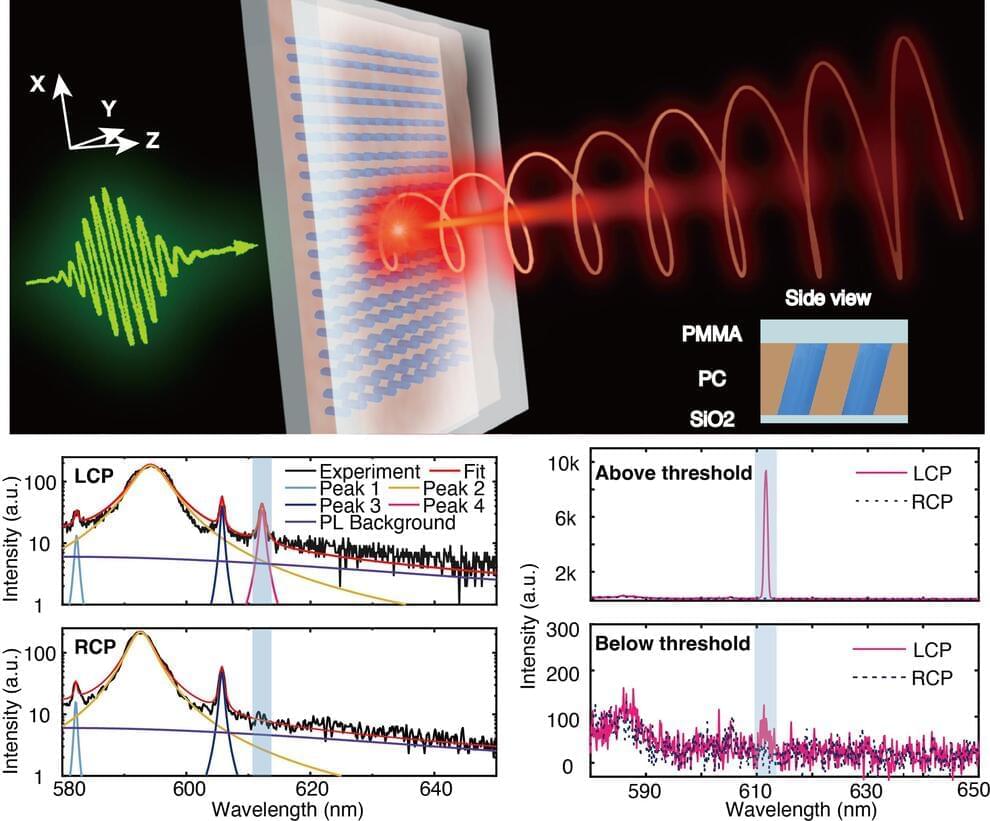
An ultracompact circularly polarized light source is a crucial component for the applications of classical and quantum optics information processing. The development of this field relies on the advances of two fields: quantum materials and chiral optical cavities. Conventional approaches for circularly polarized photoluminescence suffer from incoherent broadband emission, limited DOP, and large radiating angles. Their practical applications are constrained by low efficiency and energy waste to undesired handedness and emission directions. The chiral microlasers can have large DOPs and directional output, but only in specific power ranges. Most importantly, their subthreshold performances plummet significantly. Up to now, the strategy for simultaneous control of chiral spontaneous emission and chiral lasing is still absent.
In a new paper published in Science, researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology and Australian National University employ the physics of chiral quasi bound states in the continuum (BICs) and demonstrate the efficient and controllable emission of circularly polarized light from resonant metasurfaces.
BICs with integer topological charge in momentum space and a theoretically infinite Q factor have been explored for many applications including nonlinear optics and lasing. By introducing in-plane asymmetry, BICs turn to be quasi-BICs with finite but still high Q factors. Interestingly, the integer topological charge of BICs mode would split into two half integer charges, which symmetrically distribute in momentum space and correspond to left-and right-handed circular polarization states, also known as C points.