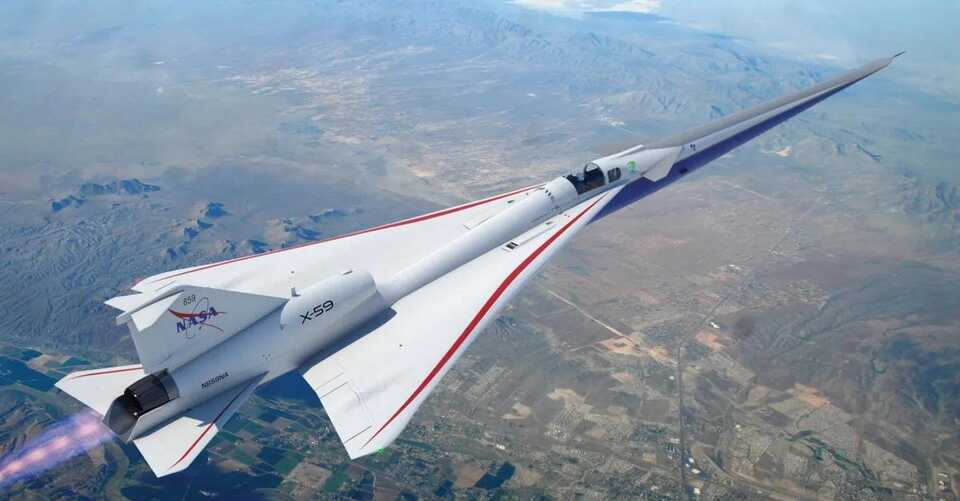
With the help of NASA’s QueSST mission, aeronautical innovators hope to break the sound barrier once more, but this time in a totally different fashion that…


In this video, you are going to learn: what dangers are waiting for us in seemingly empty places? Can physicists on Earth destroy the entire cosmos? And most importantly, can a vacuum end the world we know and love?
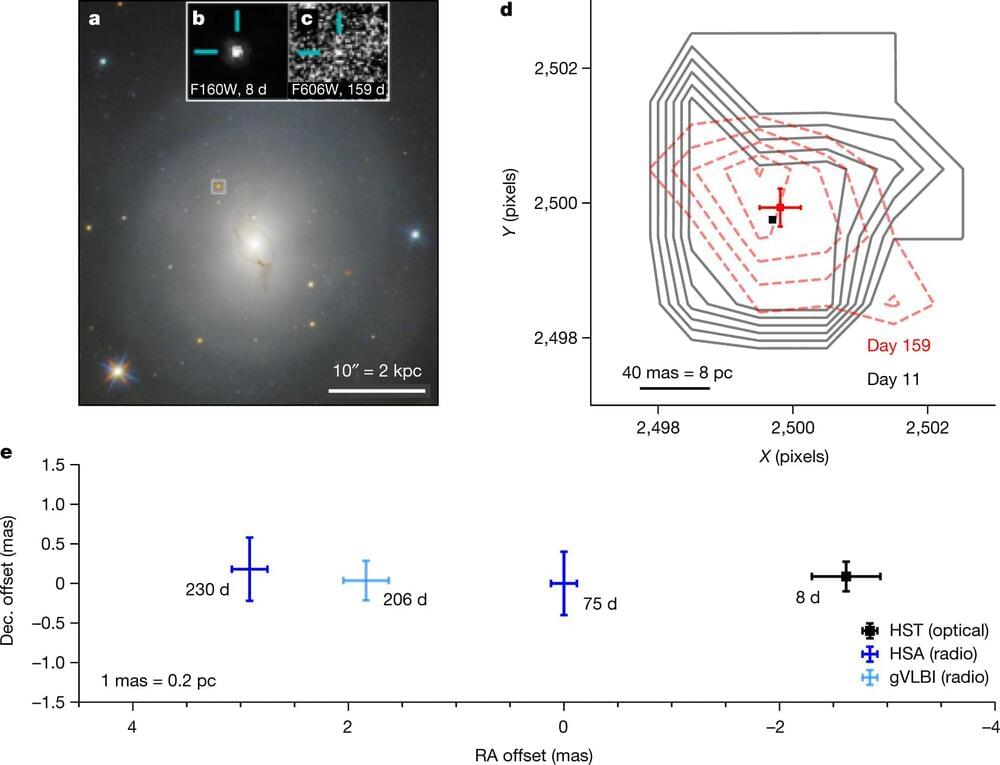
The afterglow of the binary neutron-star merger GW1708171 gave evidence for a structured relativistic jet2–6 and a link3,7,8 between such mergers and short gamma-ray bursts. Superluminal motion, found using radio very long baseline interferometry3 (VLBI), together with the afterglow light curve provided constraints on the viewing angle (14–28 degrees), the opening angle of the jet core (less than 5 degrees) and a modest limit on the initial Lorentz factor of the jet core (more than 4). Here we report on another superluminal motion measurement, at seven times the speed of light, leveraging Hubble Space Telescope precision astrometry and previous radio VLBI data for GW170817.

