‘You can imagine what it’s really going to be like.’


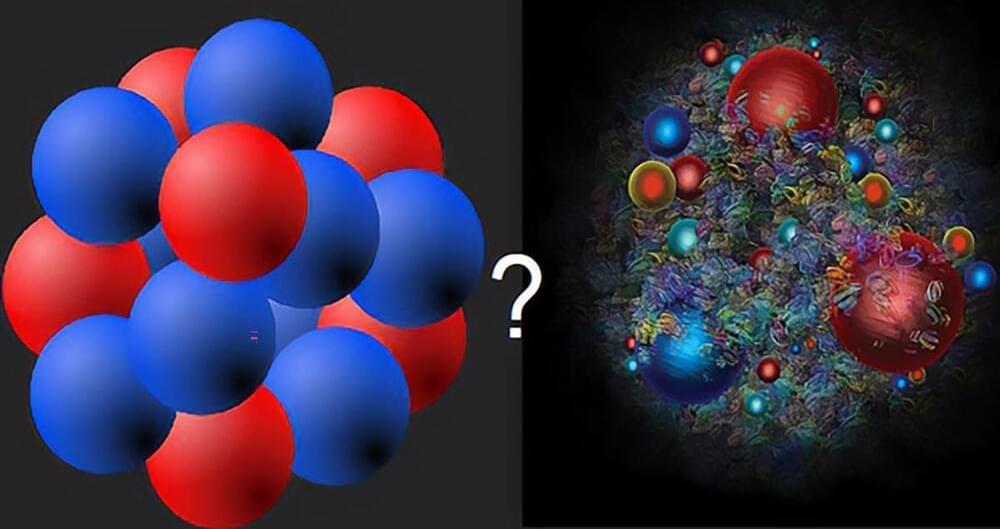
Matter inside neutron stars can have different forms: a dense liquid of nucleons or a dense liquid of quarks.
Recent studies reveal that in neutron stars, quark liquids are fundamentally different from nucleon liquids, as evidenced by the unique color-magnetic field in their vortices. This finding challenges previous beliefs in quantum chromodynamics and offers new insights into the nature of confinement.
The science of neutron star matter.
New research reveals a never-before-seen behavior in a repeating Fast Radio Burst, offering fresh insights into these mysterious cosmic phenomena.
Astronomers are continuing to unravel the mystery of deep space signals after discovering a never-before-seen quirk in a newly-detected Fast Radio Burst (FRB).
FRBs are millisecond-long, extremely bright flashes of radio light that generally come from outside our Milky Way galaxy. Most happen only once but some “repeaters” send out follow-up signals, adding to the intrigue surrounding their origin.
Research on an ancient spiral galaxy reveals crucial insights into early galaxy formation, highlighting rapid star formation and unique structural features compared to contemporary galaxies.
A new snapshot of an ancient, far-off galaxy could help scientists understand how it formed and the origins of our own Milky Way.
At more than 12 billion years old, BRI 1335–0417 is the oldest and furthest known spiral galaxy in the Universe.
Watch behind the scenes, get early access and join the private Discord by supporting us on Patreon: \
/ mlst (public discord)\
/ discord \
/ mlstreettalk \
\
DOES AI HAVE AGENCY? With Professor. Karl Friston and Riddhi J. Pitliya\
\
Agency in the context of cognitive science, particularly when considering the free energy principle, extends beyond just human decision-making and autonomy. It encompasses a broader understanding of how all living systems, including non-human entities, interact with their environment to maintain their existence by minimising sensory surprise.\
\
According to the free energy principle, living organisms strive to minimize the difference between their predicted states and the actual sensory inputs they receive. This principle suggests that agency arises as a natural consequence of this process, particularly when organisms appear to plan ahead many steps in the future. \
\
Riddhi J. Pitliya is based in the computational psychopathology lab doing her Ph.D at the University of Oxford and works with Professor Karl Friston at VERSES. \
/ riddhijp \
\
References:\
\
THE FREE ENERGY PRINCIPLE—A PRECIS [Ramstead]\
https://www.dialecticalsystems.eu/con…\
\
Active Inference: The Free Energy Principle in Mind, Brain, and Behavior [Thomas Parr, Giovanni Pezzulo, Karl J. Friston]\
https://direct.mit.edu/books/oa-monog…\
\
The beauty of collective intelligence, explained by a developmental biologist | Michael Levin\
• The beauty of collective intelligence… \
\
Growing Neural Cellular Automata\
https://distill.pub/2020/growing-ca\
\
Carcinisation\
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carcini…\
\
Prof. KENNETH STANLEY — Why Greatness Cannot Be Planned\
• #038 — Prof. KENNETH STANLEY — Why Gr… \
\
On Defining Artificial Intelligence [Pei Wang]\
https://sciendo.com/article/10.2478/j…\
\
Why? The Purpose of the Universe [Goff]\
https://amzn.to/4aEqpfm\
\
Umwelt\
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Umwelt\
\
An Immense World: How Animal Senses Reveal the Hidden Realms [Yong]\
https://amzn.to/3tzzTb7\
\
What’s it like to be a bat [Nagal]\
https://www.sas.upenn.edu/~cavitch/pd…\
\
COUNTERFEIT PEOPLE. DANIEL DENNETT. (SPECIAL EDITION)\
• COUNTERFEIT PEOPLE. DANIEL DENNETT. (… \
\
We live in the infosphere [FLORIDI]\
• WE LIVE IN THE INFOSPHERE [Prof. LUCI… \
\
Mark Zuckerberg: First Interview in the Metaverse | Lex Fridman Podcast #398\
• Mark Zuckerberg: First Interview in t… \
\
Black Mirror: Rachel, Jack and Ashley Too | Official Trailer | Netflix\
• Black Mirror: Rachel, Jack and Ashley… \
\
Prof. Kristinn R. Thórisson\
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kristin…
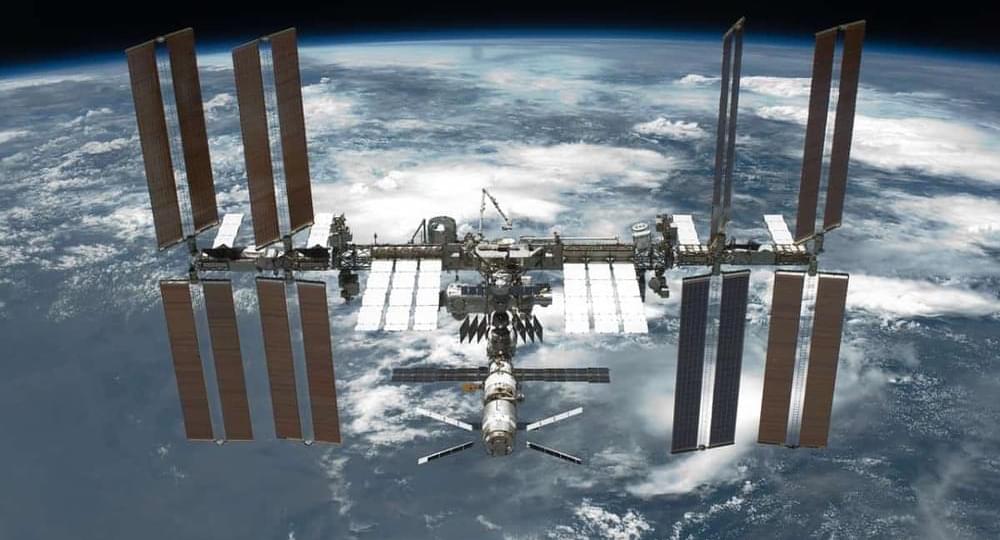

