We need to get Mars Exploration back on track after the Mars Sample Return Mission is temporarily halted:
Posted on big think and searchforlifeintheuniverse:


‘Hidden’ stars including a new type of elderly giant nicknamed an ‘old smoker’ have been spotted for the first time by astronomers.
The mystery objects exist at the heart of our Milky Way galaxy and can sit quietly for decades – fading almost to invisibility – before suddenly puffing out clouds of smoke, according to a new study published today in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
An international team of scientists led by Professor Philip Lucas, of the University of Hertfordshire, made their ground-breaking discovery after monitoring almost a billion stars in infrared light during a 10-year survey of the night sky.
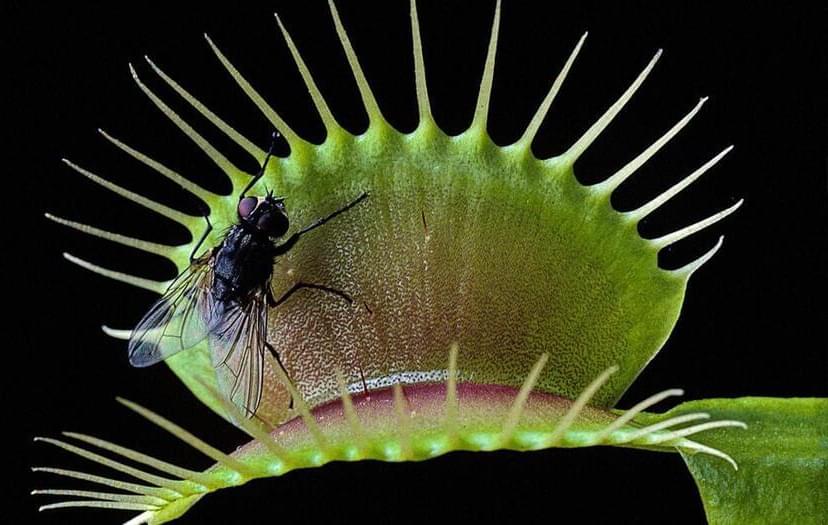

It’s “Little Shop of Horrors” meets “Terminator.”
A team of scientists successfully took control over a Venus Flytrap, a type of cultivated carnivorous plant, by implanting a tiny microchip in it.
This “artificial neutron” was able to force the plants to open and close — conventionally a way for them to devour its prey — mimicking the brain’s methods of processing and transferring information.
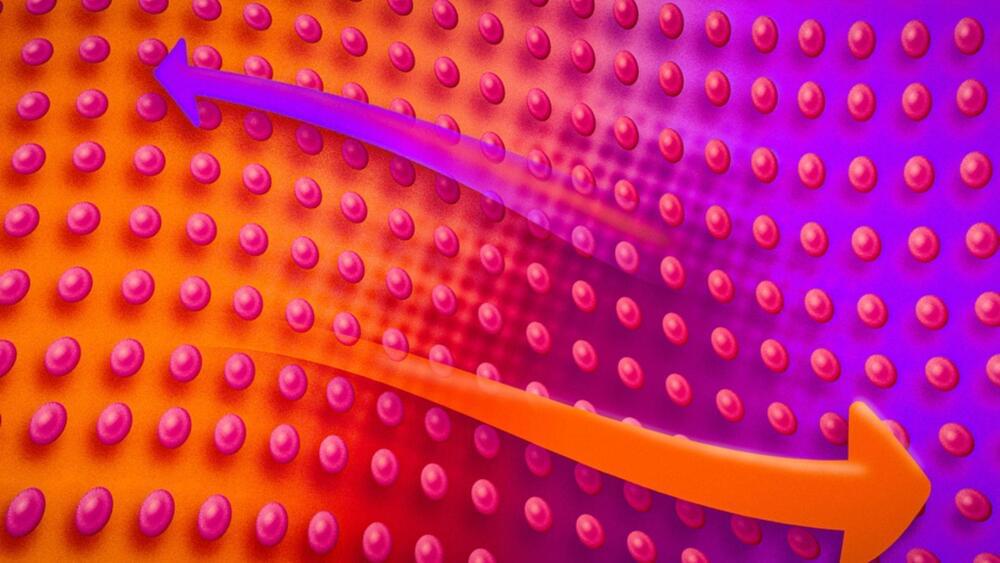
The researchers applied the higher resonant radio frequency, which prompted any normal, “hot” fermions in the liquid to ring in response. The researchers then could zero in on the resonating fermions and track them over time to create “movies” that revealed heat’s pure motion — a sloshing back and forth, similar to sound waves.
“For the first time, we can take pictures of this substance as we cool it through the critical temperature of superfluidity, and directly see how it transitions from being a normal fluid, where heat equilibrates boringly, to a superfluid where heat sloshes back and forth,” Zwierlein says.
The experiments mark the first time scientists have been able to image second sound directly and the pure motion of heat in a superfluid quantum gas. The researchers plan to extend their work to map heat’s behavior more precisely in other ultracold gases. Then, they say their findings can be scaled up to predict how heat flows in other strongly interacting materials, such as high-temperature superconductors and neutron stars.

