Webb, and Psychean editorial note by Adriano V. Autino.
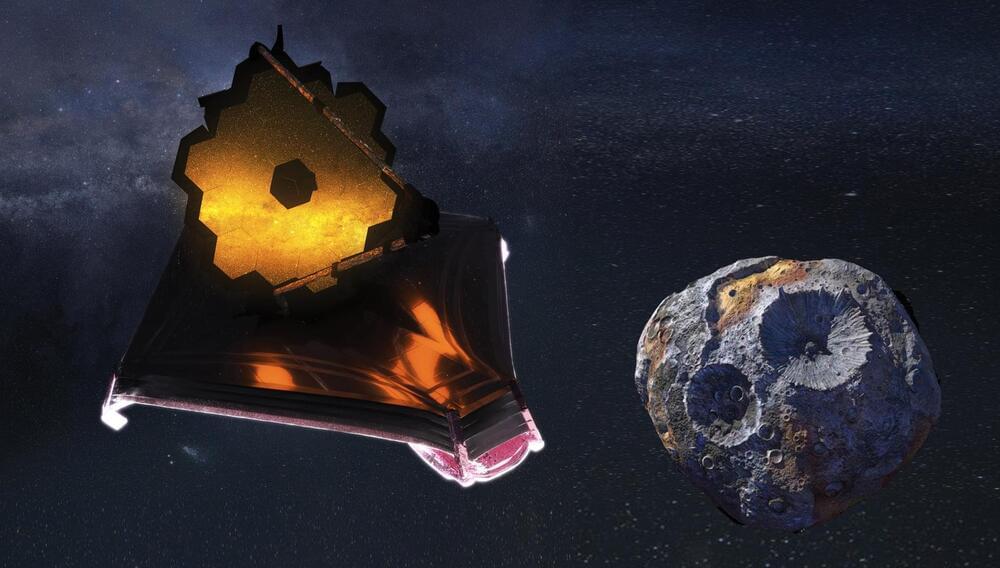
We just attended the launch of the James Webb Telescope, headed to the Earth-Sun Lagrange point 2 (L2), at 1.5 kilometers from Earth. A very ambitious project, aimed to place a human eye in a location where it will be easier to investigate the origin and the meaningful life events of the universe, of our solar system and our mother planet. What raised some thoughts in my mind is one of the characteristics of this beautiful sample of human ingenuity and hunger for knowledge: the JWST mirror has been plated with gold, due to elements properties like a high reflection of infrared light and extreme un-reactivity. My aim is not to discuss this choice from the scientific point of view. It makes me rather think about the value of precious metals, that’s not only their beauty, nor the use we make of them to realize precious jewels.
While I was in space just with my mind, it was easy to go some more million kilometers further away, reaching to the 16 Psyche Asteroid. Psyche – an M-type asteroid, fragment of a proto-planet broken up during the birth of the solar system — dwells somewhere in the middle of the Asteroid Belt, between Mars and Jupiter. The distance from Earth ranges from 252 million to 645 million kilometers.
Why Psyche owns such a great reputation, among the space expansionist community, and the space miners subassembly, in a more specific way? Its diameter is estimated not less than 227 km. Due to the gravitational perturbations it causes among other asteroids in its surroundings, Psyche is kind of under special surveillance, since long time. Such perturbations are due to high mass and density, and such properties raised further analysis, by means of ultraviolet light observation. To make short a long research story, Psyche is likely mainly composed by iron and nichel, and its global value is estimated around $10 quintillion, a figure even hard to imagine.