For the Artemis 3 mission, we will be able to reach astronauts up to 2 kilometers away from the lander.

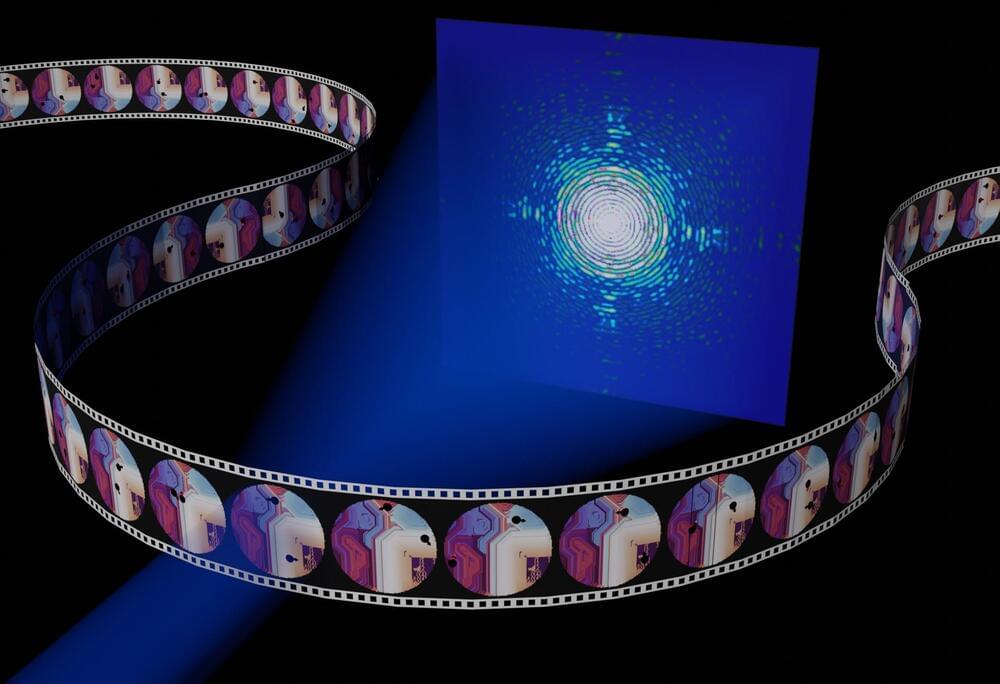
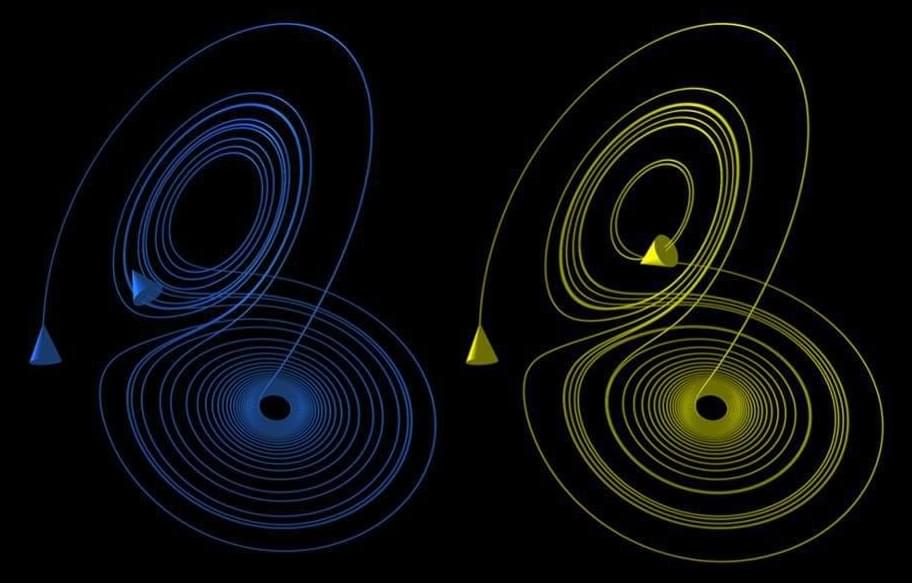
Coherent X-ray imaging has emerged as a powerful tool for studying both nanoscale structures and dynamics in condensed matter and biological systems. The nanometric resolution together with chemical sensitivity and spectral information render X-ray imaging a powerful tool to understand processes such as catalysis, light harvesting or mechanics.
