This concept animation shows just one of many potential concepts for how the first human landing site on Mars might evolve throughout the course of multiple human expeditions to the Red Planet over a decade or more. via @ NASA — National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Category: space – Page 811



Weather looks good for SpaceX’s next Starlink launch from Kennedy Space Center
The weather forecast looks mostly favorable for the Space Coast’s next launch, a mission slated to see a 230-foot SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket take flight from Kennedy Space Center on Wednesday.
Conditions are shaping up to be 70% “go” for the 11:59 a.m. liftoff from pad 39A, the Space Force said Sunday, thanks to the movement of drier air. Teams will have until 12:05 p.m. to launch.
“On Wednesday, some drier mid-level air will likely move into the area, helping to limit shower and storm coverage compared to earlier in the week,” the 45th Weather Squadron said. “The primary concern for the launch window is the cumulus cloud rule.”

NASA Is Releasing a Fragrance That Smells Like Space
NASA is bringing the smell of space to Earth with a new fragrance called Eau de Space. The fragrance was developed by chemist Steve Pearce, who was contracted by NASA in 2008 to recreate the scent of space.
With his knowledge of flavor and fragrance chemistry, Pearce used astronauts’ descriptions of the smell of space to come up with combinations to match what was described as “ozone, hot metal, and fried steak,” CNN reports.
“It’s a bitter kind of smell in addition to being smoky and burned, kind of like a smell from a gun, right after you fire the shot,” astronaut Peggy Whitson told CNN. Eau de Space product manager, Matt Richmond, said he has struggled to accurately describe the fragrance’s scent, adding that astronauts have also likened the smell to “a mix of gunpowder, seared steak, raspberries, and rum.”
Jumping From Space! — Red Bull Space Dive — BBC
Circa 2016
The moment has finally arrived, it’s time for Felix Baumgartner to perform the space dive. Taken from Red Bull Space Dive.
Want to share your views with the team? Join our BBC Studios Voice: https://www.bbcstudiosvoice.com/register
This is a commercial channel from BBC Studios. Service & Feedback https://www.bbcstudios.com/contact/contact-us/
Hubble’s Universe: Solar System Surprises
Hubble can see deep into space, but it’s also made amazing discoveries right here in our solar system! ☀️
Check out what Hubble has seen in our cosmic neighborhood over the past 30 years. Follow along over the next two days for more about Hubble’s fascinating universe.
