The U.S. isn’t the only nation preparing for space warfare.

NASA is sending a pair of astronauts on a spacewalk outside the International Space Station today (Jan. 25) to finish fixing a complicated science experiment. Here’s how to watch it live.
NASA TV began streaming the spacewalk around 5:30 a.m. EST (1030 GMT) as European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano and NASA astronaut Andrew Morgan complete their final spacewalk preparations. You can watch it live here on Space.com. The spacewalk is expected to start around 6:50 a.m. EST (1150 GMT), when the astronauts will switch their spacesuits over to battery power before heading out of the airlock.


Circa 2017
Chris Roberts built worlds for games such as Wing Commander at Electronic Arts’ Origin at the dawn of 3D games a couple of decades ago.
Those games were technologically limited, but they still inspired the imagination. Now Roberts is now head of his own company, Roberts Space Industries, and he’s contemplating how to use much more computing power to run the upcoming Star Citizen and other games of the future. He spoke about this challenge with Rich Hilleman, director of PMT at Amazon Game Studios and former chief creative director at EA.
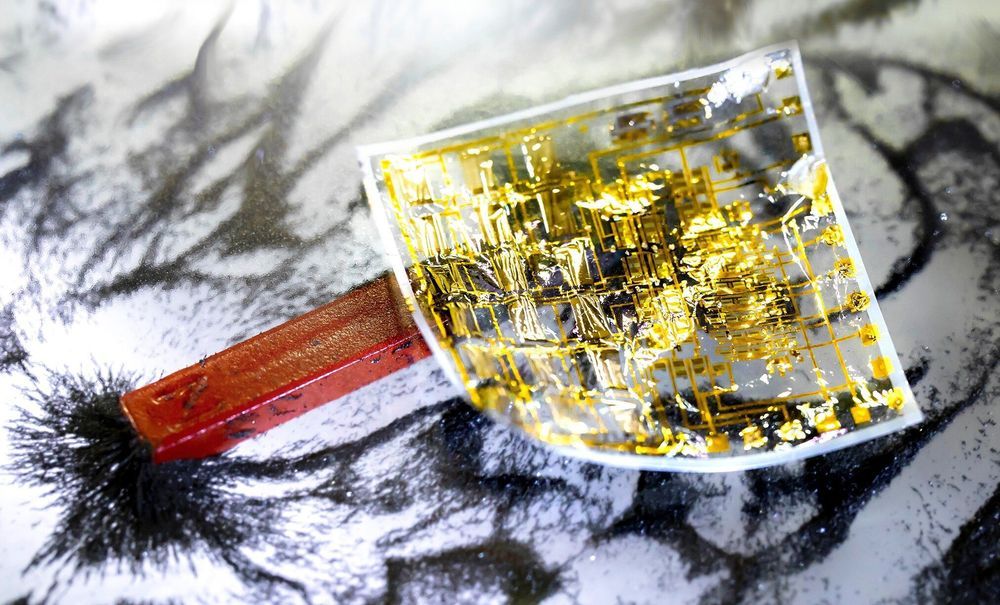

Human skin is a fascinating multifunctional organ with unique properties originating from its flexible and compliant nature. It allows for interfacing with external physical environment through numerous receptors interconnected with the nervous system. Scientists have been trying to transfer these features to artificial skin for a long time, aiming at robotic applications.
Robotic systems heavily rely on electronic and magnetic field sensing functionalities required for positioning and orientation in space. Much research has been devoted to implementation of these functionalities in a flexible, compliant form. Recent advancements in flexible sensors and organic electronics have provided important prerequisites. These devices can operate on soft and elastic surfaces, whereas sensors perceive various physical properties and transmit them via readout circuits.
To closely replicate natural skin, it is necessary to interconnect a large number of individual sensors. This challenging task became a major obstacle in realizing electronic skin. First demonstrations were based on an array of individual sensors addressed separately, which unavoidably resulted in a tremendous number of electronic connections. In order to reduce the necessary wiring, important technology had to be developed—namely, complex electronic circuits, current sources and switches had to be combined with individual magnetic sensors to achieve fully integrated devices.

SAN FRANCISCO, Jan. 21, 2020 /PRNewswire/ — Capella Space, an information services company providing Earth observation data on demand, today unveiled its evolved satellite design to enable on-demand observations of anywhere on Earth. Informed by extensive customer feedback and findings from the launch of Denali, Capella’s testbed satellite, the re-engineered design features a suite of technological innovations to deliver timely, flexible and frequent sub-0.5 meter very high quality images to the market. The enhanced technology package will deliver the most advanced offering for small satellite SAR imagery on the market.
Scientists have long assumed that fungi exist mainly to decompose matter into chemicals that other organisms can then use. But researchers at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University have found evidence that fungi possess a previously undiscovered talent with profound implications: the ability to use radioactivity as an energy source for making food and spurring their growth.
“The fungal kingdom comprises more species than any other plant or animal kingdom, so finding that they’re making food in addition to breaking it down means that Earth’s energetics—in particular, the amount of radiation energy being converted to biological energy—may need to be recalculated,” says Dr. Arturo Casadevall, chair of microbiology & immunology at Einstein and senior author of the study, published May 23 in PLoS ONE.
The ability of fungi to live off radiation could also prove useful to people: “Since ionizing radiation is prevalent in outer space, astronauts might be able to rely on fungi as an inexhaustible food source on long missions or for colonizing other planets,” says Dr. Ekaterina Dadachova, associate professor of nuclear medicine and microbiology & immunology at Einstein and lead author of the study.

Circa 2019
A gamma-ray burst registered in December of 2017 turns out to be “one of the closets GRBs ever observed”. The discovery is featured in Nature – and it has yielded valuable information about the formation of the most luminous phenomenon in the universe. Scientists from the Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen helped carrying out the analysis.
Jonatan Selsing frequently receives text messages from a certain sender regarding events in space. It happens all around the clock, and when his cell phone goes ‘beep’ he knows that yet another gamma-ray burst (GRB) notification has arrived. Which, routinely, raises the question: Does this information — originating from the death of a massive star way back, millions if not billions of years ago – merit further investigation?
“GRBs represent the brightest phenomenon known to science – the luminous intensity of a single GRB may in fact exceed that of all stars combined! And at the same time GRBs – which typically last just a couple of seconds – represent one of the best sources available, when it comes to gleaning information about the initial stages of our universe”, explains Jonatan Selsing.
An out-of-this-world building experience is coming! 🌙 ⭐️ The LEGO International Space Station is available February 1st!