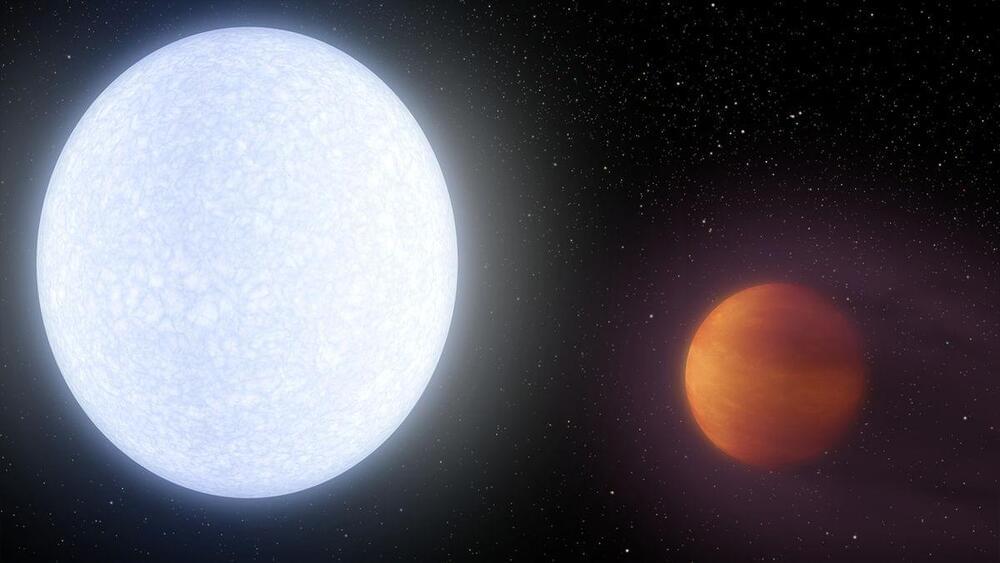
This Jupiter-size object is 80 times denser than a planet and hotter than the sun.
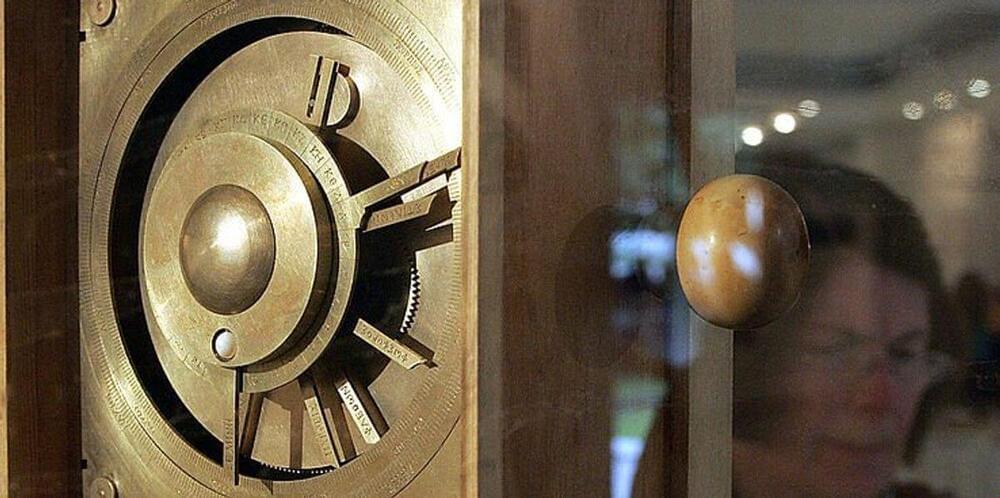



Scientists have been left baffled by the discovery of the wreck of a 2,000-year-old “computer” that is amazingly complex.
The Antikythera mechanism – an astronomical calendar – has been dubbed “‘the first computer” and has baffled scientists for generations after it was first discovered inside a Greek shipwreck in 1901.
The device is a hand-powered time-keeping instrument that used a wing-up system to track the sun, moon and planets’ celestial time. It also worked as a calendar, tracking the phases of the Moon and the timing of eclipses.