Researchers have demonstrated a quantum sensor that can power itself using sunlight and an ambient magnetic field, an achievement that could help reduce the energy costs of this energy-hungry technology.
No longer the realm of science fiction, quantum sensors are today used in applications ranging from timekeeping and gravitational-wave detection to nanoscale magnetometry [1]. When making new quantum sensors, most researchers focus on creating devices that are as precise as possible, which typically requires using advanced—energy-hungry—technologies. This high energy consumption can be problematic for sensors designed for use in remote locations on Earth, in space, or in Internet-of-Things sensors that are not connected to mains electricity. To reduce the reliance of quantum sensors on external energy sources, Yunbin Zhu of the University of Science and Technology of China and colleagues now demonstrate a quantum sensor that directly exploits renewable energy sources to get the energy it needs to operate [2].

Jim McDivitt, an astronaut who played a key role in making America’s first spacewalk and moon landing possible, has died. He was 93.
NASA confirmed his death to NPR on Monday, adding that he was surrounded by family and friends when he died on Thursday.
Known for being a courageous test pilot and dedicated leader, McDivitt commanded two of the most crucial flights in the early space race — Gemini 4 and Apollo 9.

Thanks to NASA, the world may soon have access to chargers that can top off an EV in as little as five minutes. One of the biggest obstacles to fast charging is dealing with temperature. According to NASA, for an EV to be charged in five minutes, the charger must deliver an electric current of 1,400 amperes. For reference, the fastest chargers currently available max out at around 520 amperes. More amperes equals more heat. A lot more heat. Companies and research organizations are pursuing solutions to the problem; Ford and Purdue University, for example, are exploring liquid-cooled charging cables.
A team sponsored by NASA’s Biological and Physical Sciences Division is working on technology that could provide another solution needed for ultra fast EV charging. The technology has been developed for use in space, in which massive temperature differentials require massive heat transfer capabilities. An experiment to prove the new tech, the Flow Boiling and Condensation Experiment (FBCE), was installed on the International Space Station and is providing data that NASA will use to determine if the system will provide the claimed orders-of-magnitude benefits in heat transfer efficiency.
We’re definitely not NASA-level engineers but we will try to explain the FBCE the best we can. The FBCE is made up of several modules; one of which is called a “Flow Boiling Module” (FBM). When cooling liquid inside the FBM begins to boil, the bubbles formed draw liquid from the inner part of the flow channel to its walls. The process “efficiently transfers heat by taking advantage of both the liquid’s lower temperature and the ensuing change of phase from liquid to vapor.” The technique has been dubbed “subcooled flow boiling.”

It may have all started with a moon.
So it is not very likely that random minor impacts caused one planet to almost 70 degrees more than the other while not affecting their spin rates.
Similar spin rates point to much “smoother” processes that took place over eons but dramatically affected the properties of the two gas giants.
Scientists have already hypothesized the “Great Migration” of the outer planets through the inner solar system and its cloud of early planetessimals, which was likely the cause of events such as the Late Heavy Bombardment, which is responsible for many of the craters visible on our Moon.

AI image generator Dall-E2 is about to find a new host. Microsoft will integrate the AI-based image generator with Microsoft Designer, a video-making tool to be available within the Microsoft Office suite. Till recently, Dall-E2 which is looked down upon as an app meant for only playing around with text prompts will be a part of Microsoft’s AI graphic design app. Designers and video makers who find it difficult to search for unique images can now leverage Microsoft’s Designer app to compose videos with imagery of their choice. Microsoft’s venture is seen as a step toward competing with design major Canva, which boasts more than 100 million active users. During the Ignite Conference held recently, Microsoft announced that it would integrate Dall-E 2 into the yet-to-be-released Designer app as well as existing Bing and Edge.

On Sunday, October 9th, astronomers around the world were privy to an unusually bright and long-lasting pulse of high-energy radiation that swept over Earth, according to a NASA statement published on Thursday. The source of the event was a gamma-ray burst (GRB), one of the most luminous events ever known.

The Moon rotates around the Earth at about the same speed, as it does around its axis, that’s why we can only see one side of it. It means that 41% of its surface hasn’t been explored yet! This fact surprises many people, as we are used to thinking that we know everything about all things in the world. While even our own planet remains a mystery to us.