Unfortunately these processes might be random or stochastic in nature. In order to obtain freeze-frame images to study stochastic dynamics, the X-ray fluxes must be very high, potentially heating or even destroying the samples.
Also, detectors acquisition rates are insufficient to capture the fast nanoscale processes. Stroboscopic techniques allow imaging ultrafast repeated processes. But only mean dynamics can be extracted, ruling out measurement of stochastic processes, where the system evolves through a different path in phase space during each measurement. These two obstacles prevent coherent imaging from being applied to complex systems.
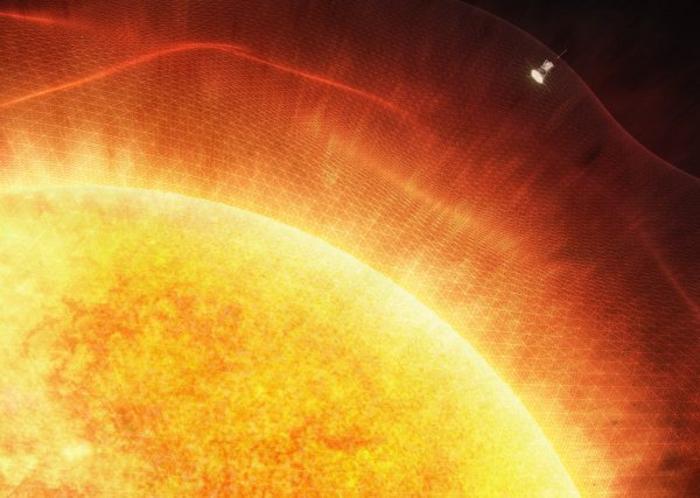

What processes provide energy to the solar wind as it travels away from the Sun and throughout the solar system? This is what a recent study published in Science hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated the processes responsible for providing energy to the solar wind as it leaves the Sun and traverses the rest of the solar system. This study holds the potential to help astronomers better understand the Sun’s processes, which could also provide insight into the processes of other stars, as well.
“Our study addresses a huge open question about how the solar wind is energized and helps us understand how the Sun affects its environment and, ultimately, the Earth,” said Dr. Yeimy Rivera, who is a postdoctoral fellow at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian and lead author of the study. “If this process happens in our local star, it’s highly likely that this powers winds from other stars across the Milky Way galaxy and beyond and could have implications for the habitability of exoplanets.”
For the study, the researchers used solar wind data from NASA’s Parker Solar Probe and the joint NASA-ESA Solar Orbiter collected within two days of each other due to the spacecraft being aligned with each other, enabling this research to be conducted. For context, the Parker Solar Probe is currently orbiting inside the Sun’s corona while Solar Orbiter is orbiting approximately halfway between the Earth and the Sun. In the end, the researchers found the solar wind’s acceleration that occurs between the Sun and the Earth is due to what are called “Alfvén waves”, which transport energy through the solar plasma. However, researchers haven’t been able to measure Alfvén waves until now.