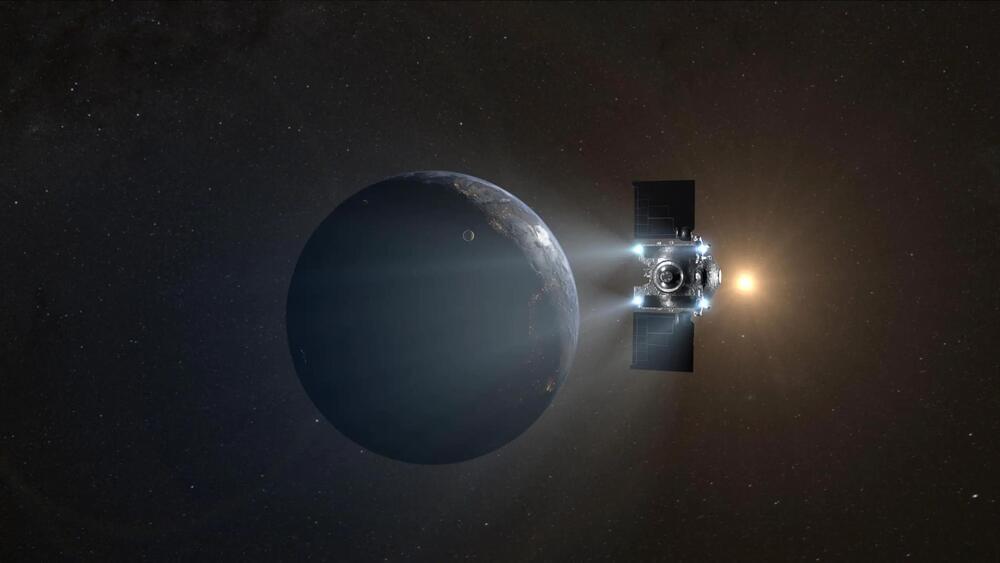
A team led by NASA in Utah’s West Desert is in the final stages of preparing for the arrival of the first U.S. asteroid sample – slated to land on Earth in this month.
A mockup of NASA’s OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, and Security–Regolith Explorer) sample capsule was dropped last Wednesday from an aircraft and landed at the drop zone at the Department of Defense’s Utah Test and Training Range in the desert outside Salt Lake City. This was part of the mission’s final major test prior to the arrival of the actual capsule on September 24 with its sample of asteroid Bennu, collected in space almost three years ago.
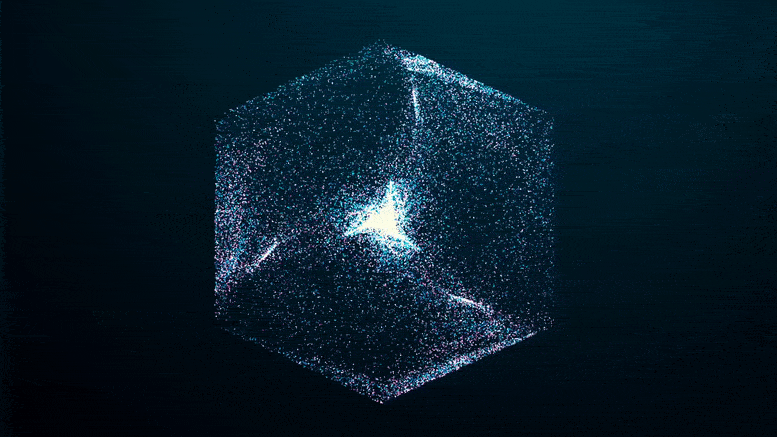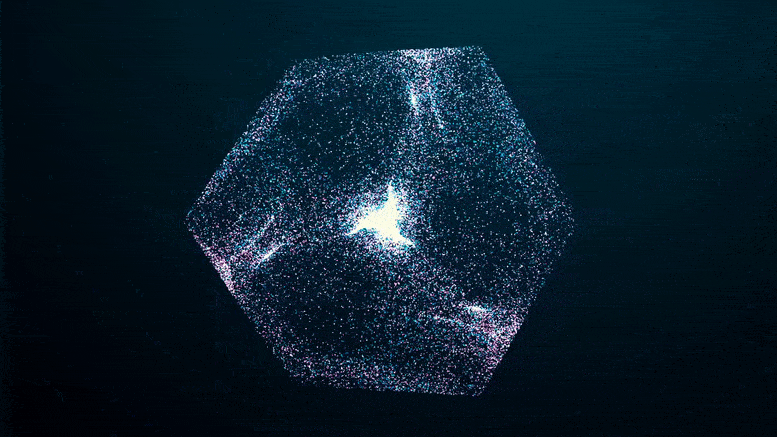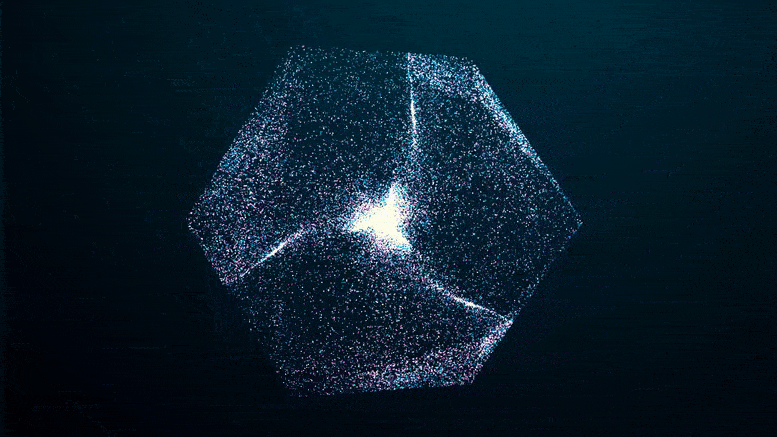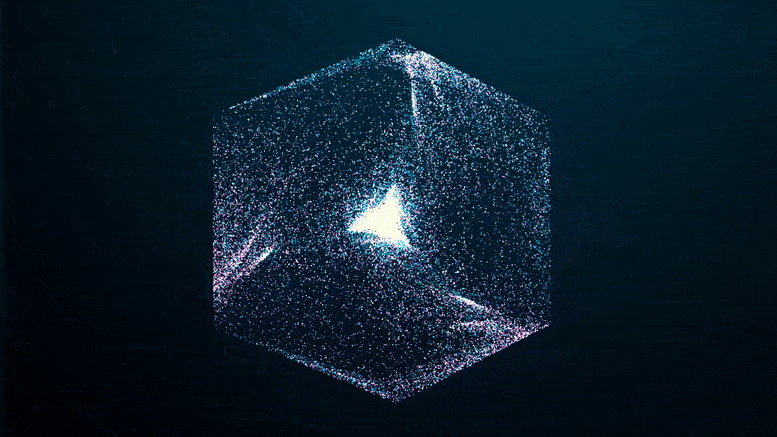
A study recently published in the journal Nanophotonics reveals that by rapidly modulating the refractive index – which is the ratio of the speed of electromagnetic radiation in a medium compared to its speed in a vacuum – it’s possible to produce photonic time crystals (PTCs) in the near-visible part of the spectrum.
The study’s authors suggest that the ability to sustain PTCs in the optical domain could have profound implications for the science of light, enabling truly disruptive applications in the future.
PTCs, materials in which the refractive index rises and falls rapidly in time, are the temporal equivalent of photonic crystals in which the refractive index oscillates periodically in space causing, for example, the iridescence of precious minerals and insect wings.

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch a humanoid robot into space as part of its Gaganyaan mission, its first human spaceflight mission.
The much-delayed mission is back on track after ISRO successfully landed its probe on the moon’s South Pole, a world first.
According to the ISRO, the Gaganyaan project was established to demonstrate human spaceflight capability by launching a three-person crew to an orbit of 248 miles for a three-day mission and then bring them back to Earth safely, landing in Indian sea waters.

