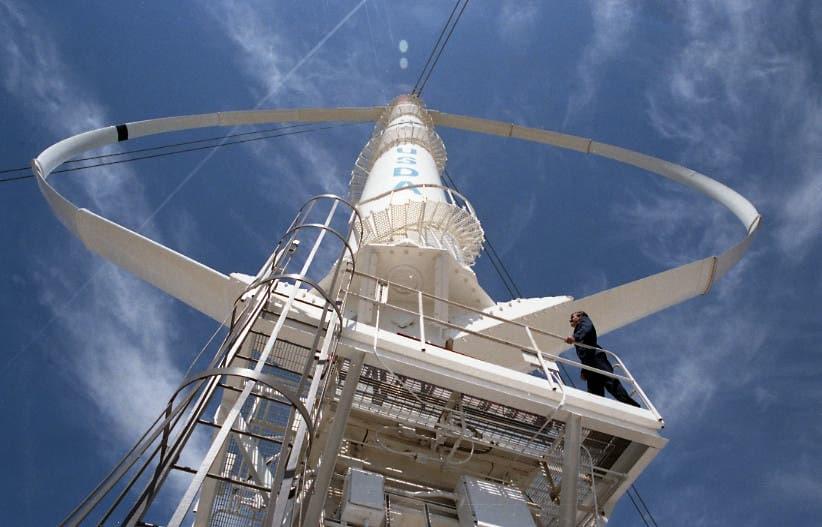
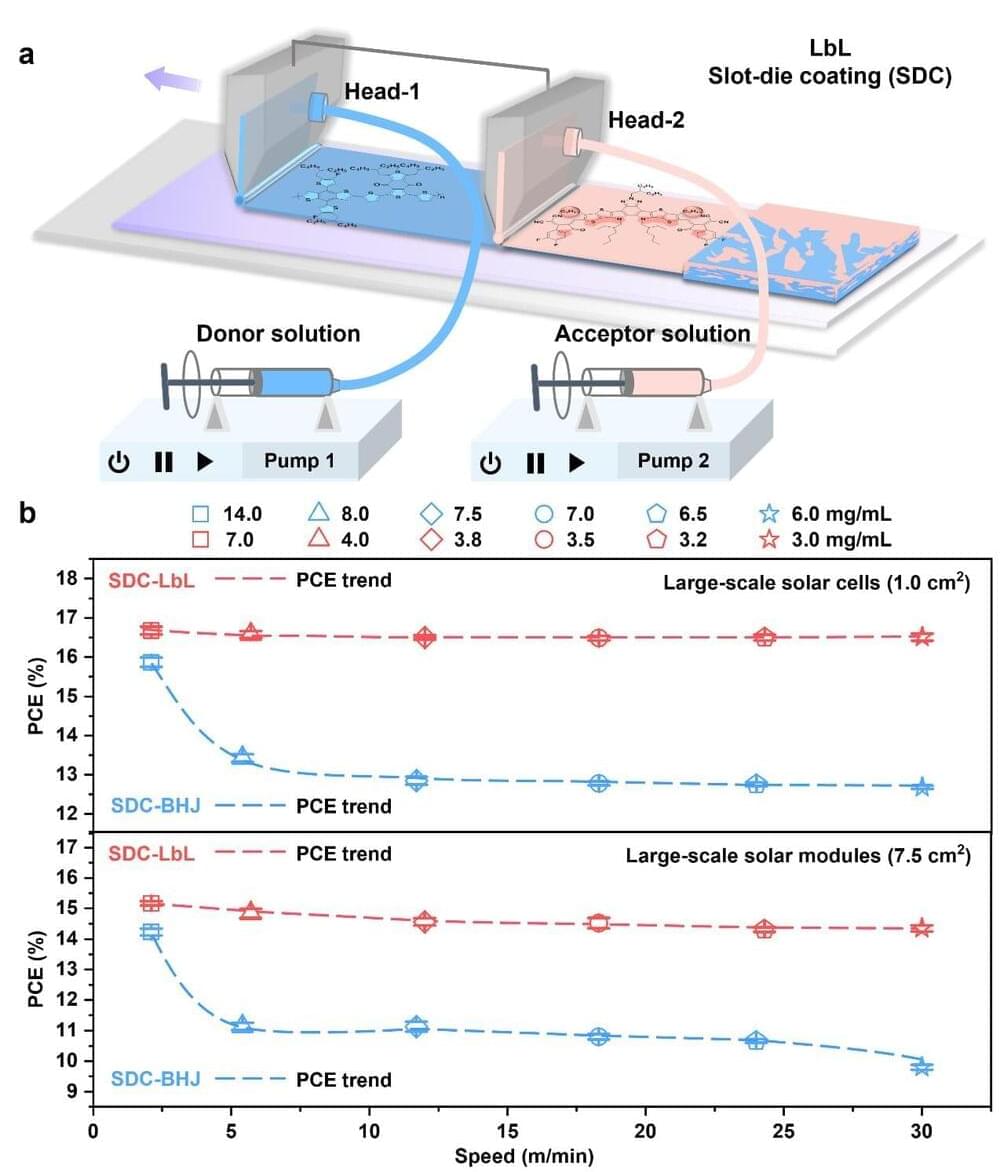
Vertical axis turbines missed their moment in the 1980s, but they are back, and they are getting bigger. That may come as a surprise. The technology was confined to niche applications and all but written off just a few years ago. Now they are poised for a new growth spurt in the rooftop field, and they are even heading out to sea.
The Long Road To Vertical Axis Wind Turbines
For those of you new to the topic, vertical axis wind turbines are engineered to make curved blades rotate around a central, upright pole. The US Department of Energy’s Sandia National Laboratory was experimenting with a scaled up design that resembled an egg beater back in the 1980s, as depicted in the photo at the top of this article.