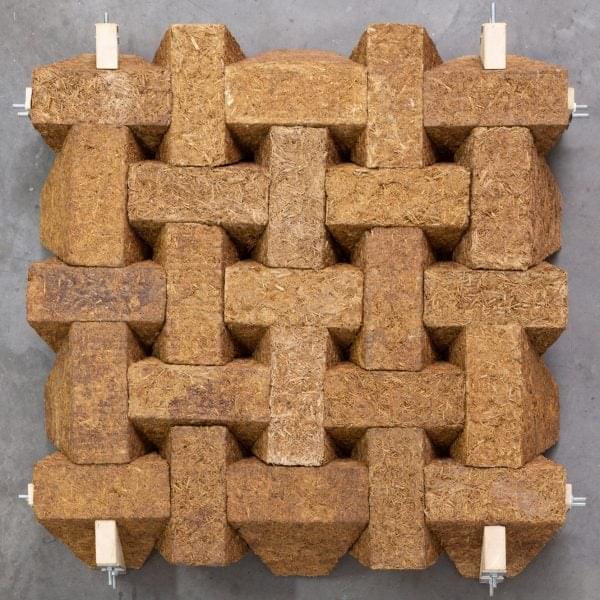
Using sugarcane waste as bricks for construction.
Architecture studio Grimshaw and the University of East London have collaborated to create Sugarcrete, a biomaterial construction block with an interlocking shape made from the sugarcane by-product bagasse.
Sugarcrete was developed to be a low-cost and low-carbon reusable construction-material alternative to brick and concrete.
The concept, design and fabrication of the material were led by staff and fellows of the University of East London (UEL), including senior architecture lecturer Armor Gutierrez Rivas, Sustainability Research Institute co-director Alan Chandler and research fellow Bamdad Ayati.