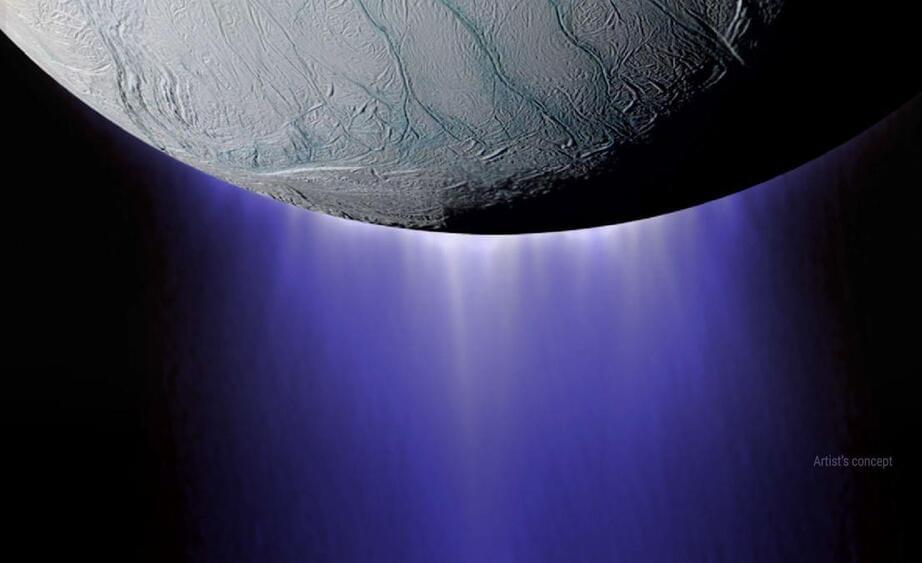
The underground ocean of Saturn’s moon Enceladus may contain significant amounts of phosphorus, which is vital for life as we know it.




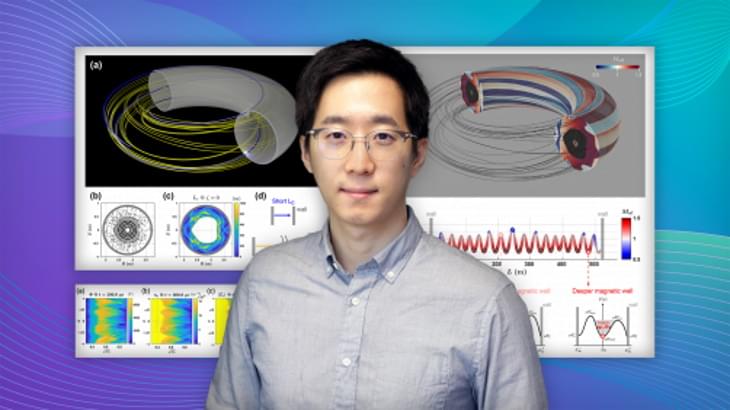
Physicists at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have proposed that the formation of “hills and valleys” in magnetic field lines could be the source of sudden collapses of heat ahead of disruptions that can damage doughnut-shaped tokamak fusion facilities. Their discovery could help overcome a critical challenge facing such facilities.
The research, published in a Physics of Plasmas paper in July, traced the collapse to the 3D disordering of the strong magnetic fields used to contain the hot, charged plasma gas. “We proposed a novel way to understand the [disordered] field lines, which was usually ignored or poorly modelled in the previous studies,” said Min-Gu Yoo, a post-doctoral researcher at PPPL and lead author of the paper.
Fusion is the process that powers the Sun and stars as hydrogen atoms fuse together to form helium, and matter is converted into energy. Capturing the process on Earth could create a clean, carbon-free and almost inexhaustible source of power to generate electricity, but comes with many engineering challenges: in stars, massive gravitational forces create the right conditions for fusion. On Earth those conditions are much harder to achieve.
The ensemble of sounds in this video captured on Mars by NASA’s Perseverance rover includes a dust removal tool for rock analysis, the Ingenuity Mars helicopter, and the impact of a laser on rocks. A new study of some of those sounds, captured mostly by the rover’s SuperCam microphone during the first 216 Martian days of the mission, reveals how sound differs on Mars, including traveling slower than on Earth. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech.
A new study based on recordings made by the rover finds that the speed of sound is slower on the Red Planet than on Earth and that, mostly, a deep silence prevails.
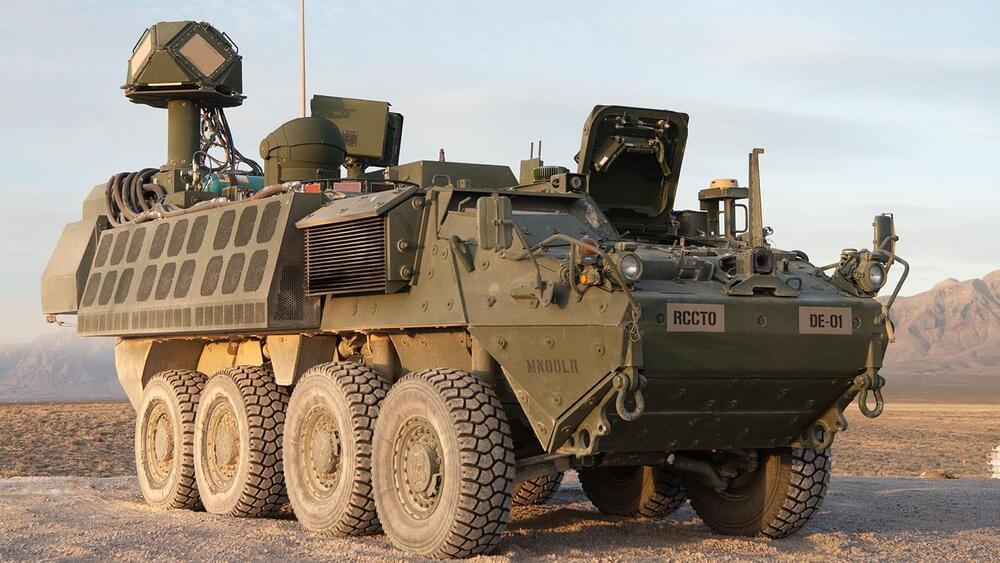

