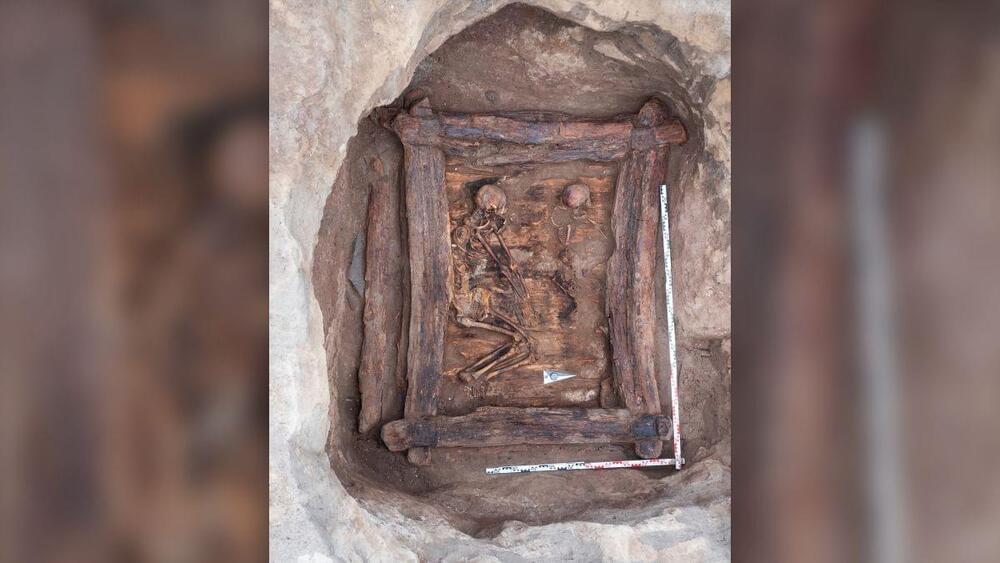
A 50-year-old woman was buried with a unique “male” pendant.
Archaeologists have discovered a large burial mound in the Siberian “Valley of the Kings” dating to more than 2,500 years ago. The ancient tomb holds the remains of five people, including those of a woman and toddler who were buried with an array of grave goods, such as a crescent moon-shaped pendant, bronze mirror and gold earrings.
The mounds were made by the Scythians — a term used to describe culturally-related nomadic groups that lived on the steppes between the Black Sea and China from about 800 B.C. to about A.D. 300.