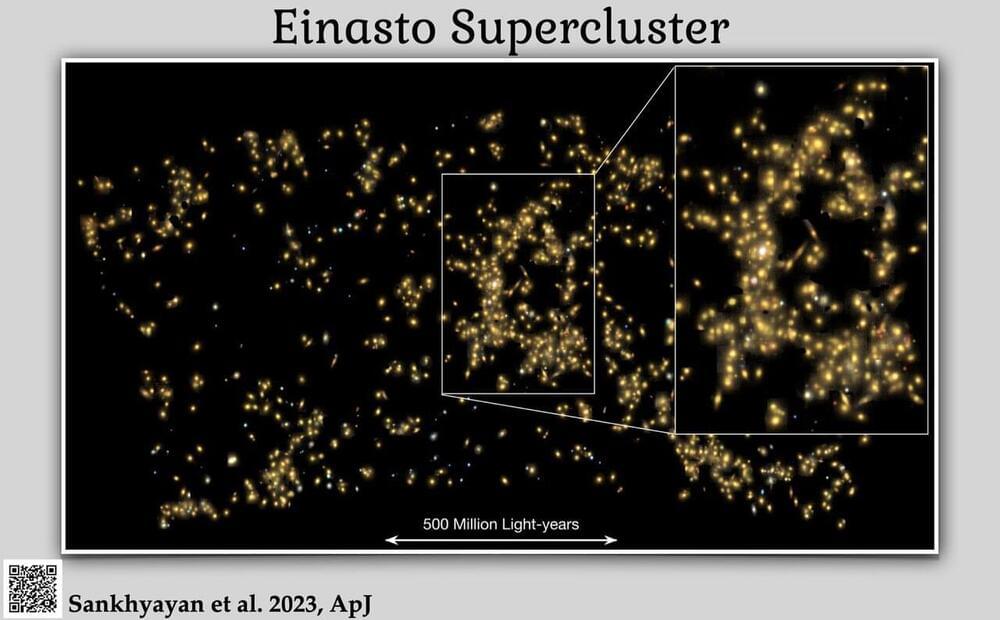
An international team of scientists led by astronomers from Tartu Observatory of the University of Tartu has discovered many superclusters in the universe, with the most prominent among them named the ‘Einasto Supercluster’ in honor of Prof. Jaan Einasto, a pioneering figure in the field, who celebrated his 95th birthday on 23 February.
Superclusters, akin to vast metropolitan cities in space, represent the largest and most massive collections and clusters of galaxies in the universe. The team’s findings not only expanded our understanding of these vast structures but also paved the path to shed light on the ongoing mystery of their formation.
In their study, the scientists determined that the typical mass of superclusters is an astonishing 6 million times billion that of the sun, with an average size of 200 million light-years. To put this into perspective, these superclusters are approximately 2,000 times larger than our own Milky Way galaxy.