Using observations from a NASA suborbital rocket, an international team of scientists, for the first time, has successfully measured a planet-wide electric field thought to be as fundamental to Earth as its gravity and magnetic fields.
Category: space – Page 208
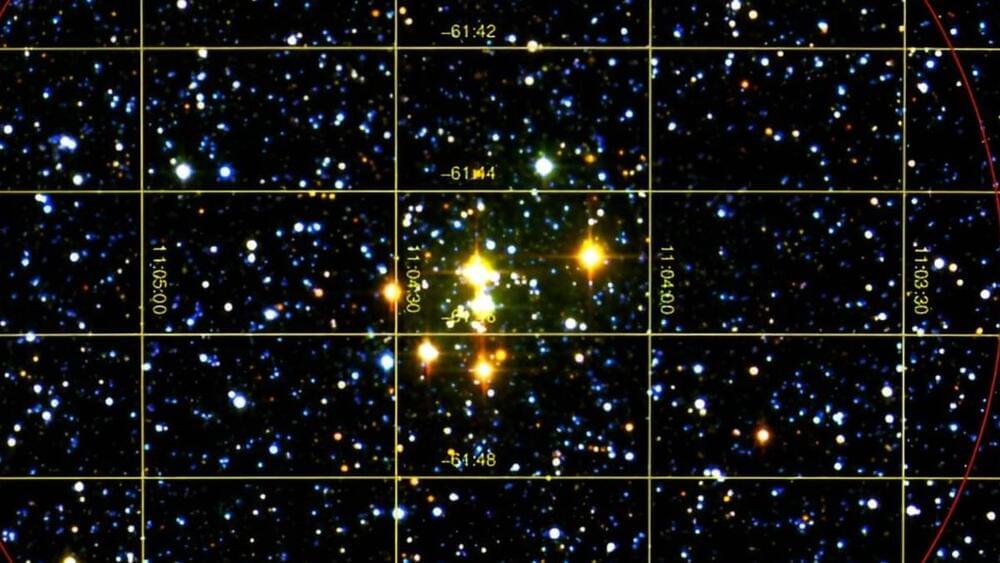

Rare Milky Way star cluster is packed with red supergiants 1 million times brighter than the sun
“There are many open clusters in the galaxy. However, not all open clusters have the same level of interest to astronomers,” Ignacio Negueruela, a researcher at the Universidad de Alicante who was part of the team behind the discovery of supergiants in Barbá 2, told Space.com. “Clusters rich in red supergiants are very rare and tend to be very far away, but they play a crucial role in understanding key aspects in the evolution of massive stars.”
The intimidating size and power of supergiants means these monster stars burn through their nuclear fuel much faster than stars like the sun. Whereas our star will exist in its main sequence lifetime for around 10 billion years, supergiants are estimated to last just a few million years.
The short lifetime of supergiants means that while open clusters like Barbá 2 are common, with over 1,100 already discovered in the Milky Way alone, finding one packed with red supergiants is extremely rare.
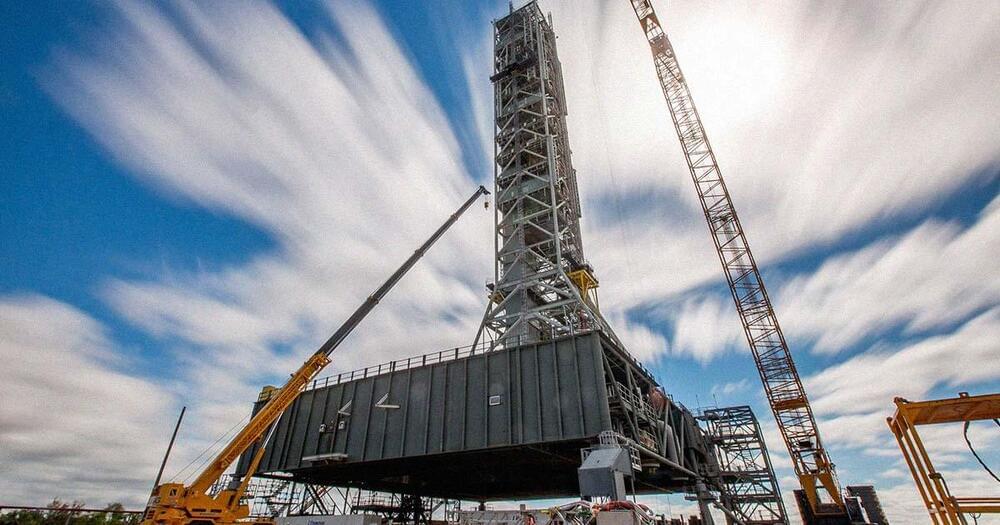

NASA’s Moon Launcher Is in Big Trouble
Reports that each of NASA’s Artemis launches could cost as much as $4.1 billion…
“Costs going up faster than the tower,” self-described internet rocket scientist Scott Manley joked at the time.
