Japan’s ispace aimed to make Hakuto-R the first privately funded lander to reach the moon. Reports show the landing has failed.
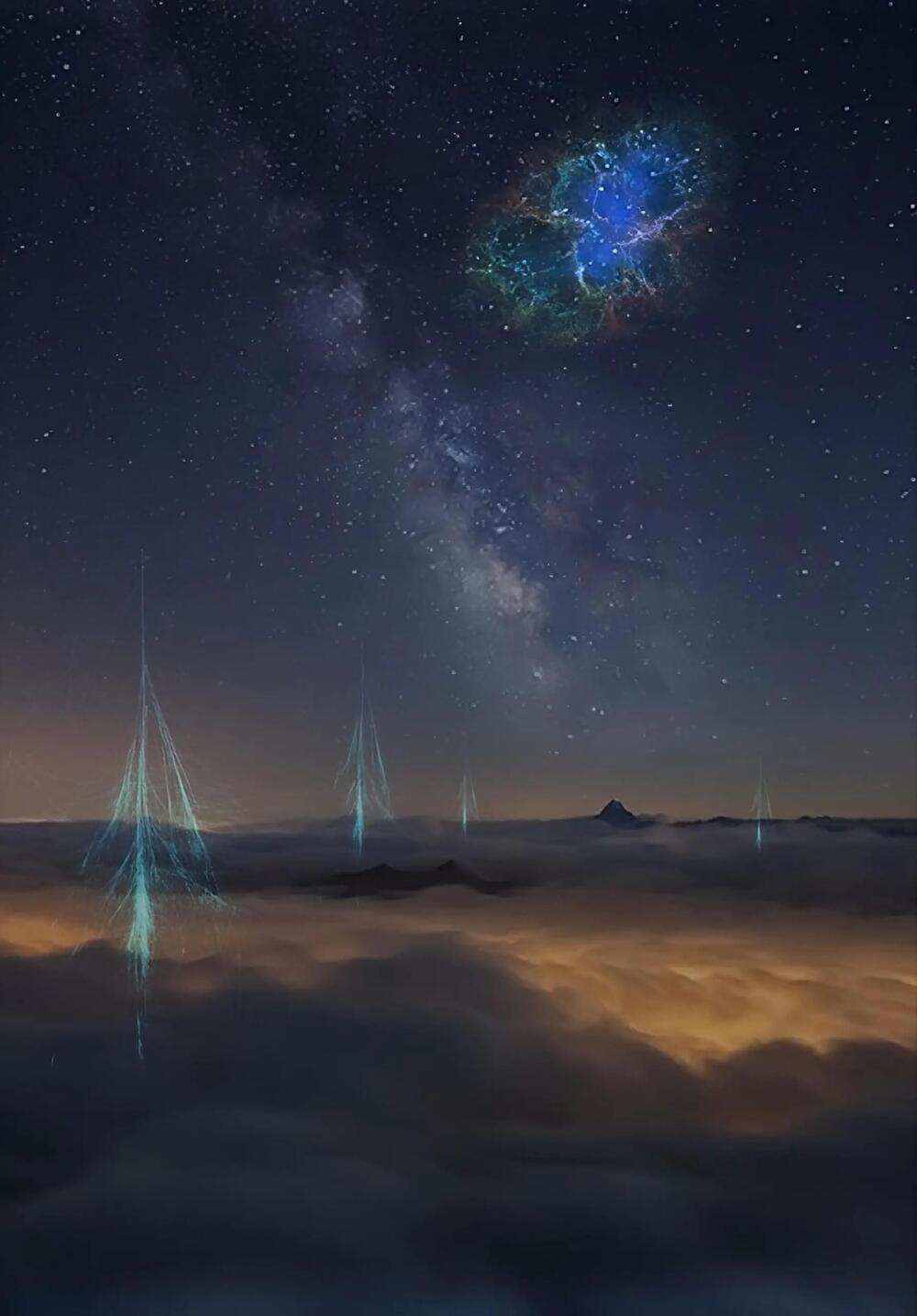




A new study published in Ecology and Evolution by Henrik Svensmark of DTU Space has shown that the explosion of stars, also known as supernovae, has greatly impacted the diversity of marine life over the past 500 million years.
The fossil record has been extensively studied, revealing significant variations in the diversity of life forms throughout geological history. A fundamental question in evolutionary biology is identifying the processes responsible for these fluctuations.
The new research uncovers a surprising finding: the fluctuation in the number of nearby supernovae closely corresponds to changes in biodiversity of marine genera over the last 500 million years. This correlation becomes apparent when the marine diversity curve is adjusted to account for changes in shallow coastal marine regions, which are significant as they provide habitat for most marine life and offer new opportunities for evolution as they expand or shrink. Thus, alterations in available shallow marine regions play a role in shaping biodiversity.

