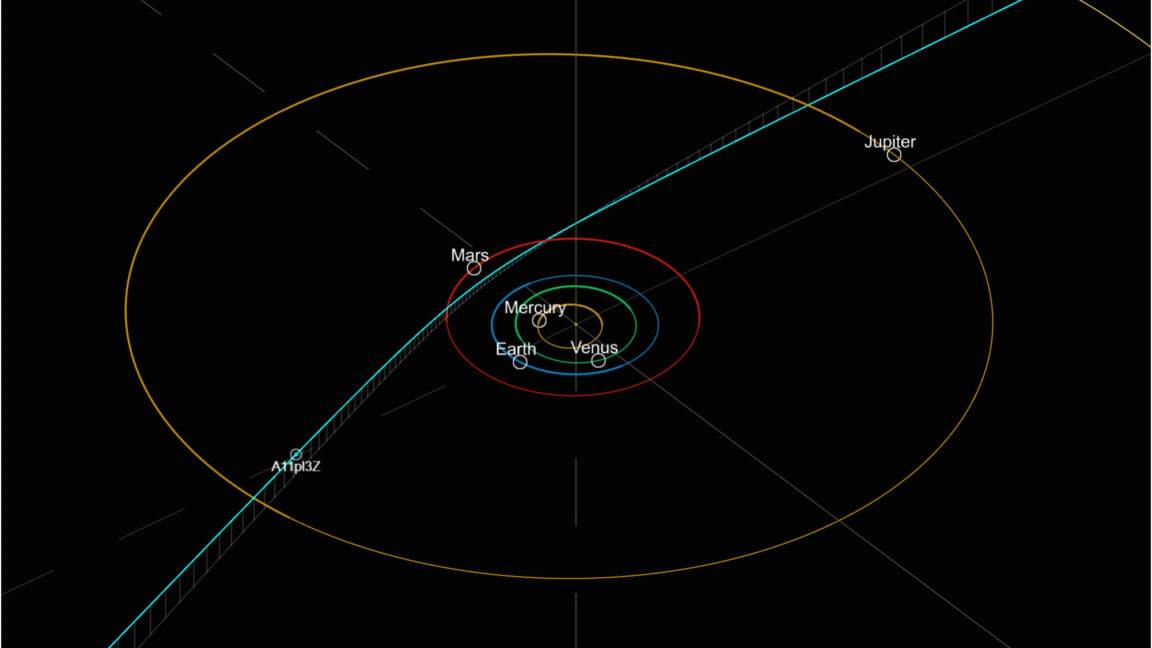
The object has a very high eccentricity.
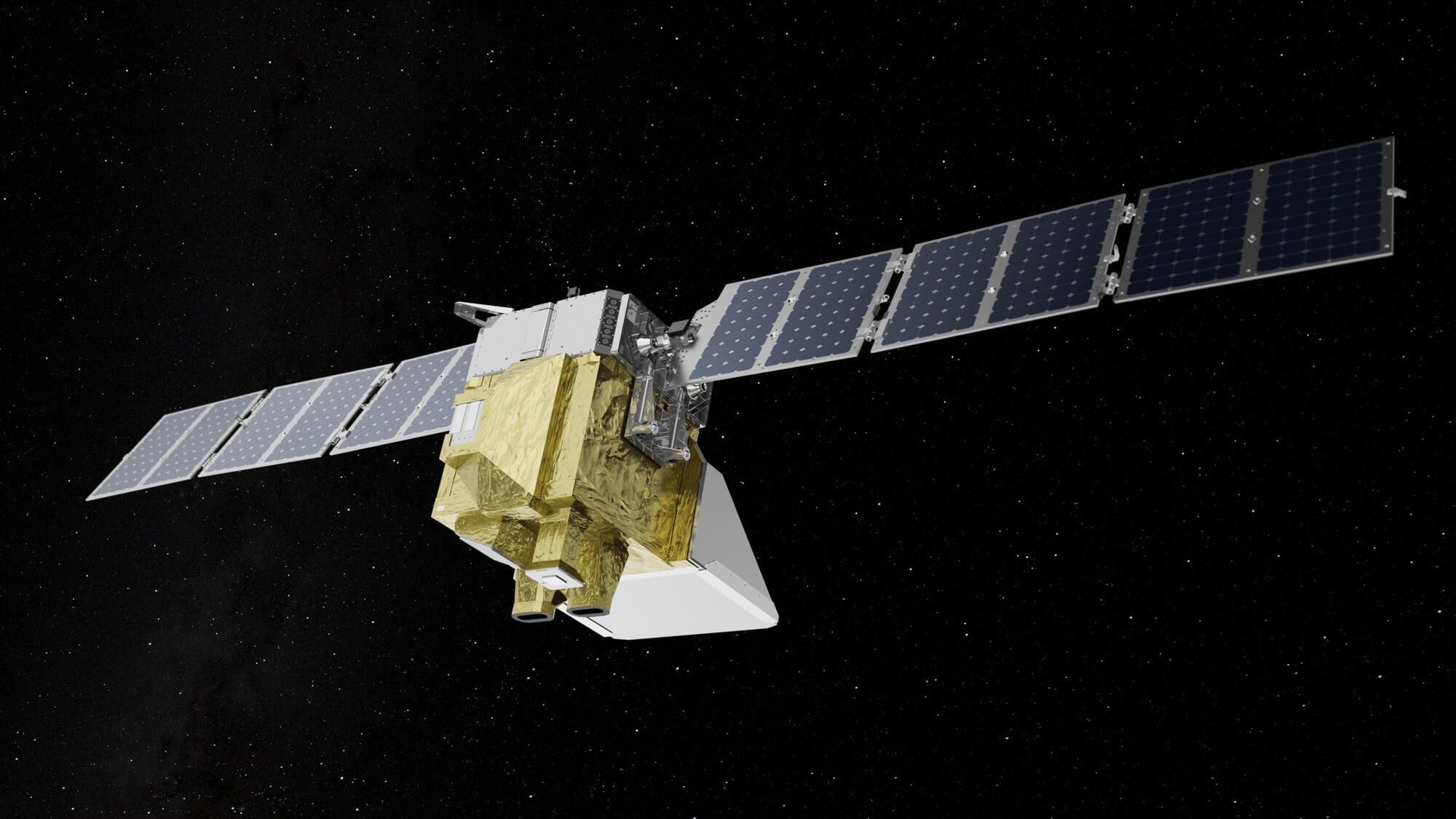


MethaneSAT was designed as a sort of check against commercial climate measurements in order to help policymakers independently verify industry emissions reports. “MethaneSAT is specifically designed to catalyze methane reductions by creating unprecedented transparency,” the mission’s website states.
EDF lists 10 mission partners credited with bringing the $88 million satellite to fruition, including BAE Systems, Harvard University, the New Zealand Space Agency, Bezos Earth Fund, Google and more. Though MethaneSAT is now out of service, mission operators say they’re still committed to turning the data they were able to collect into actionable results.