Two new sleep studies on the International Space Station are helping astronauts and folks here on earth get a better night’s rest.
“Have you ever been told not to look at your phone before bed? This is because the blue light affects your Circadian rhythm — your natural response to changes of daylight,” reads a European Space Agency (ESA) X post from Friday.
Two studies: Circadian light and sleep in orbit
ESA astronaut Andreas Mogensen is currently conducting sleep research on the International Space Station. His mission is called Huginn and it consists of two studies that seek to understand more about Circadian light and sleep in orbit.
“Astronauts on the Space Station do a full circle of Earth every 90 minutes and experience 16 sunsets and sunrises every day. With this unearthly routine, astronauts can struggle to find a natural daily rhythm in space. The Space Station follows Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), which helps keep a consistent schedule, along with regular wake-up and bedtime routines,” said the ESA press release published on Thursday.
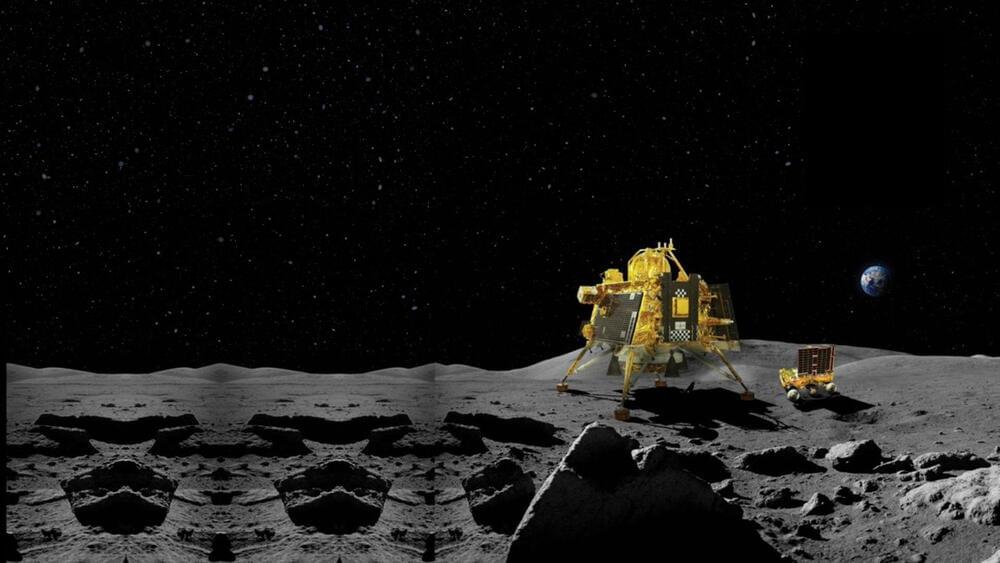

The lander and the rover, which landed on the Moon on August 23, were designed to operate for only one lunar day.
As the lunar day draws to a close, ISRO has decided to put its Chandrayaan-3 rover Pragyan in sleep mode to conserve its battery and protect it from the extreme cold of the lunar night. The rover, which has completed its assigned tasks, is now parked safely and has transmitted the data collected by its payloads to the lander, which in turn relays it to Earth.
Credits: ISRO/twitter.
Lunar Night

Sriharikota (AP), September 2
ISRO on Saturday launched the country’s ambitious Solar mission, Aditya L1, eyeing history again after its successful lunar expedition, Chandrayan-3, a few days ago.
Also read: Apart from India’s Aditya-L1, 5 missions are currently observing the sun.

Could you mine all the resources needed for space exploration from space itself? China reveals plans to achieve this goal by 2100.
Chinese space scientists have unveiled a preliminary roadmap that aims to establish a comprehensive space resources system spanning the solar system by the year 2100.
The ambitious initiative, named after the Ming dynasty scientist Song Yingxing’s work, “Tiangong Kaiwu” or “The Exploitation of the Works of Nature,” has the potential to transform the global space economy and elevate China’s standing in the world of space exploration, reported South China Morning Post.