The kardeshev scale of possible future technological advance.
In 1964, Russian astrophysicist Nikolai Kardashev figured that civilizations can be categorized by the total amount of energy available to them. He called it the Kardashev Scale. He initially came up with 3 civilization types; type 1, type 2, and type 3. However, other astronomers have recently extended the scale from type 0 all the way to type 7 as new theories in modern physics have emerged. Check out the complete playlist as we unveil each level of the Kardashev Scale! Enjoy the videos, and do let us know your thoughts in the comments!
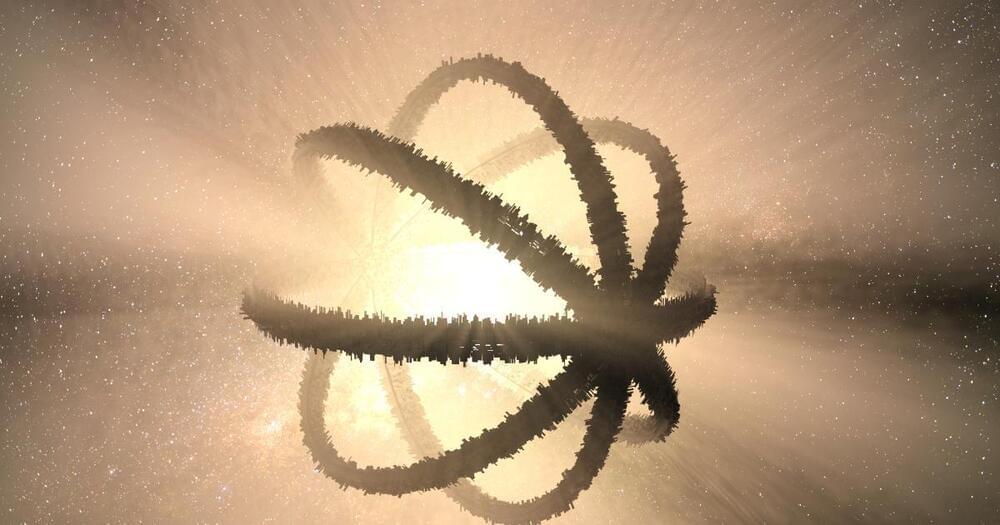

The gargantuan artificial construct enveloping your local star is going to be rather difficult to miss, even from a few light years away. And given the literally astronomical costs of resources needed to construct such a device — the still-theoretical-for-humans Dyson Sphere — having one in your solar system will also serve as a stark warning of your technological capacity to ETs that comes sniffing around.
Or at least that’s how 20th century astronomers like Nikolai Kardashev and Carl Sagan envisioned our potential Sol-spanning distant future going. Turns out, a whole lot of how we predict intelligences from outside our planet will behave is heavily influenced by humanity’s own cultural and historical biases. In The Possibility of Life, science journalist Jaime Green examines humanity’s intriguing history of looking to the stars and finding ourselves reflected in them.
Excerpted from The Possibility of Life by Jaime Green, Copyright © 2023 by Jaime Green. Published by Hanover Square Press.
Start listening with a 30-day Audible trial and your first audiobook is free. Visit http://www.audible.com/isaac or text “isaac” to 500–500.
A Galaxy of trillion of worlds, all separated by vast gulfs of time and space, it is very easy for pioneers and colonists to disappear. But what happens to these lost space colonies?
International Space Development Conference Registration: https://isdc2022.nss.org.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-arthur.
Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Isaac_A_Arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: https://discord.gg/53GAShE
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: Episode’s Audio-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/lost-space-colonies.
Episode’s Narration-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/lost-space-colonies-narration-only.
Credits:
Rogue Civilizations: Lost Space Colonies.
Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur.
Episode 342a, May 15, 2022
Written, Produced & Narrated by Isaac Arthur.
Editors:
Curt Hartung.
Jason Burbank.
Keith Blockus.
Graphics:


Remark: This article is from The Conversation France written by Victor DOS SANTOS PAULINO & Nonthapat PULSIRI (V&N) — Experts from Toulouse Business School and The SIRIUS Chair (France)
Lorsque nous parlons d’espace, nous pensons aux étoiles que nous voyons la nuit ou à de bons films de science-fiction. Or, l’espace comprend également tous les satellites et engins qui sont lancés depuis la Terre. Dans certains engins spatiaux, il y a des astronautes, comme l’Américaine Christina Koch ou le Français Thomas Pesquet, qui voyagent pendant plusieurs jours ou mois pour de nombreuses missions.
Pendant ce temps, plus de 8 000 satellites non habités opèrent sur les orbites terrestres pour améliorer la vie quotidienne. Par exemple, les satellites de communication contribuent à améliorer l’accès à Internet dans les zones blanches, les satellites d’observation sont essentiels pour les prévisions météorologiques et les satellites de navigation (GPS) sont indispensables pour les besoins de transport actuels et futurs tels que les véhicules autonomes.
Les progrès dans le secteur spatial offrent aujourd’hui de nouvelles opportunités dans la mise en orbite de constellations de milliers de satellites (par exemple, la flotte Starlink lancée par SpaceX, la société de l’homme d’affaires américain Elon Musk) ou encore dans l’exploitation minière spatiale et le tourisme spatial. Certains pays (dont la France et les États-Unis) ont par ailleurs annoncé que soutenir leur écosystème spatial constituait une priorité pour dynamiser l’économie.