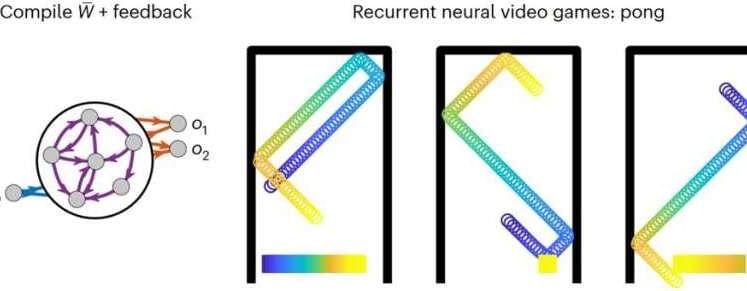
In 2003, the data visualization expert Edward Tufte traced that year’s Columbia disaster—in which seven astronauts died when their shuttle disintegrated—to a piece of software. It was PowerPoint, he argued, that prevented people at NASA from understanding the gravity of the risks facing the shuttle. PowerPoint all but forced “breaking up narratives and data into … minimal fragments,” “a preoccupation with format not content,” and “a smirky commercialism that turns information into a sales pitch.” Serious dangers got buried at the bottom of a multilevel hierarchy of bullet points under a bigger, sunnier title. If only the information had been delivered in a proper technical report, Tufte implied, the astronauts might still be alive.
Twenty years later, there’s a new office tool keeping us from fully expressing and processing important information: the digital whiteboard. These boards are vast canvases on which you can add and drag around virtually limitless quantities of text, images, tables, diagrams, emoji, and shapes. In their typical state, they are mostly covered with sticky notes on which people have written a word or three. What the words signify in context can quickly become hard to remember, but that’s OK. Like books used as decorations, they get their value from the fact that they signify something.