By illustrator, tagged space, comic, cartoon, character, china, chinese, guy, noodles, problem, rocket, nudeln, rakete„ raumschiff, rakete, raumshuttle, astronaut, china, sprache, kultur, raumfahrt, weltall, weltraum, universum, akzent, nudeln, kultur, chinapfanne, essen, nahrung, lebensmittel, schwerkraft, schwerelos, sandwich — Category Education & Tech — rated 3.50 / 5.

It’s been hiding it this whole time: https://trib.al/QyWET9o
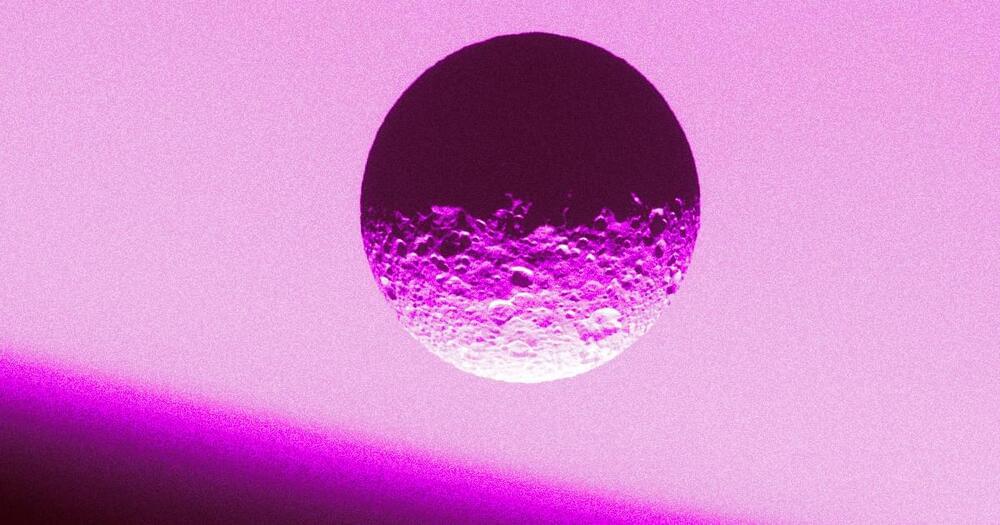
Minas, known for its Death Star like crater on its surface, is home to a relatively young ocean that’s influencing its orbit.
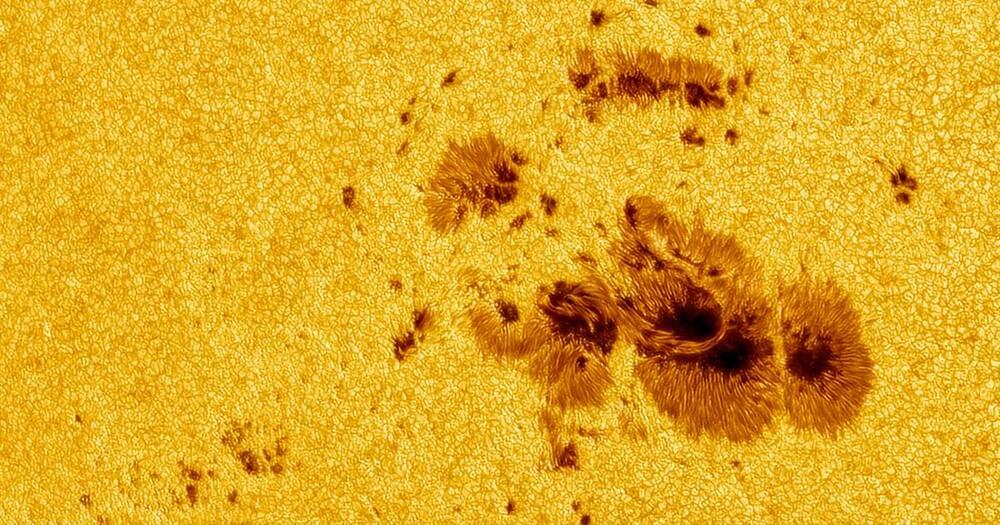

