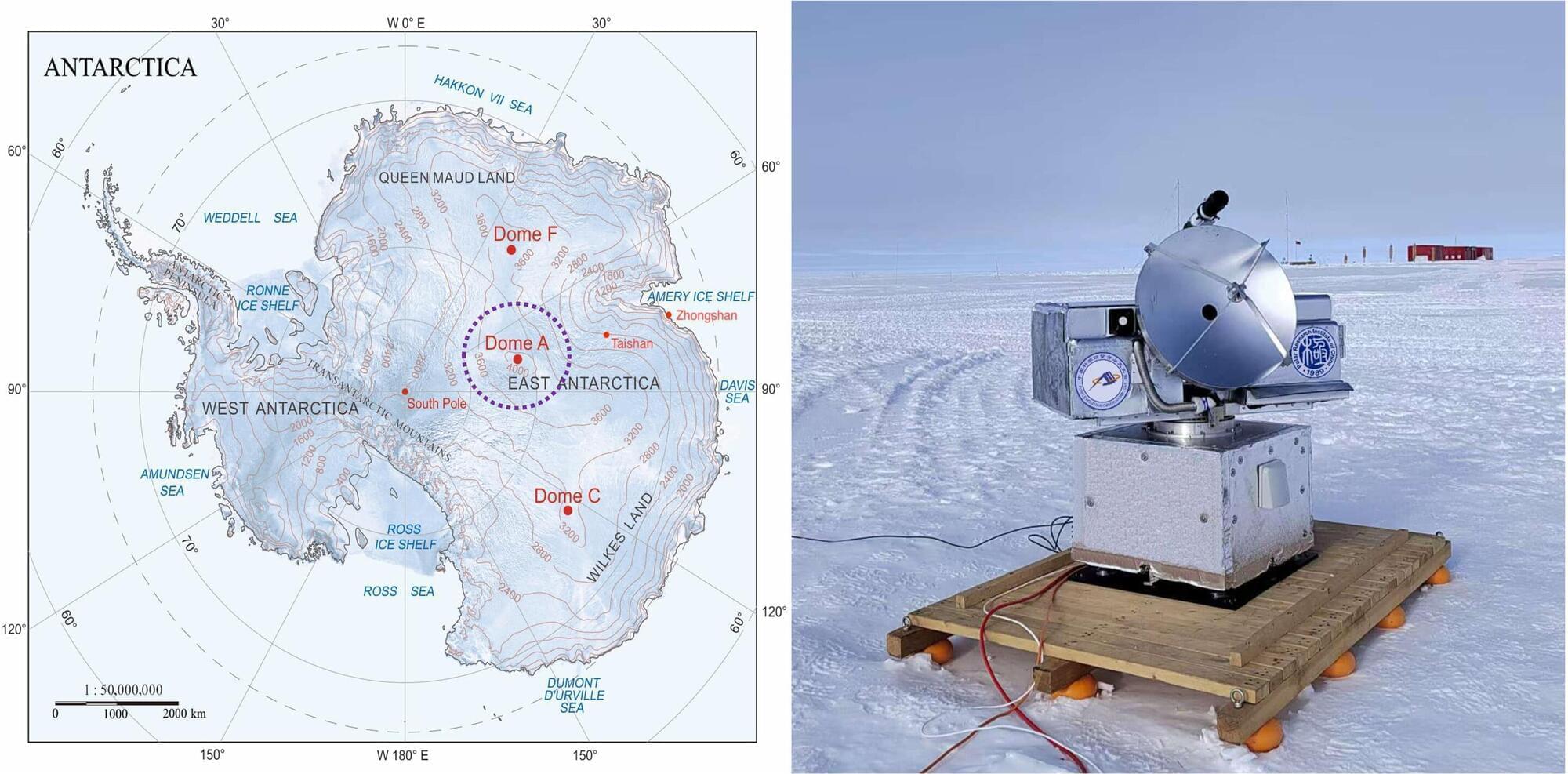
Chinese researchers have braved the cold and harsh environment of Antarctica in order to get a unique view of star formation in the interstellar medium (ISM). The Chinese National Antarctica and Arctic Research Expedition (CHINARE) has managed to complete a study at Dome A—the highest ice dome on the Antarctic Plateau—and successfully collected submillimeter data to form a better understanding of carbon cycling in the ISM. Their research is published in Science Advances.
In most places on Earth, the detection of submillimeter wavelengths (terahertz frequencies) from space is inhibited by water vapor in the atmosphere, which absorbs radiation at these wavelengths. This is a major roadblock to the study of carbon phases in the ISM, as carbon cycles between ionized (C+), atomic (C0), and molecular (CO) forms in the interstellar medium. These transitions produce emissions in submillimeter wavelength bands, making them difficult to detect from most locations.
While prior ground-based telescopes have detected some [CI] emissions, coverage is limited compared to CO surveys, and not all carbon phases have been mapped together. However, Dome A in Antarctica offers the dry, high altitude conditions needed for submillimeter astronomy, but successful observations have been elusive due to the harsh environment and technical challenges.