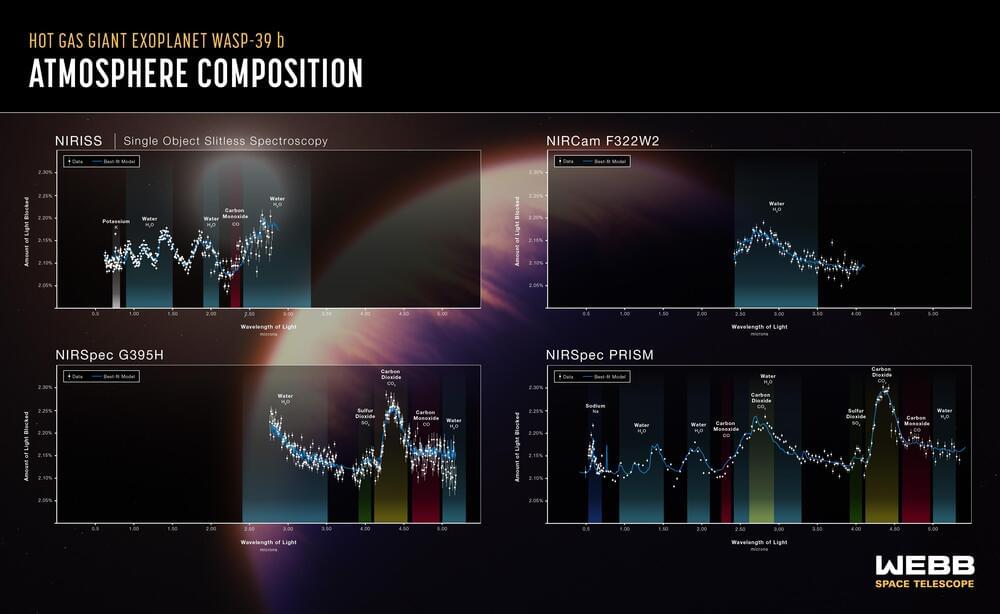
The latest data improves our understanding of how clouds in “hot Jupiter” exoplanets like this might appear up close. They are likely to be broken up, rather than a single, uniform blanket over the planet.
Photochemistry is the result of light triggering chemical reactions. This process is fundamental to life on Earth: it makes ozone, for example, which protects us from harsh ultraviolet (UV) rays.
New observations of WASP-39 b, a Jupiter-sized planet orbiting a Sun-like star found 700 light years away, confirm the presence of a never-before-seen molecule in the atmosphere – sulfur dioxide – among other details.
The James Webb Space Telescope has previously studied WASP-39 b. In August, it captured the first clear evidence for carbon dioxide. Now, it has focused its array of highly sensitive instruments on the planet once again, revealing not just an isolated ingredient, but a full menu of atoms, molecules, and even signs of active chemistry and clouds in the broiling atmosphere. This latest data, far more detailed than any previous telescope, shows the amazing capabilities of Webb, and hints at the potential for future discoveries that may reveal biosignatures.