Astronomers thought they were looking at one distant galaxy, but new Webb images reveal two — on a collision course with a third.
Category: space – Page 480
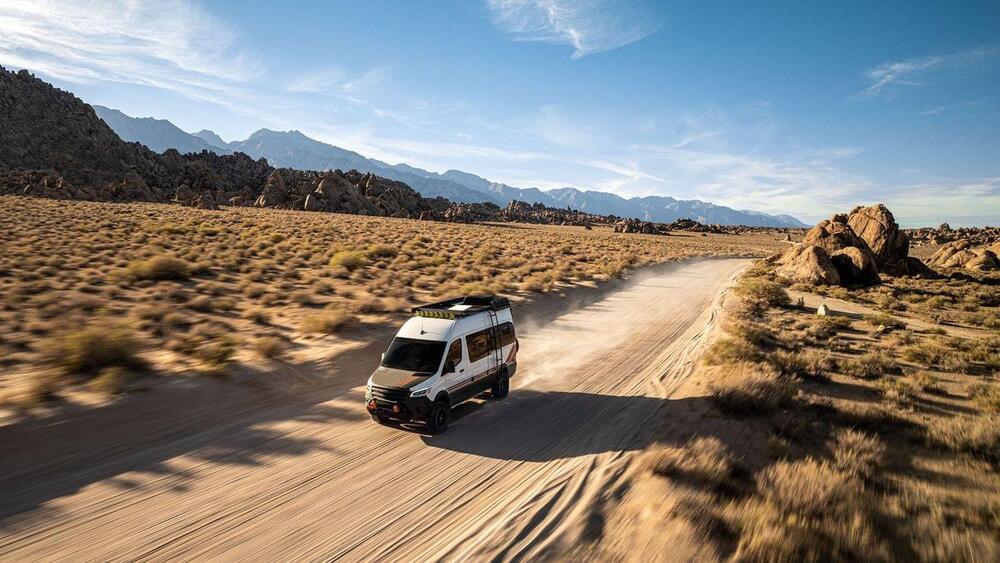


SpaceX announces a new ‘flat high performance’ Starlink dish for internet on moving vehicles
The newly-designed dish allows users to have a permanent high-performance Starlink installation on their vehicles.
SpaceX announced it is now accepting orders for its new “flat high-performance” Starlink dish for moving vehicles.
In a Tuesday tweet, the private space firm explained that the new offering allows customers to “enjoy high-speed, low-latency internet while on the move!”
NASA-funded space robots will grab objects in orbit using arms controlled from Earth
The company that will work with US Space Force has also won some NASA contracts.
It’s official: robots are here to stay in space. Robotics software and engineering company PickNik Robotics announced on Tuesday that it has won a SpaceWERX contract to work on robotics for the US Space Force, according to a press release acquired by IE
In addition, the company recently won a NASA Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) Phase I contract for continued work on supervised autonomy for space robotics, as well as a Colorado Advanced Industries Accelerator (AIA) grant for space robotics.
Three wins.
The company has three big wins: a SpaceWERX contract, a NASA Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) Phase I contract and a Colorado Advanced Industries Accelerator (AIA) grant for space robotics.





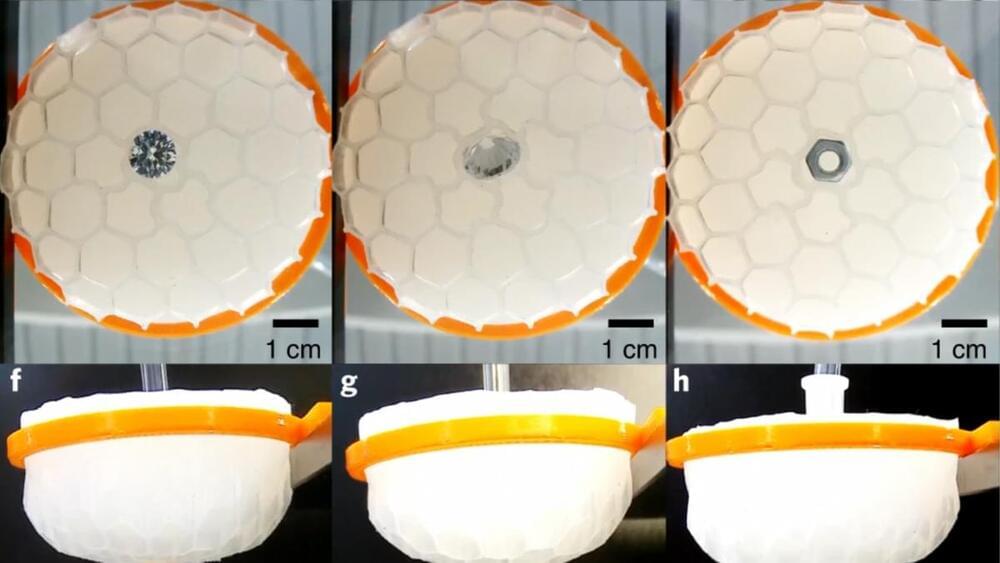
Space-cleaning robots could be developed thanks to novel device that was inspired by wilting passion fruits
Turns out, dehydrated passion fruits exhibit a type of symmetry not previously known, inspiring self-adapting robots that could one day ‘grasp’ space junk.
A previously unknown type of wrinkling pattern on the surface of dehydrated passion fruits inspired the invention of a device that could be used to clean up space debris and hazardous materials, according to South Morning China Post (SMCP)
The real-life application comes after Fan Xu, Xi-Qiao Feng and colleagues at Fudan University in Shanghai reported an unknown type of chiral wrinkling pattern on the surface of dehydrated passion fruits in their study published in the journal Nature Computational Science the same day. previously unknown type of wrinkling pattern on the surface of dehydrated passion fruits inspired the invention of a device that could be used to clean up space debris and hazardous materials, according to South Morning China Post (SMCP).