“We will continue to process data that we have retrieved from the satellite and will be releasing additional scenes of global oil and gas production region-scale emissions over the coming months,” EDT officials said. “To solve the climate challenge requires bold action and risk-taking and this satellite was at the leading edge of science, technology and advocacy. ”
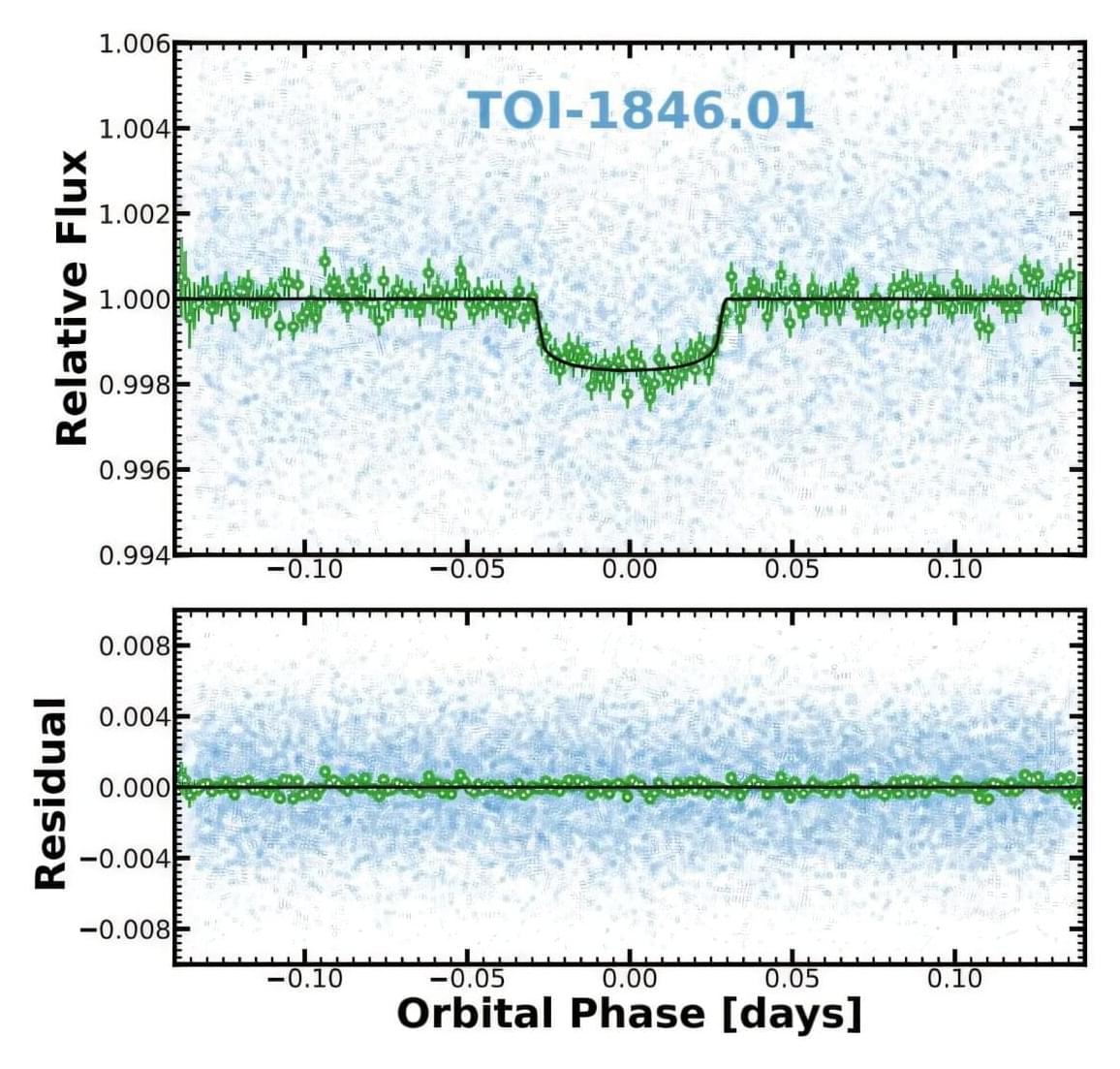
Using NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), an international team of astronomers has discovered a new super-Earth exoplanet that orbits a nearby M dwarf star. The newfound alien world, designated TOI-1846 b, is about two times larger and four times more massive than Earth. The finding was detailed in a paper published June 23 on the arXiv preprint server.
