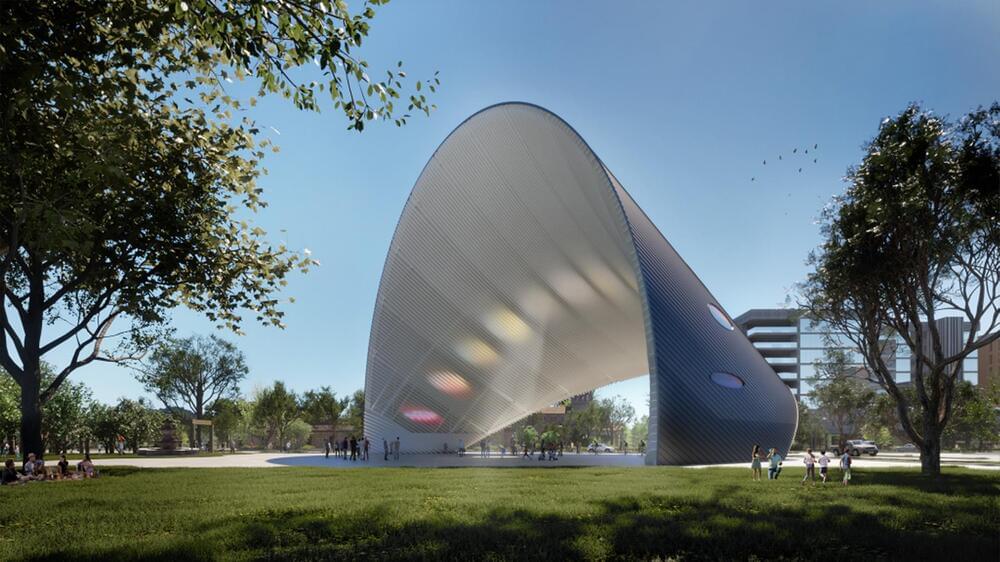
The project, called the Arch of Time, will stand 100 feet tall and generate enough solar power every year to offset 40 Texans’ home energy use.
Berlin architect Riccardo Mariano has designed an innovative new project for the city of Houston, Texas, that will generate nearly 400,000 kWh of electricity every year while acting as a public sundial.
The project, named the Arco del Tiempo (Arch of Time), will be a 100-foot-tall triumphal archway that will serve as the gateway to the city’s East End, part of the Second Ward district for the city. It will have a roof covered in photovoltaic modules to produce electricity as well.