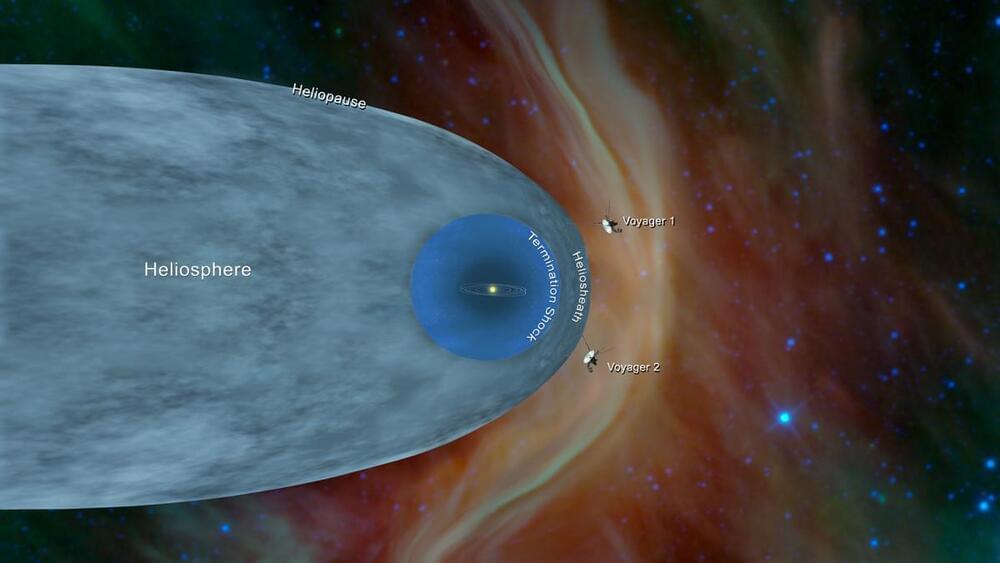
Thanks to Scopely for sponsoring this video — Download Star Trek Fleet Command on iOS & Android and battle in the Star Trek universe here: https://pixly.go2cloud.org/SH3UL
Check out how it would launch here:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qXxl5Ef5lFg.
Discord: https://discord.gg/WXb565P9nQ
My News Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCD3cl0MmX6fGZzeAHt4JWJA
Join this channel to get access to perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpM4zrZ9c_apiEj6CApj2yw/join.
Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/foundandexplained