NASA used its Mobile Launcher 1 for its inaugural — albeit uncrewed — Artemis mission in late 2022. According to a 2020 audit, the tower, which was originally built for NASA’s canceled Constellation program, cost $234 million to develop.
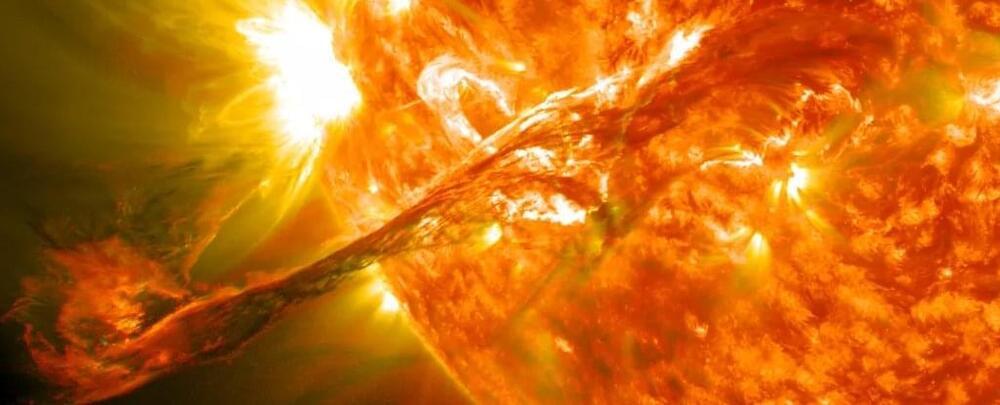

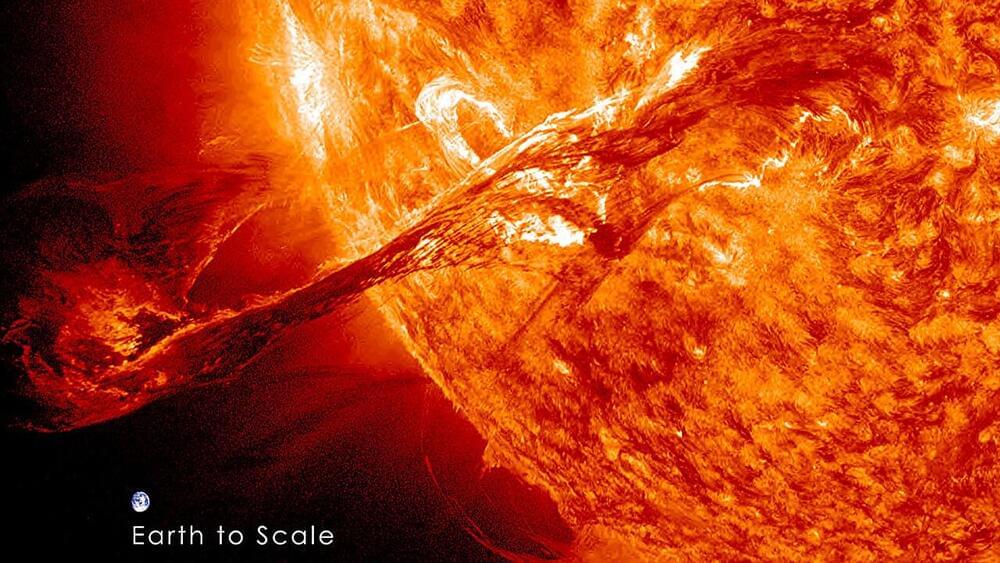
The Sun Is More Active Than Scientists Anticipated. Here’s What It Means For Us
From afar, the Sun looks calm and peaceful in our daytime skies. But up close, it’s an erupting, chaotic display of solar activity the likes of which astrophysicists didn’t expect until the last year or so.
