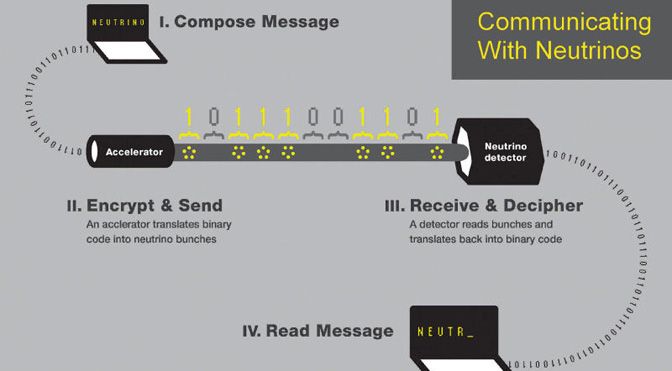
Scientists working at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab) near Chicago have successfully communicated a short digital message using a stream of neutrinos. While this sounds cool, the truly exceptional bit is that the message was transmitted through 790 feet (240m) of solid stone.
Neutrinos are subatomic particles (like electrons or quarks, or the theorized Higgs boson) that have almost zero mass, a neutral charge (thus their name), and travel at close to the speed of light. Unlike almost every other particle in the universe, neutrinos are unaffected by electromagnetism (because of their neutral charge), and only subject to gravity and weak nuclear force. This means that neutrinos can easily pass through solid objects as large as planets. Every second, 65 billion neutrinos from the Sun pass through each square centimeter of the Earth at almost the speed of light.
To recreate this effect, the Fermilab scientists used a particle accelerator (NuMI) to shoot a stream of neutrinos through 240 meters of stone at the MINERvA neutrino detector. If MINERvA detected neutrinos, it registered as a binary 1; no neutrinos, binary 0. Using this technique (pictured above), the scientists, with a burst of originality to rival Alexander Graham Bell himself, transmitted the word “neutrino.”
Read more