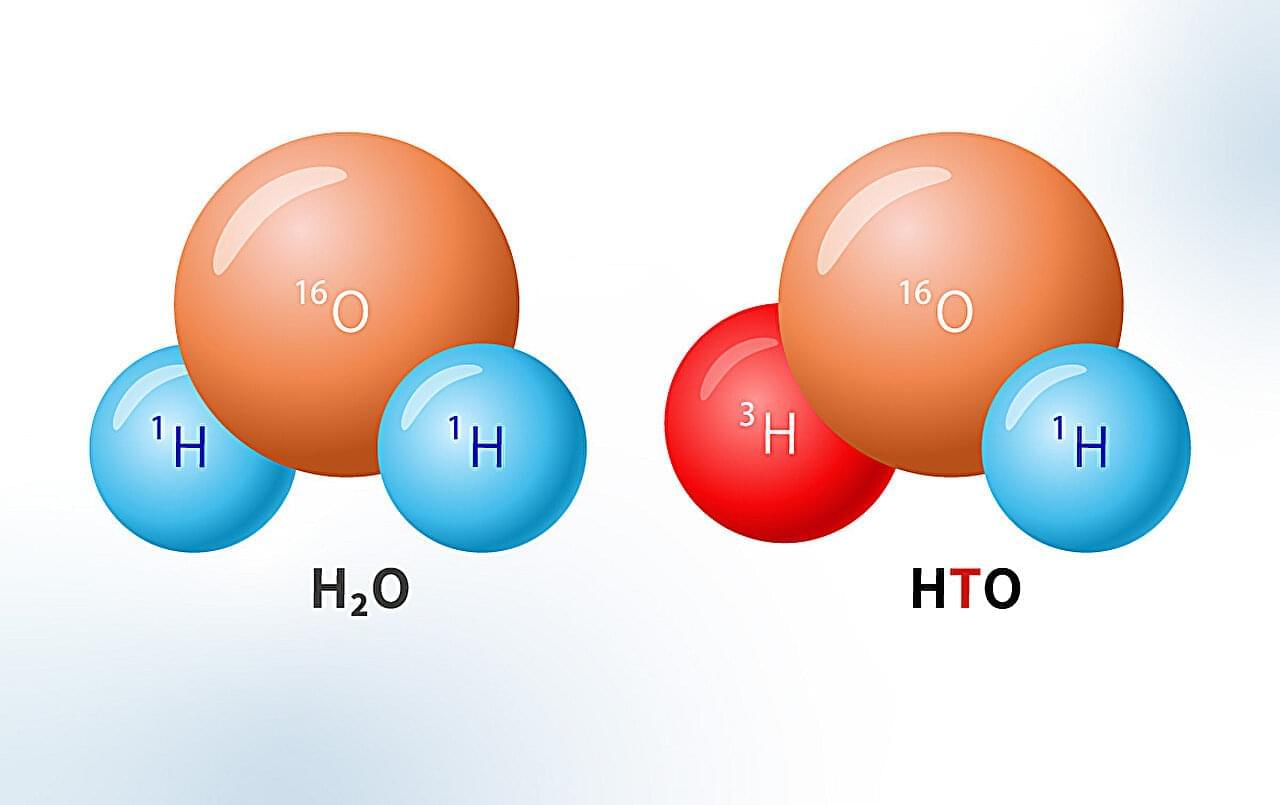
Operators have pumped water to cool the nuclear reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) since the accident in 2011 and treated this cooling water with the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS), which is a state-of-the-art purification system that removes radioactive materials, except tritium.
As part of the water molecule, tritium radionuclide, with a half-life of 12.32 years, is very costly and difficult to remove. The ALPS-treated water was accumulating and stored at the FDNPP site and there is limited space to store this water. Therefore, in 2021, the Government of Japan announced a policy that included discharging the ALPS-treated water via an approximately one-kilometer-long tunnel into the ocean. Planned releases of the ALPS-treated water diluted with ocean water began in August 2023 and will be completed by 2050.
In a new numerical modeling study, researchers have revealed that the simulated increase in tritium concentration in the Pacific Ocean due to the tritium originating from the ALPS-treated water is about 0.1% or less than the tritium background concentration of 0.03−0.2 Bq/L in the vicinity of the discharge site (within 25 km) and beyond.