#NASA #Hubble #video #solarsystem #planet #space #science #discovery #universe #astronomy
A remnant planetary core in the hot-Neptune desert
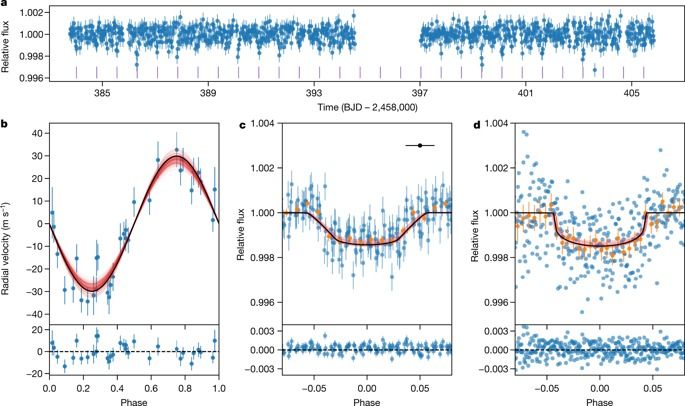
The interiors of giant planets remain poorly understood. Even for the planets in the Solar System, difficulties in observation lead to large uncertainties in the properties of planetary cores. Exoplanets that have undergone rare evolutionary processes provide a route to understanding planetary interiors. Planets found in and near the typically barren hot-Neptune ‘desert’1,2 (a region in mass–radius space that contains few planets) have proved to be particularly valuable in this regard. These planets include HD149026b3, which is thought to have an unusually massive core, and recent discoveries such as LTT9779b4 and NGTS-4b5, on which photoevaporation has removed a substantial part of their outer atmospheres. Here we report observations of the planet TOI-849b, which has a radius smaller than Neptune’s but an anomalously large mass of \(39.1{\,}_{-2.6}^{+2.7}\) Earth masses and a density of \(5.2{\,}_{-0.8}^{+0.7}\) grams per cubic centimetre, similar to Earth’s. Interior-structure models suggest that any gaseous envelope of pure hydrogen and helium consists of no more than \({3.9}_{-0.9}^{+0.8}\) per cent of the total planetary mass. The planet could have been a gas giant before undergoing extreme mass loss via thermal self-disruption or giant planet collisions, or it could have avoided substantial gas accretion, perhaps through gap opening or late formation6. Although photoevaporation rates cannot account for the mass loss required to reduce a Jupiter-like gas giant, they can remove a small (a few Earth masses) hydrogen and helium envelope on timescales of several billion years, implying that any remaining atmosphere on TOI-849b is likely to be enriched by water or other volatiles from the planetary interior. We conclude that TOI-849b is the remnant core of a giant planet.
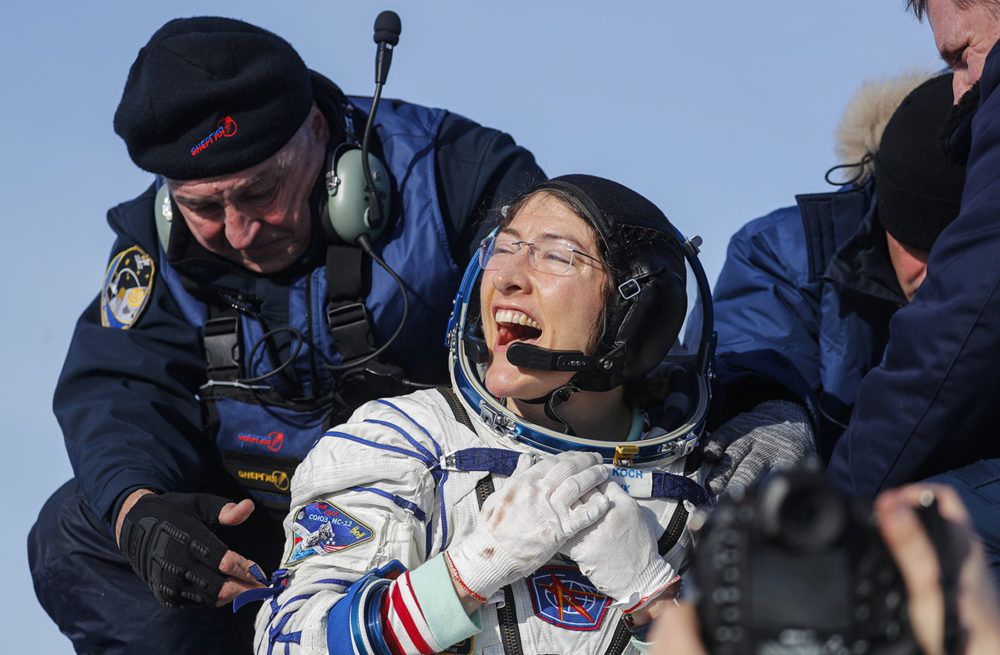

Astronaut Christina Koch On Her Journey From Space To A Nation In Lockdown
Astronaut Christina Koch spent a record 11 months in space, the longest spaceflight of any woman. She returned to Earth in February and is just completing her NASA-mandated readjustment period. What’s life like when you leave a space station, only to be confined in your own home under lockdown?
Guests
Christina Koch, NASA astronaut and former flight engineer on the International Space Station. She set the record for longest single spaceflight by a woman: 328 days. She and Jessica Meir performed the first all-female spacewalk. Koch has performed a total of six spacewalks. (@Astro_Christina)