Last fall, NASA’s Mars rover spotted a massive spot on the surface of the Sun — and now, that ginormous maw is looking directly at the Earth.
First reported by SpaceWeather.com, the sunspot is expected to blast a coronal mass ejection (CME) out towards Earth and will be “not just a near miss, but an actual glancing blow.”
CMEs occur when storms on the surface of the Sun blast plasma out into the solar system, leaving planets in its path — including our own Earth — to handle the geomagnetic consequences.

For most of humanity’s existence, we have observed the universe using light, but these days photons aren’t the only game in town, says Chanda Prescod-Weinstein

Battelle Memorial Institute, Columbus, Ohio (FA8684-24D-B018); The Boeing Co., St. Louis, Missouri (FA8684-24D-B019); The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory Inc., Cambridge, Massachusetts (FA8684-24D-B014); Chip Scan Inc., Rockaway Beach, New York (FA8684-24D-B004); General Dynamics Mission Systems Inc., Dedham, Massachusetts (FA8684-24D-B006); GE Aviation Systems LLC Grand Rapids, Michigan (FA8684-24D-B008); Honeywell International, Clearwater, Florida (FA8684-24D-B010); Idaho Scientific LLC, Boise, Idaho (FA8684-24D-B012); Kratos SRE Inc., San Diego, California (FA8684-24D-B005); L3Harris Technologies Inc., Palm Bay, Florida (FA8684-24D-B007); Lockheed Martin Corp., Orlando, Florida (FA8684-24D-B009); Mercury Systems Inc., Andover, Massachusetts (FA8684-24D-B016); Microsemi SOC Corp., San Jose, California (FA8684-24D-B011); Northrop Grumman Systems Corp., Linthicum Heights, Maryland (FA8684-24D-B003); Radiance Technologies Inc., Huntsville, Alabama (FA8684-24D-B013); Raytheon Co., McKinney, Texas (FA8684-24D-B015); and Sabre Systems Inc., Warminster, Pennsylvania (FA8684-24D-B017), were awarded a $499,000,000 multiple award, indefinite-delivery/indefinite-quantity contract for the design, build, test, and delivery of functioning anti-tamper solutions that will be ready for follow-on production to be integrated into a broad range of Department of Defense programs. The development of these solutions enables the necessary protection of critical program information from adversarial tamper efforts. Work will be performed in the continental United States and is expected to be completed Feb. 28, 2030. This contract was a competitive acquisition, and 20 offers were received. Fiscal 2024 research, development, test, and evaluation funds in the amount of $1,000 per awardee are being obligated at time of award. The Air Force Life Cycle Management, Wright Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio, is the contracting activity.
Roundhouse PBN LLC, Colorado Springs, Colorado, was awarded a $13,619,953 commercial, fixed-firm-price contract for a temporary and relocatable Program Integration Office/Program Management Office facility for the Sentinel Program at F. E. Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming. This contract provides for a one-time procurement for a secure, prefabricated, nominal 26,000-square-foot temporary facility, that will satisfy immediate requirements for additional office space for up to 200 Sentinel project personnel. This will be a commercial supply contract to procure a facility and furnishings, with a limited construction service component to conduct site preparation. Work will be performed at F.E. Warren AFB, Wyoming, and is expected to be completed by Feb. 7, 2025. This contract was a sole source acquisition. Fiscal 2024 operation and maintenance funds in the amount of $1,923,839; and fiscal 2024 procurement funds in the amount of $11,696,114, are being obligated at time of award.