The sun is growing more active in its regular 11-year-cycle and has a huge sunspot serving as a hotbed of flares and other activity.


Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic.
Sorry, IGNORING A C Clarks PLOTS FOR 2010 AND 3001!!!!!!!!!!! Some 203 years and 2 months after astronaut Frank Poole (Gary Lockwood, this short approved by the self same actor) is murdered by the Discovery’s A.I. HAL 9,000, his body encounters a Monolith. Using practical models and digital versions of the analogue VFX tricks used in the original, with respect to Stanley Kubrick, Douglas Trumbull and Wally Veevers.
For the people who dont read the first line in this description…
Music by Richard Strauss and Gyorgy Ligeti.
2001 A Space Odyssey © Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer 1968.
How many galaxies are there in the universe, and is it possible to compute them? As per BBC Sky and Night, the number of galaxies in the universe will be equal to the Universe’s size multiplied by the average number density of galaxies. In practice, estimating these two figures properly is tough.
The universe’s overall size is unknown. Recent studies suggest that the number of galaxies may be limitless, meaning that there are an endless number of galaxies.

Above the islands of Hawaii o n January 28, a green laser was seen piercing the night sky, silently tracing a path towards the horizon like a stutter in the Matrix’s code.
The scene was caught on camera from a telescope atop Hawaii’s tallest peak.
You can check out the scanning laser in the footage below.

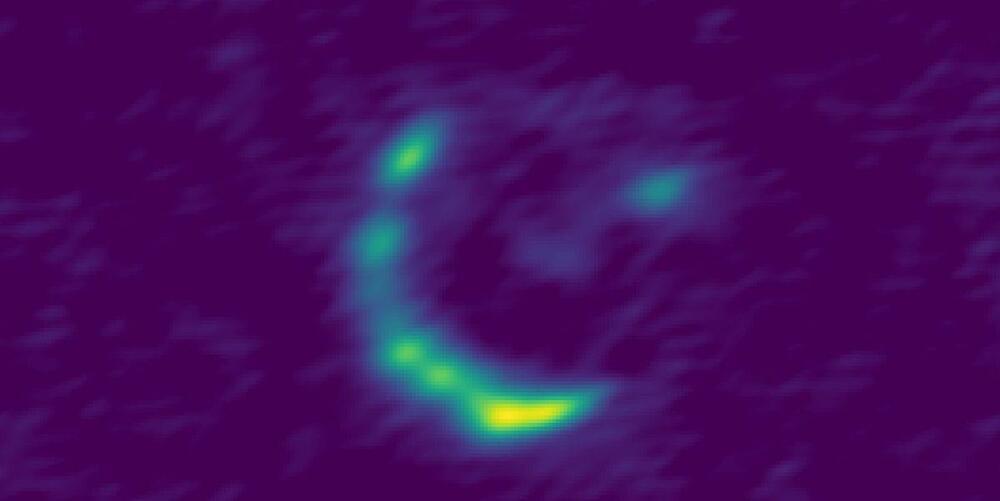
A newly discovered structure located deep in the heart of a thick cloud of gas and dust more than 450 light-years away is the signature of a pair of baby stars in the throes of formation.
A team of astronomers have identified a previously unseen bubble at the center of a stellar nursery called Barnard 18 in the Taurus molecular cloud complex, likely carved from the surrounding gas as two emerging stars therein formed and grew.
It’s only the second time astronomers have identified such a bubble with the ejection of material or ‘outflow’ associated with a growing star. The newly discovered structure could help scientists learn more about how stars affect their environment as they grow.
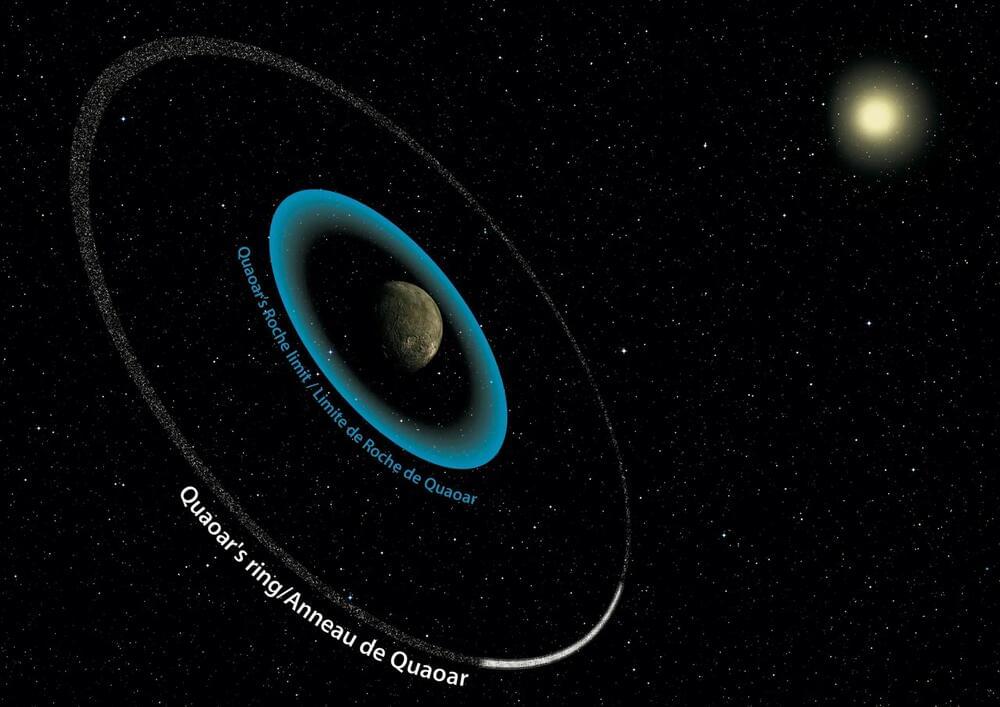
During a break from looking at planets around other stars, the European Space Agency’s CHaracterising ExOPlanet Satellite (Cheops) mission has observed a dwarf planet in our own Solar System and made a decisive contribution to the discovery of a dense ring of material around it.
The dwarf planet is known as Quaoar. The presence of a ring at a distance of almost seven and a half times the radius of Quaoar, opens up a mystery for astronomers to solve: why has this material not coalesced into a small moon?

The fate of galaxies is determined by the initial mass distribution at the birth of a new population of stars in the diverse and vast Universe. This relationship is referred to as the Initial Mass Function (IMF
In the field of astronomy, initial mass function (IMF) is an empirical function that details the distribution of stellar masses in a newly formed population of stars.
