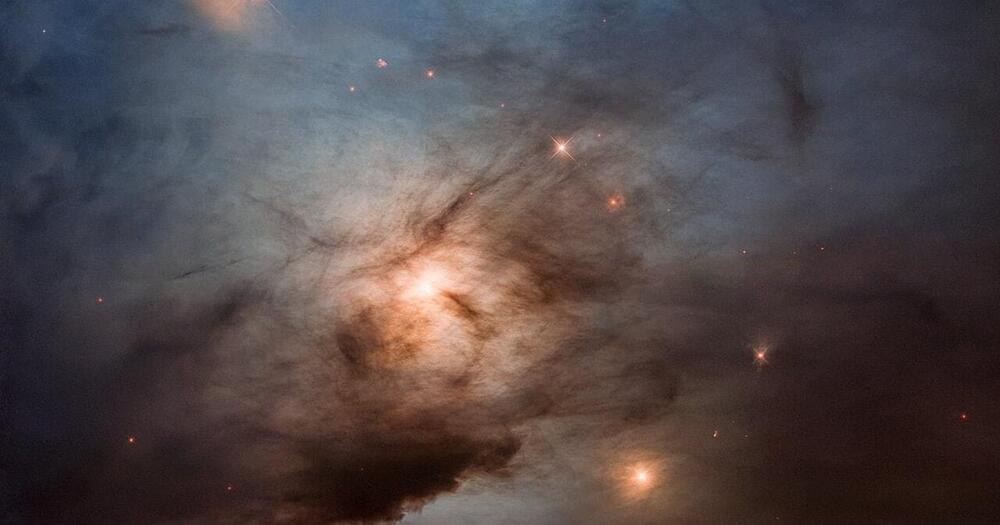
Behold a stellar nursery, where starlight scatters through interstellar dust — and sometimes can’t pierce the space soot.
This gorgeous Hubble image is a celebration of the telescope’s 33rd space birthday.

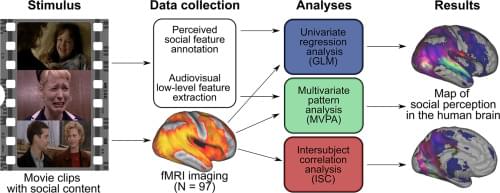
Humans rapidly extract diverse and complex information from ongoing social interactions, but the perceptual and neural organization of the different aspects of social perception remains unresolved. We showed short movie clips with rich social content to 97 healthy participants while their haemodynamic brain activity was measured with fMRI. The clips were annotated moment-to-moment for a large set of social features and 45 of the features were evaluated reliably between annotators. Cluster analysis of the social features revealed that 13 dimensions were sufficient for describing the social perceptual space. Three different analysis methods were used to map the social perceptual processes in the human brain. Regression analysis mapped regional neural response profiles for different social dimensions. Multivariate pattern analysis then established the spatial specificity of the responses and intersubject correlation analysis connected social perceptual processing with neural synchronization. The results revealed a gradient in the processing of social information in the brain. Posterior temporal and occipital regions were broadly tuned to most social dimensions and the classifier revealed that these responses showed spatial specificity for social dimensions; in contrast Heschl gyri and parietal areas were also broadly associated with different social signals, yet the spatial patterns of responses did not differentiate social dimensions. Frontal and subcortical regions responded only to a limited number of social dimensions and the spatial response patterns did not differentiate social dimension. Altogether these results highlight the distributed nature of social processing in the brain.


Physicists have recreated the double-slit experiment in time rather than space, using materials that change their optical properties in femtoseconds. This research could lead to ultrafast optical switches and advancements in time crystals and metamaterials.
Metamaterials are engineered materials that have properties not usually found in nature.
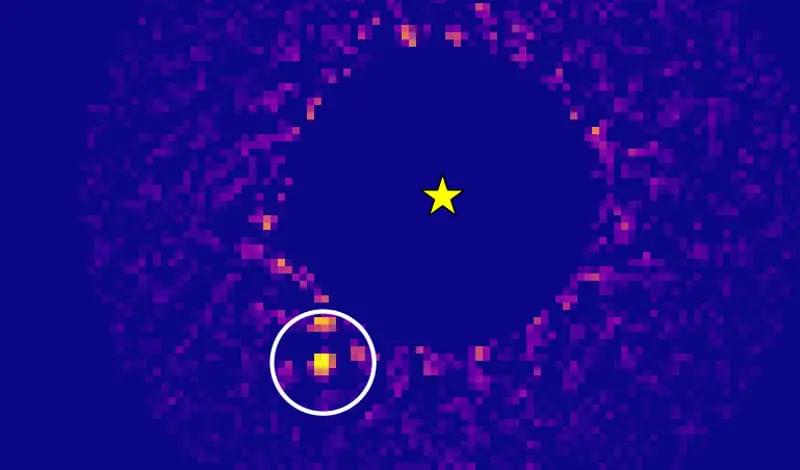
The discovery of HIP 99,770 b, a new exoplanet located 133 light years away, is reported in the journal Science. A team of astronomers used a new detection method that combines direct imaging with astrometry.
As of today, there are 5,363 confirmed exoplanets in 3,960 planetary systems. However, only a handful have been seen via direct imaging. Exoplanets are extremely faint compared with their parent stars, making it difficult to spot them in visible light.

