A spontaneous hole in the fabric of reality could theoretically end the universe, but don’t worry: physicists are studying the idea for what it can teach us about the cosmos.


Feature image ‘Psychonaut’ courtesy of Tetramode.
Follow the Daily Grail on Facebook and on Twitter.
The last half century has seen humanity take its first, tentative steps into outer space. Initially, through American and Russian astronaut missions into Earth orbit and then to the Moon, though more recently robotic probes have ventured beyond our solar system entirely.

The scientific revolution was ushered in at the beginning of the 17th century with the development of two of the most important inventions in history — the telescope and the microscope. With the telescope, Galileo turned his attention skyward, and advances in optics led Robert Hooke and Antonie van Leeuwenhoek toward the first use of the compound microscope as a scientific instrument, circa 1665. Today, we are witnessing an information technology-era revolution in microscopy, supercharged by deep learning algorithms that have propelled artificial intelligence to transform industry after industry.
One of the major breakthroughs in deep learning came in 2012, when the performance superiority of a deep convolutional neural network combined with GPUs for image classification was revealed by Hinton and colleagues [1] for the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC). In AI’s current innovation and implementation phase, deep learning algorithms are propelling nearly all computer vision-intensive applications, including autonomous vehicles (transportation, military), facial recognition (retail, IT, communications, finance), biomedical imaging (healthcare), autonomous weapons and targeting systems (military), and automation and robotics (military, manufacturing, heavy industry, retail).
It should come as no surprise that the field of microscopy would ripe for transformation by artificial intelligence-aided image processing, analysis and interpretation. In biological research, microscopy generates prodigious amounts of image data; a single experiment with a transmission electron microscope can generate a data set containing over 100 terabytes worth of images [2]. The myriad of instruments and image processing techniques available today can resolve structures ranging in size across nearly 10 orders of magnitude, from single molecules to entire organisms, and capture spatial (3D) as well as temporal (4D) dynamics on time scales of femtoseconds to seconds.
Bottomline: DON’T PANIC!
This is a Cary prodocution!
If you’d like to use this video in your own projects, contact me through Twitter DMs at @realCarykh! I almost always say yes, but just make sure it’s ok with me first. Thanks!
Humany “behind-the-scenes” channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCx_JS-Fzrq-bXUYP0mk9Zag
Sources: https://pastebin.com/R4N9m94g


In 2016, the European Space Agency announced a call for medium-size missions within their Cosmic Vision Program. In layman’s terms, “medium-size” means moderate-cost (less than 550 million euros, or $610 million) and low-risk, and this is achieved by keeping payloads small and by using proven, heritage technology for both spacecraft and payload. Alongside these common-sense conditions is a third and less tangible quality, that the project be scientifically robust. But when comparing excellent cases from vastly different fields, the merits of one scientific mission over another can seem subjective. It’s not enough to lament the dearth of data in said field, or to establish how a project will discover this or that, or even to show exactly how said “groundbreaking technology” will work. ESA wants a mission that will stir up an unprecedented level of excitement, support, and interest within the scientific community. Here is how they attempt to measure a project’s relevance.
“Each member state has a representative in the Science Programme Committee, and it’s their duty to define the content of the program,” said Luigi Colangeli, head of ESA’s Science Coordination Office. “Study groups work with the various proposals to arrive at something that is compatible with the boundary conditions, in this case, of a M-5, or medium-class mission. Right now, we are studying the evolution of the three missions. And then next year we will put together a peer review panel, who will analyze the three candidates and recommend the best selection to our Director of Science.”
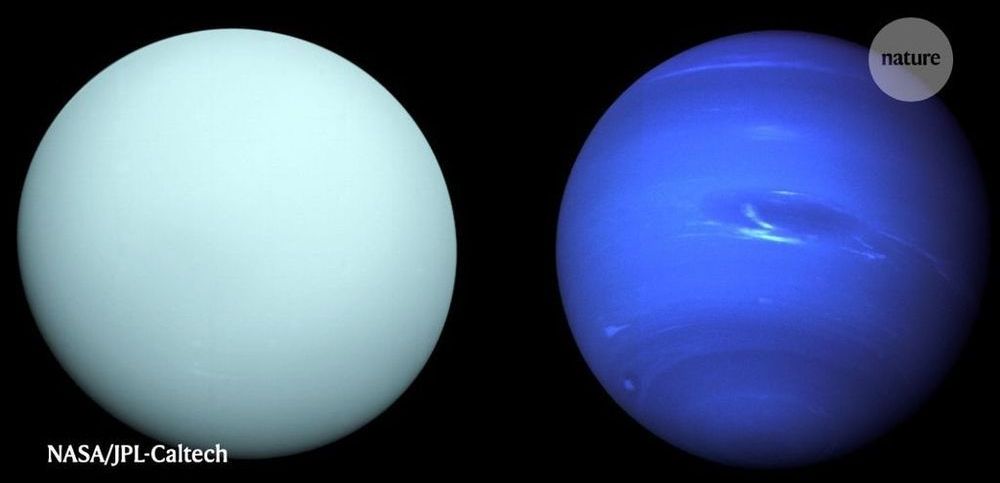
Since the call went out four years ago, ESA have been whittling down proposals, from 25 at the beginning to only three now: Envision, Theseus, or SPICA. In February the EnVision conference took place at the National Centre for Space Studies (CNES) in Paris. EnVision is a low-altitude polar orbiter that is meant to perform high-resolution radar mapping, surface composition, and atmospheric studies of Venus. The purpose of the meeting was to call the Venus community to attention, because the clock is ticking. Consortium members, ESA representatives, and interested scientists from all over the world were in attendance.
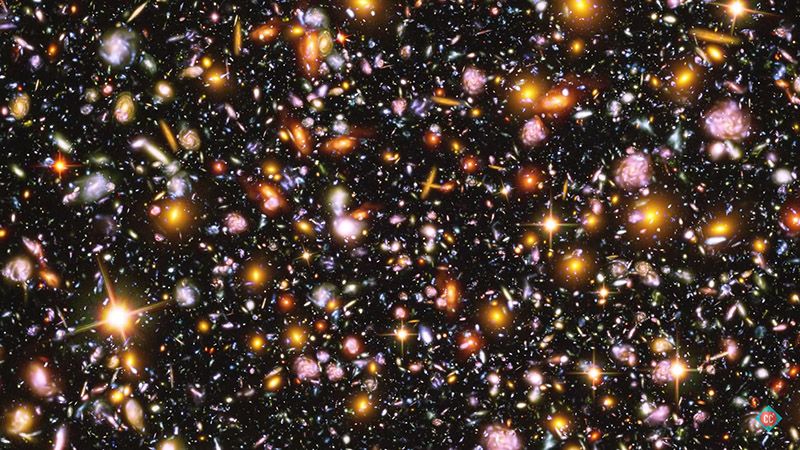


The universe just got a lot more crowded. According to a new study, there may be three times as many stars in the universe as previously thought. How many? Three-hundred sextillion. How many is 300 sextillion? Behold:
300,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
That is, as the Associated Press points out, three trillion times 100 billion.

A new discovery could be a clue for us to see if life could emerge elsewhere in the Solar System. Using a new analysis technique, scientists think they have found an extraterrestrial protein, tucked inside a meteorite that fell to Earth 30 years ago.
If their results can be replicated, it will be the first protein ever identified that didn’t originate here on Earth.
“This paper characterises the first protein to be discovered in a meteorite,” the researchers wrote in a paper uploaded to preprint server arXiv. Their work is yet to be peer reviewed, but the implications of this finding are noteworthy.