But by analyzing data taken from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, which studies galaxies illuminated by powerful quasars bursts, the researchers teased apart the evidence for a ring far bigger than the theoretical upper size limit — a stunning coil-like structure aligned face-on with Earth.
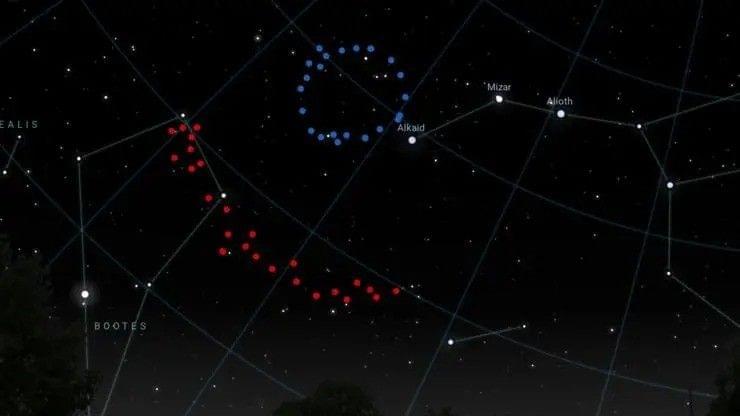
“The Big Ring and Giant Arc are the same distance from us, near the constellation of Boötes the Herdsman, meaning they existed at the same cosmic time when the universe was only half of its present age,” Lopez said. “They are also in the same region of sky, at only 12 degrees apart when observing the night sky … [This] raises the possibility that together they form an even more extraordinary cosmological system.”
Although the cause of the gigantic structure is unclear, the researchers first speculated that it could be a remnant of a baryon acoustic oscillation (BAO), a type of sound wave that rippled through the hot plasma of the early universe. Yet further analysis found that the Big Ring was too large and, due to its corkscrew shape, not spherical like BAOs. Alternative explanations suggest that it could possibly be a cosmic string, a hypothetical clumping of matter created in the early universe, or a remnant of something else that could demand an entirely new model to explain it.