If you missed this episode live, here is another chance for you to watch! Please share with your network so others can enjoy. Please follow The Mars Society and visit our website at marssociety.org for more content and updates. #mars #space #stem #redplanetlive
Category: space – Page 625
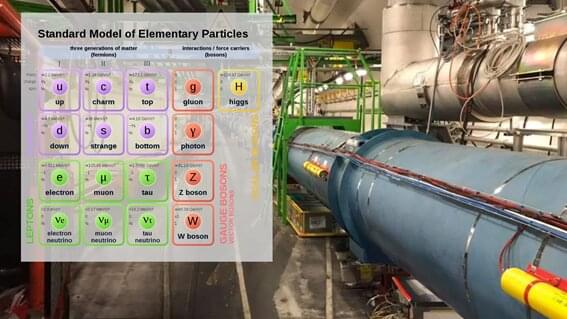
Leptoquarks and the physics beyond the Standard Model
The hunt is on for leptoquarks, particles beyond the limits of the standard model of particle physics —the best description we have so far of the physics that governs the forces of the Universe and its particles. These hypothetical particles could prove useful in explaining experimental and theoretical anomalies observed at particle accelerators such as the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) and could help to unify theories of physics beyond the standard model, if researchers could just spot them.
A new paper published in Nuclear Physics B by Anirban Karan, Priyotosh Bandyopadhyay, and Saunak Dutta, of the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, Kandi, together with Mahesh Jakkapu, Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI), Kanagawa, Japan, examines the potential signatures of leptoquarks at the LHC to see how they could arise from proton-proton collisions for the possible mass ranges of these particles.
The main objective of this research is how to distinguish the signatures of different leptoquarks at proton-proton colliders like LHC or its proposed successor, Karan says.

Asteroid Nereus Cruised Past Earth Today. In 39 Years It Could Be Mined For $5 Billion In Precious Metals
The possibility of space mining in future was thrown into sharp relief this weekend as a Near Earth Asteroid (NEA) called 4,660 Nereus passed our planet.
Worth an estimated $5 billion in precious metals and measuring 330 meters across, Nereus at no point came anywhere near being dangerous, getting no closer than 2.4 million miles/3.9 million kilometers at 13:51 UTC on Saturday, December 11, 2021.
That’s about 10 times the distance between the Earth and the Moon.
So why so much attention on Nereus?
There seemed to be a lot of misunderstanding about how dangerous—or otherwise—Nereus could be to Earth.
That’s because Nereus belongs to the subgroup of NEAs known as Apollo asteroids, which means that it will cross the path of Earth’s orbit at some point.
Full Story:
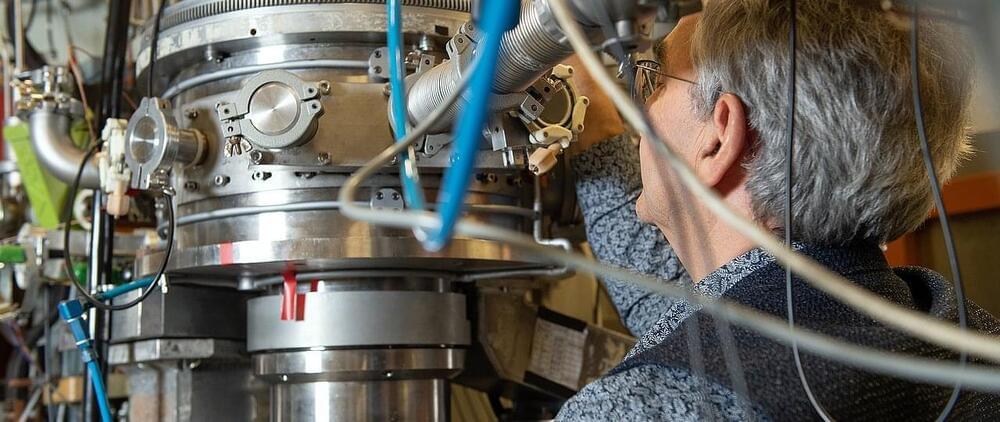

Experiment finds evidence for a long-sought particle comprising four neutrons
While all atomic nuclei except hydrogen are composed of protons and neutrons, physicists have been searching for a particle consisting of two, three or four neutrons for over half a century. Experiments by a team of physicists of the Technical University of Munich (TUM) at the accelerator laboratory on the Garching research campus now indicate that a particle comprising four bound neutrons may well exist.
While nuclear physicists agree that there are no systems in the universe made of only protons, they have been searching for particles comprising two, three or four neutrons for more than 50 years.
Should such a particle exist, parts of the theory of the strong interaction would need to be rethought. In addition, studying these particles in more detail could help us better understand the properties of neutron stars.




Top Space Force official: China is developing space capabilities at ‘twice the rate’ of US
Gen. David Thompson, vice chief of space operations for the US Space Force, said Saturday China is developing its space capabilities at “twice the rate” of the US.
On a panel of US space experts and leaders speaking at the Reagan National Defense Forum in a panel moderated by CNN’s Kristin Fisher, Gen. Thompson warned China could overtake the US in space capabilities by the end of the decade.
“The fact, that in essence, on average, they are building and fielding and updating their space capabilities at twice the rate we are means that very soon, if we don’t start accelerating our development and delivery capabilities, they will exceed us,” Gen. Thompson said, adding, “2030 is not an unreasonable estimate.”
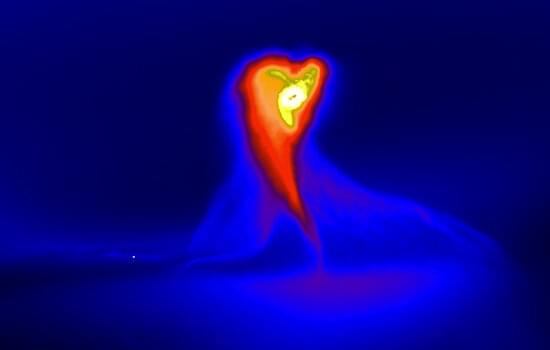
Astronomers find clue to solar system formation through little-known star
An international study led by Monash University astronomers focusing on an infamous star in Orion may help to shed light on how the solar system formed.
In 1936, over the course of the year, a previously unremarkable faint star in Orion, FU Ori, became 250 times brighter.
“FU Ori has remained bright ever since,” said Elisabeth Borchert, the lead author of the study to be published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS).