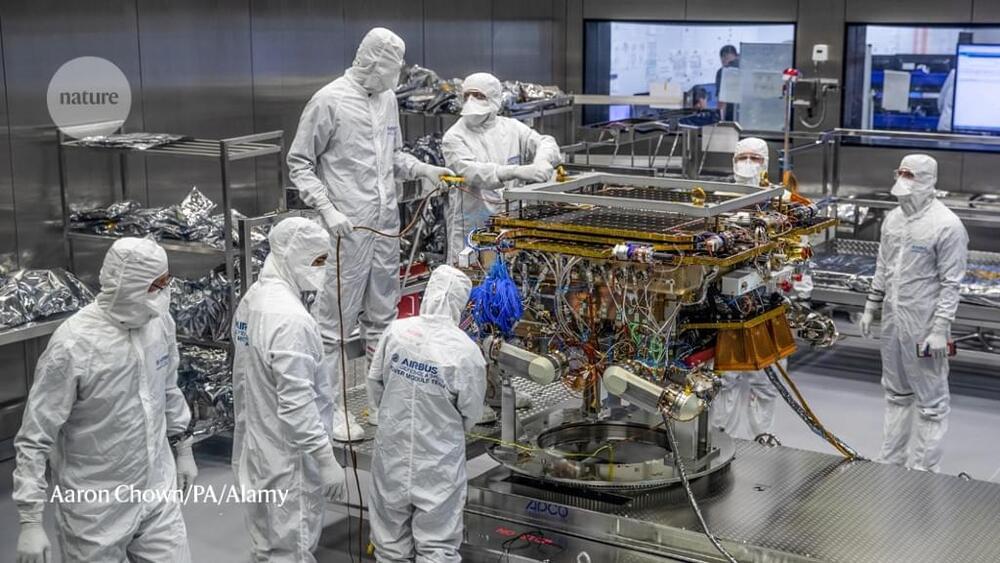
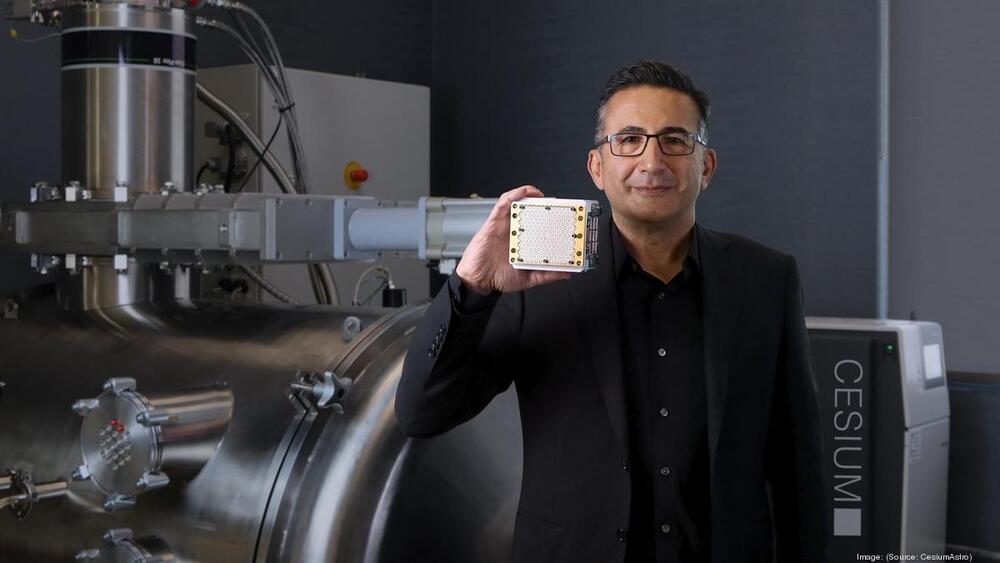
Austin is home to many of the players in the new space race, like CEO Shey Sabripour, whose startup just raised tens of millions to make satellite-based communications more efficient.


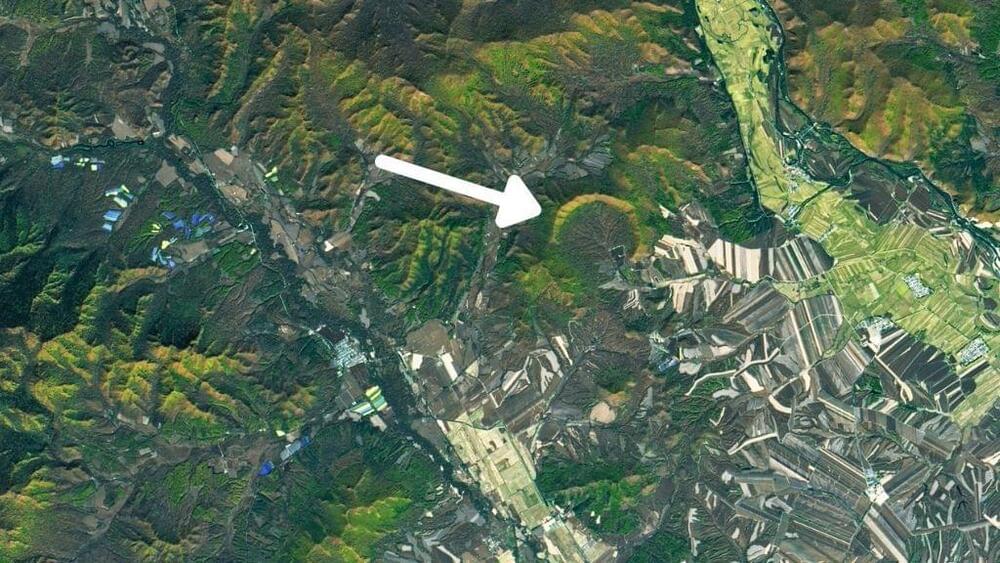
The impact crater is the second discovered in China.
A crescent-shaped crater in Northeast China holds the record as the largest impact crater on Earth that formed in the last 100,000 years.
Prior to 2020, the only other impact crater ever discovered in China was found in Xiuyan county of the coastal province of Liaoning, according to a statement from the NASA Earth Observatory. Then, in July 2021, scientists confirmed that a geological structure in the Lesser Xing’an mountain range had formed as a result of a space rock striking Earth. The team published a description of the newfound impact crater that month in the journal Meteoritics and Planetary Science.
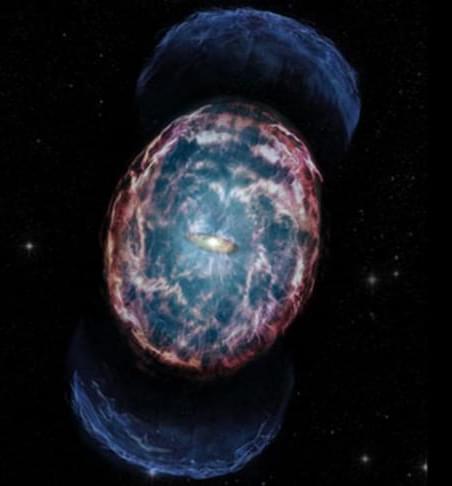


Researchers at the Northwestern University and Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences may have potentially come across a kilonova afterglow, the first of its kind ever to be observed, according to a university press release.
A kilonova is the merger of two neutron stars that creates a blast 1,000 times brighter than a classical nova. On August 17, 2017, astronomers observed the first-ever neutron star merger, GW170817, using light as well as gravitational waves. Ever since researchers across the globe have been pointing ground and space telescopes towards this event to study it across the electromagnetic spectrum.




Interfacing technology and electronics with the real world is often fairly tricky. Complexity and edge cases work their way in to every corner of a project like this; just ask anyone who has ever tried to operate a rover on Mars, make a hydroponics garden, or build almost any robotics project. Even those of us who simply own a consumer-grade printer are flummoxed by the ways in which they can fail when manipulating single sheets of paper. This robotic lawnmower is no exception, driving its creator [TK] to extremes to get it to mow his lawn.
[TK] actually had a platform for his autonomous mower ready to go thanks to a previous build using this solar-powered robot to explore the Australian outback. Adding another motor to handle the grass trimming seemed simple at first and he set about wiring it all up and interfacing it to the robot. After the first iteration he found the robot was moving too fast to effectively cut the grass, so he added a more powerful cutting motor and a gearbox to help the mower crawl more slowly over the lawn. Disaster struck when his 3D printed mount for the steel cutting blades shattered, but with [TK] uninjured he pushed on with more improvements.
As it stands right now, the mower can effectively cut the grass moving forward even with the plastic-only cutting blades that [TK] is using now for safety reasons. The mower stripped its reverse gear so there still are some improvements to make before this robot is autonomously cutting the lawn without supervision. Normally we see lawnmowers retrofitted with robotics rather than robotics retrofitted with a lawnmower, but we’re excited to see any approach that lets us worry about one less household chore.