LAS CRUCES, N.M., May 16, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — In four weeks of continuous live-fire exercises, an industry team led by Raytheon Intelligence & Space, a Raytheon Technologies (NYSE: RTX) business, and Kord, a wholly owned subsidiary of KBR, defeated multiple 60mm mortar rounds with a 50kW-class high energy laser integrated on a Stryker combat vehicle.
The directed energy weapon system — part of the U.S. Army’s Directed Energy Maneuver-Short Range Air Defense, or DE M-SHORAD — acquired, tracked, targeted and defeated multiple mortars and successfully accomplished multiple tests simulating real-world scenarios.
Continuing to put the DE M-SHORAD system to the test, the recent operational assessment at White Sands Missile Range also included defeating several small, medium and large drones.

Crucially, they showed that the synapses were capable of Hebbian learning, the process by which the strength of the connection between two neurons increases or decreases based on activity. This is key to the way information is encoded into the brain, with the strengths of connections between neurons controlling the function of different brain circuits.
In biological neurons this ability to alter the strength of connections—known as plasticity—operates at two distinct timescales. Over shorter timescales, regular firing of the neuron leads to a buildup of ions that temporarily increase the ease with which signals pass across. In the long term though, regular activity can cause new receptors to grow at a synapse, resulting in more durable increases in the strength of the connection.
With the artificial synapses, short-term plasticity operates in much the same way due to a buildup of ions. But boosting the connection strength in the long term relies on using voltage pulses to essentially grow new material out of a soup of chemical precursors at the synapse, which increases its conductivity.


Finding definitive evidence for past primitive life in ancient Mars rock and soil samples may be well-nigh impossible, renowned geologist and astrobiologist Frances Westall told me at the recent Europlanet Science Congress (EPSC) in Granada, Spain. And she should know. Westall is someone who still claims the discovery of Earth’s oldest-known microfossils, dating back some 3.45-billion-years ago.
But it’s hard enough to identify primitive microfossils in Earth’s oldest rocks, much less from robotic samples taken on Mars. Thus, if we have a hard time identifying past life on Earth, what hope do we have of doing it with Mars samples?
“I think it’s going to be really difficult,” said Westall, a researcher at France’s Center for Molecular Biophysics in Orleans. “I can tell you, there’s going to be a lot of arguments about it.”

Digitalization generated 4 percent of the total greenhouse emissions in 2020.
More than half of the digital data firms generate is collected, processed, and stored for single-use purposes. Often, it is never re-used. This could be your multiple near-identical images held on Google Photos or iCloud, a business’s outdated spreadsheets that will never be used again, or data from internet of things sensors that have no purpose.
This “dark data” is anchored to the real world by the energy it requires. Even data that is stored and never used again takes up space on servers — typically huge banks of computers in warehouses. Those computers and those warehouses all use lots of electricity.
Gorodenkoff/iStock.
This is a significant energy cost that is hidden in most organizations. Maintaining an effective organizational memory is a challenge, but at what cost to the environment?