“We didn’t think the Sun was going to be as active this particular cycle, but the observations are completely opposite,” Andrew Gerrard, the department chair and director of the Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research at New Jersey Institute of Technology, told Business Insider.
Solar cycles typically occur every 11 years. Within that time, the Sun oscillates from minimum to maximum solar activity, with maximum activity peaking in the middle of the cycle when the Sun’s magnetic fields flip.
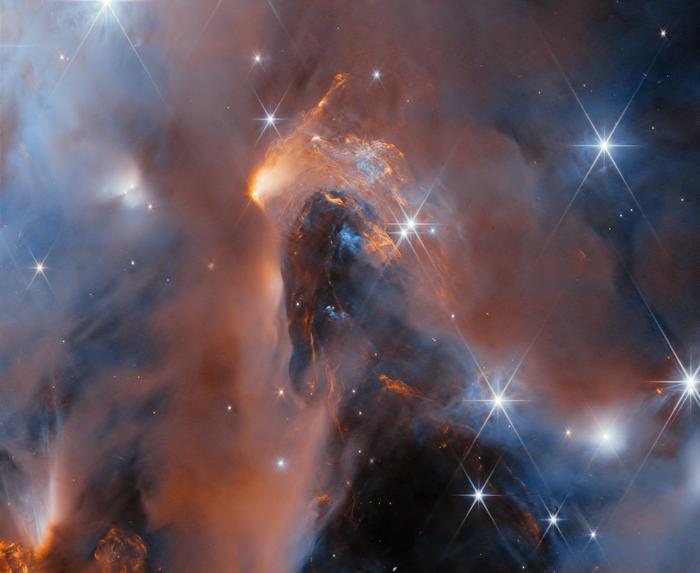

James Webb Space Telescope Uncovers Six Likely Rogue Worlds with Dusty Disks
“Those tiny objects with masses comparable to giant planets may themselves be able to form their own planets,” said Dr. Aleks Scholz.
What can rogue planets teach us about the formation and evolution of stars and planets? This is what a recent study published in The Astronomical Journal hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated NGC 1,333, which is a star-forming cluster located just under 1,000 light-years from Earth. This study holds the potential to help scientists better understand the formation and evolution of stars and planets while challenging previous hypotheses about these processes.
“We are probing the very limits of the star forming process,” said Dr. Adam Langeveld, who is an assistant research scientist at Johns Hopkins University and lead author of the study. “If you have an object that looks like a young Jupiter, is it possible that it could have become a star under the right conditions? This is important context for understanding both star and planet formation.”
For the study, the researchers used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to observe brown dwarfs that comprise NGC 1,333 in hopes of learning more about how stars form. in the end, the researchers discovered six new rogue planet candidates—officially called free-floating planetary-mass objects (FFPMOs)—with masses ranging between 5–10 Jupiters and that exhibit dusty disks orbiting them. This indicates they are some of the smallest objects formed from processes that are traditionally responsible for creating stars and brown dwarfs, the latter of which never reach appropriate sizes to produce nuclear fusion in their cores.
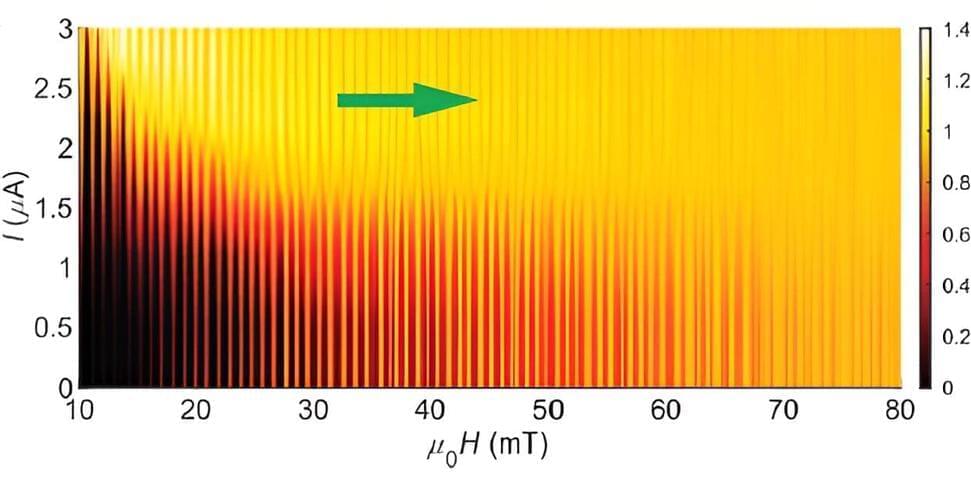
Superconductivity study confirms existence of edge supercurrents
Topological materials are materials that have unusual properties that arise because their wavefunction—the physical law guiding the electrons—is knotted or twisted. Where the topological material meets the surrounding space, the wavefunction must unwind. To accommodate this abrupt change, the electrons at the edge of the material must behave differently than they do in the main bulk of the material.