COLORADO SPRINGS — Axiom Space has introduced a new program to allow countries to create human spaceflight programs without needing to develop their own infrastructure or other capabilities.
The Axiom Space Access Program, announced April 17, offers countries a tiered approach to conducting research on the International Space Station or Axiom’s future commercial space station, as well as flying their own astronauts.
The program is effectively a “space program in a box,” said Tejpaul Bhatia, chief revenue officer at Axiom, in an interview during the 38th Space Symposium. “The real key is that turnkey access at affordable, sustainable and predictable rates.”
PBS Member Stations rely on viewers like you. To support your local station, go to: http://to.pbs.org/DonateSPACE
↓ More info below ↓
Sign Up on Patreon to get access to the Space Time Discord!
https://www.patreon.com/pbsspacetime.
Physicists have a long history of sticking our noses where they don’t belong — and one of our favorite places to step beyond our expertise is the question of consciousness and free will. Sometimes our musings are insightful, sometimes incoherent, and usually at least somewhat naive. Which a fair description of this show, so of course Space Time needs to weigh in physics and free will…
Check out the Space Time Merch Store.
https://pbsspacetime.com/
Sign up for the mailing list to get episode notifications and hear special announcements!
https://mailchi.mp/1a6eb8f2717d/spacetime.
Hosted by Matt O’Dowd.
THE CHALLENGE, FIRST FEATURE FILM SHOT IN SPACE: Thoracic surgeon Evgenia Belyaeva has one month to prepare for a flight to the International Space Station, where she must operate on a crew member. Will she be up for the challenge? Can she overcome her fears and insecurities? Will she be able to perform the complicated surgery in zero gravity, and give the cosmonaut a chance to return to Earth alive?
The Russians have long been at the forefront of scientific and technological innovation. With the historic launch of Yuri Gagarin into space in 1961, they made history by becoming the first country to send a human being into orbit. Decades later, they have once again made headlines by being the first in the world to develop a COVID-19 vaccine, a remarkable achievement in the face of a global pandemic. And now, they have again beaten everyone else by shooting the first-ever movie in space.
Watch the trailer:
#TheChallenge #FirstMovieShotinSpace

Year 2023 face_with_colon_three
If humanity is ever to consider substantial, long-term colonization of Mars, the resources needed are going to be extensive. For a long-term human presence on Mars to be established, serious thought would need to be given to terraforming the planet. One major requirement for such terraforming is having the protection of a planetary magnetic field — which Mars currently does not have. The Earth’s magnetosphere helps protect the planet from the potential sterilizing effects of cosmic rays and also helps retain the atmosphere, which would otherwise by stripped by large solar storms as they pass over the planet. Mars does have small patches of remnant surface magnetic field, but these are localized in the southern hemisphere and are not of sufficient size or magnitude to protect the planet or a colony.
In this article we explore comprehensively for the first time, the practical and engineering challenges that affect the feasibility of creating an artificial magnetic field capable of encompassing Mars. This includes the concerns that define the design, where to locate the magnetic field generator and possible construction strategies. The rationale here is not to justify the need for a planetary magnetosphere but to put figures on the practicalities so as to be able to weigh the pros and cons of the different engineering approaches.
The optimum solution proposed is completely novel, although inspired by natural situations and fusion plasma techniques. The solution with the lowest power, assembly and mass is to create an artificial charged particle ring (similar in form to a ‘radiation belt’), around the planet possibly formed by ejecting matter from one of the moons of Mars (in a fashion similar to that which forms the Jupiter-Io plasma torus), but using electromagnetic and plasma waves to drive a net current in the ring(s) that results in an overall magnetic field.
It has been almost a week since the last solar storm hit the Earth. And it was a relatively minor storm that did not really affect us much. The worst was experienced over the Indian Ocean region where a temporary radio blackout was observed. But things are about to change quickly for the worse. NASA has issued a warning over a major solar storm strike on Earth. The initial hit is expected tomorrow, April 19, when glancing blows are expected and on April 20, a massive direct hit has been predicted. If this solar storm does strike the Earth, the impact can be far more dangerous.
The information comes from space weather physicist Tamitha Skov, who is popularly known as Space Weather Woman. In a recent tweet, she said, “Ready for #aurora? A #solarstorm direct hit is coming. NASA predicts impact 20 April. Additional glancing storms launched earlier mean activity could pick up late on April 19. Expect extended aurora at high latitudes with good chance of views down to mid-latitudes by the 20th”.
The source of this solar storm is a massive coronal mass ejection (CME) cloud that is headed for the Earth. The cloud is moving in a crescent shape and that is why glancing blows are expected earlier than a direct hit. However, this partial strike can have a concerning effect. It can weaken the magnetic fields of the Earth enough to create cracks on it, which can allow CME to escape into the upper atmosphere and cause a far more intense storm.