Well, many of those who partied hard on New Year’s may be regretting their decision because of the hangover. But once the clutches of alcoholic after-effects decide to free you, you are ready to party again. But even the most hardcore partygoers would not dare to face this challenge. How about having 16 New Years’ Party in a single day? Tough right? But if partying would be high on the list of astronauts at the International Space Station (ISS), they would really have been able to do it.
The reason?
They witness 16 sunrises and sunsets in a ‘single day’ aboard the ISS.
The molecules found are similar to smoke, soot, or fog on Earth and were observed in light that traveled from the galaxy when the cosmos was less than 1.5 billion years-old.
Learn More about Brilliant: https://brilliant.org/SpaceTime/Take the Space Time Fan Survey Here: https://forms.gle/wS4bj9o3rvyhfKzUAPBS Member Stations rely…

NASA’s spacecraft Juno just had a super-close encounter with the most volcanic world in the solar system—but its stunning first image could be among its last after 56 orbits of Jupiter.
On December 30, the bus-sized spacecraft—orbiting Jupiter since 2016—got very close to Io, the giant moon of Jupiter. It reached a mere 930 miles (1,500 kilometers) from the moon’s surface. However, the spacecraft’s camera has suffered radiation damage and may not last much longer.
The first image to come back from this, the closest pass since NASA’s Galileo probe imaged the volcanic moon in October 2001, was published on social media by NASA on December 31. “The JunoCam instrument aboard our Juno Mission acquired six images of Jupiter’s moon Io during its close encounter today,” read the tweet. “This black-and-white view was taken at an altitude of about 1,500 miles (2,500 kilometers).”