DART Impact Reshapes Asteroid Moon Dimorphos, Alters Future Exploration Plans
What did NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft on the asteroid moon, Dimorphos, teach astronomers about altering the trajectory of asteroids and asteroids’ formation and evolution? This is what a recent study published in The Planetary Science Journal hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated the potential geological changes made to Dimorphos, which orbits its parent asteroid, Didymos, when DART impacted the former in September 2022. This study holds the potential to help scientists better understand the formation and evolution of asteroids throughout, and potentially beyond, the solar system, which could hold implications for the early history of the solar system, as well.
“For the most part, our original pre-impact predictions about how DART would change the way Didymos and its moon move in space were correct,” said Dr. Derek Richardson, who is a professor of astronomy at the University of Maryland, a DART investigation working group lead, and lead author on the study. “But there are some unexpected findings that help provide a better picture of how asteroids and other small bodies form and evolve over time.”
For the study, the researchers analyzed post-impact data of the DART spacecraft on Dimorphos based on predictions made prior to the impact, which could help in planning for the European Space Agency’s upcoming Hera spacecraft mission to Didymos, which is slated to launch in October 2024 and arrive at Didymos in December 2026. In the end, the researchers found that along with Dimorphos’ orbital parameters being influenced by the impact, its physical shape was altered, as well. This resulted in the small asteroid moon becoming elongated towards its poles, whereas its poles were squished prior to impact. This indicates varying formation and evolutionary processes regarding its geologic composition.
Massive Solar Wind Disturbance caused Earth’s Magnetosphere to Fly Without its Usual Tail
Like a supersonic jet being blasted with high-speed winds, Earth is constantly being bombarded by a stream of charged particles from the sun known as solar wind.
Just like wind around a jet or water around a boat, these solar wind streams curve around Earth’s magnetic field, or magnetosphere, forming on the sunward side of the magnetosphere a front called a bow shock and stretching it into a wind sock shape with a long tail on the nightside.
Dramatic changes to the solar wind alter the structure and dynamics of the magnetosphere. An example of such changes provides a glimpse into the behavior of other bodies in space, such as Jupiter’s moons and extrasolar planets.
The Universe is on the Move
Our universe is defined by the way it moves, and one way to describe the history of science is through our increasing awareness of the restlessness of the cosmos.
For millennia the brightest scientific minds in Europe and the Middle East believed that the Earth was perfectly still and that the heavens revolved around it, with a series of nested crystal spheres carrying each of the heavenly objects. Those early astronomers busied themselves with attempts to explain and predict the motion of those objects – the Sun, the Moon, each of the known planets, and the stars. Those predictions were excellent, and their systems able to explain the data well into the 16th century.
But that cosmological system of motion, initially developed by Claudius Ptolemy in the 2nd century, wasn’t perfect. In fact, it was an ungainly mathematical mess, relying on small circular orbits nested within larger ones, with some centered on the Earth and some centered on other points. On his deathbed in 1,543, the Polish astronomer Nicolas Copernicus published On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres, a radical reformulation of the old Ptolemaic system that put the Sun at the center of the universe – still and motionless – with the Earth set in motion around it along with all the other planets.

Space missions are getting more complex − lessons from Amazon and FedEx can inform satellite and spacecraft management in orbit
Logistics companies on the ground solve similar problems every day and transport goods and commodities across the globe. So, researchers can study how these companies manage their logistics to help space companies and agencies figure out how to successfully plan their mission operations.
One NASA-funded study in the early 2000s had an idea for simulating space logistics operations. These researchers viewed orbits or planets as cities and the trajectories connecting them as routes. They also viewed the payload, consumables, fuel and other items to transport as commodities.
This approach helped them reframe the space mission problem as a commodity flow problem – a type of question that ground logistics companies work on all the time.