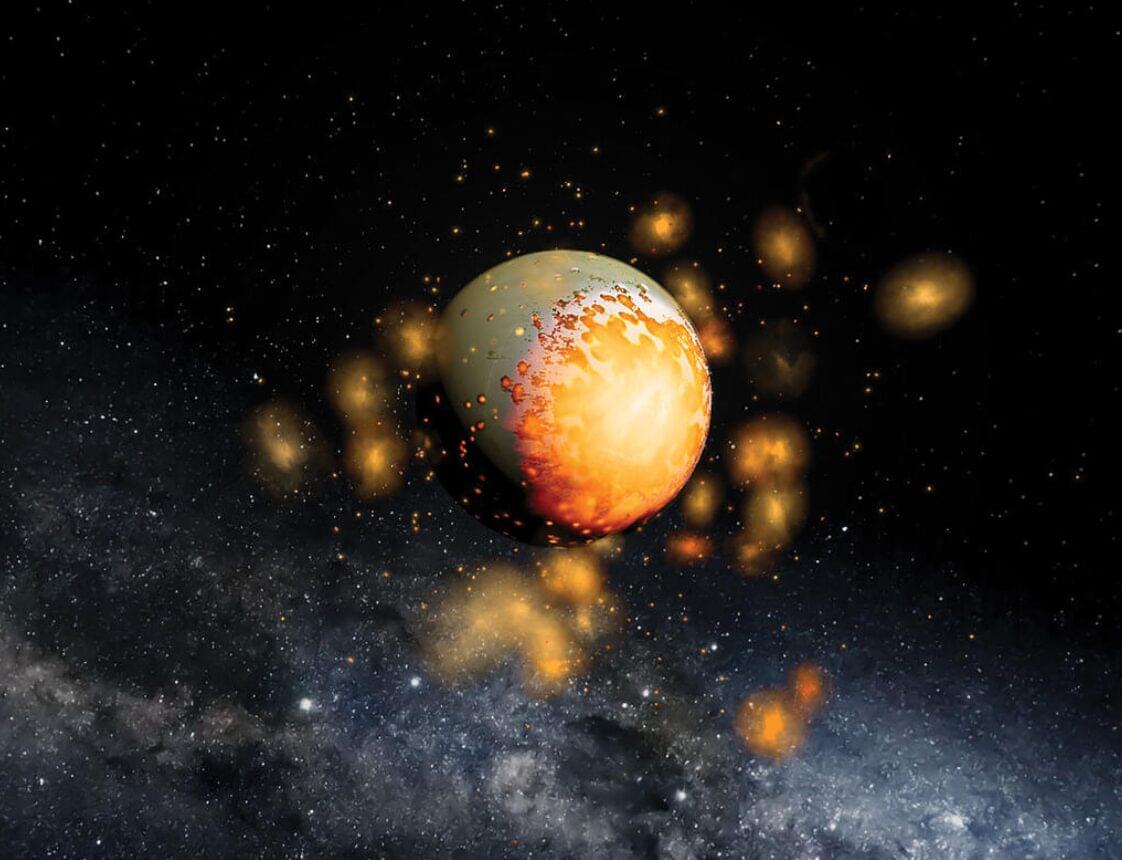


Southwest Research Institute has collaborated with Yale University to summarize the scientific community’s notable progress in advancing the understanding of the formation and evolution of the inner rocky planets, the so-called terrestrial planets. Their paper focuses on late accretion’s role in the long-term evolution of terrestrial planets, including their distinct geophysical and chemical properties as well as their potential habitability.
The Review paper is published in the journal Nature.
Solar systems form when clouds of gas and dust begin to coalesce. Gravity pulls these elements together, forming a central star, like our sun, surrounded by a flattened disk of consolidating materials. Our terrestrial planets—Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—formed as smaller rocky objects accumulated, or accreted, into larger planetesimals and eventually protoplanets, when late impacts made critical contributions. Earth was probably the last terrestrial planet to form, reaching about 99% of its final mass within about 60–100 million years after the first solids began to consolidate.

Using the Australia Telescope Compact Array (ATCA), astronomers have performed large-scale radio observations of a star-forming region known as the Chamaeleon cloud complex. The observational campaign, which detected five young stars in Chamaeleon, may shed more light on the properties of this complex. The findings were detailed in a paper published June 19 on the arXiv pre-print server.