Imagine walking into a room at night, turning out all the lights and closing the shades. Yet an eerie glow comes from the walls, ceiling, and floor. The faint light is barely enough to see your hands before your face, but it persists.
Sounds like a scene out of “Ghost Hunters?” No, for astronomers this is the real deal. But looking for something that’s close to nothing is not easy. Astronomers searched through 200,000 archival images from Hubble Space Telescope and made tens of thousands of measurements on these images to look for any residual background glow in the sky.
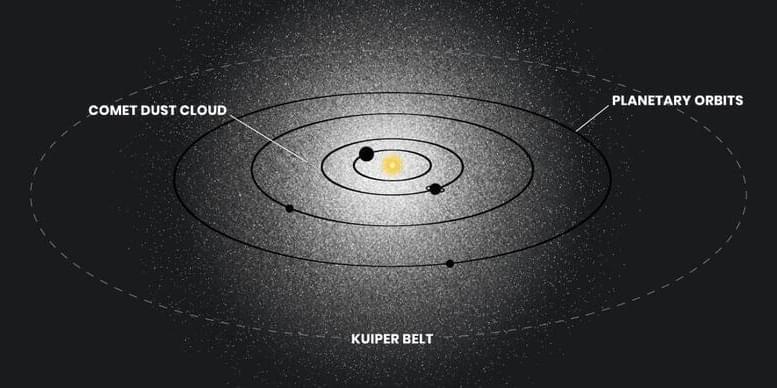
Like turning out the lights in a room, they subtracted the light from stars, galaxies, planets and the zodiacal light. Surprisingly, a ghostly, feeble glow was left over. It’s equivalent to the steady light of ten fireflies spread across the entire sky.