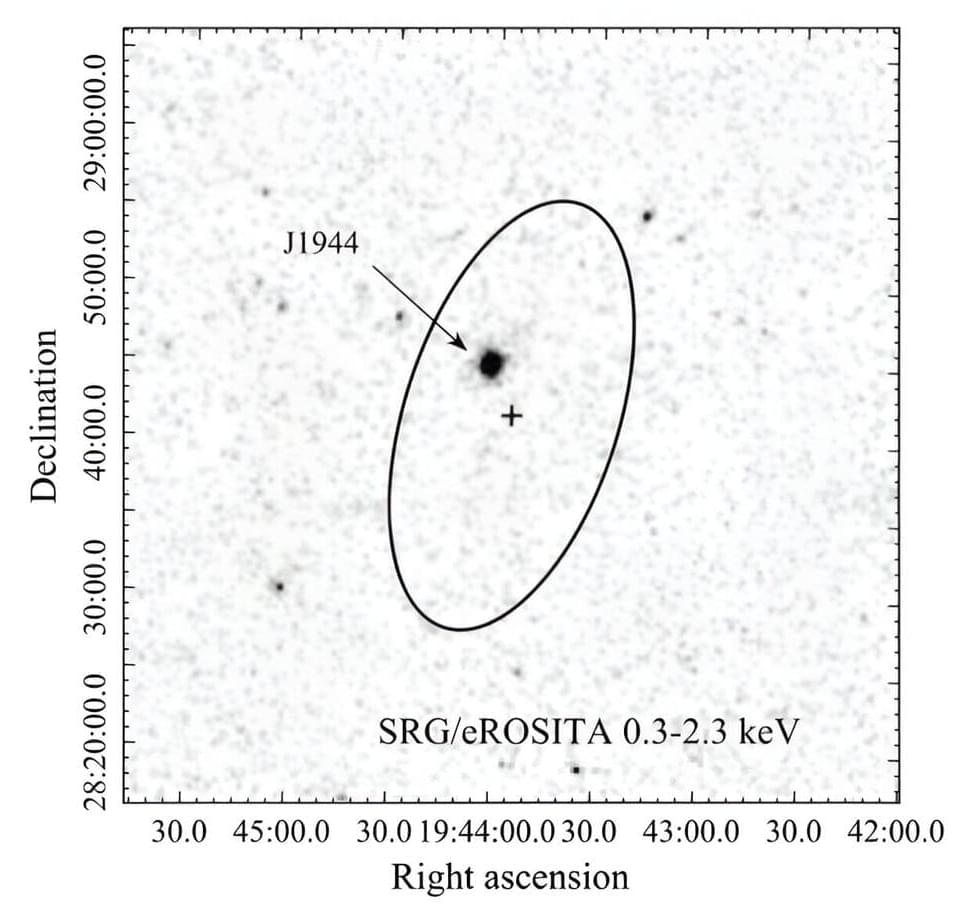
Astronomers from the Special Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) in Russia and elsewhere report the discovery of a new cataclysmic variable system, designated SRGe J194401.8+284452, which is located some 1,350 light years away. The finding was detailed in a research paper published August 26 on the pre-print server arXiv.

A Space Force officer will command a mission later this month to safely bring home two astronauts who have been unexpectedly stuck aboard the International Space Station, or ISS, marking the first time a Guardian will launch into space for such a high-profile operation.
Col. Nick Hague, an active-duty Space Force Guardian, will be joined by Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov aboard the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft for NASA’s Crew-9 mission. Originally, Hague and Gorbunov were supposed to be joined by two other astronauts for a trip to space, but problems with the Boeing Starliner spacecraft that have left astronauts Barry Wilmore and Sunita Williams stuck aboard the space station for months longer than anticipated shifted the mission objective, date and staffing.
Hague and Gorbunov will launch no earlier than Sept. 24, NASA said in a Friday news release, and will return to Earth with Wilmore and Williams in February 2025. The Guardian and the cosmonaut were chosen for their particular experience and skill sets, the agency said.
This belief is slightly paradoxical as we have zero evidence that aliens even exist. What’s more, given the vast distances between star systems, it seems odd we’d only learn about them from a visit. Evidence for aliens is more likely to come from signals from faraway planets.
In a paper accepted for publication in the Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union, I argue that the belief in alien visitors is no longer a quirk, but a widespread societal problem.

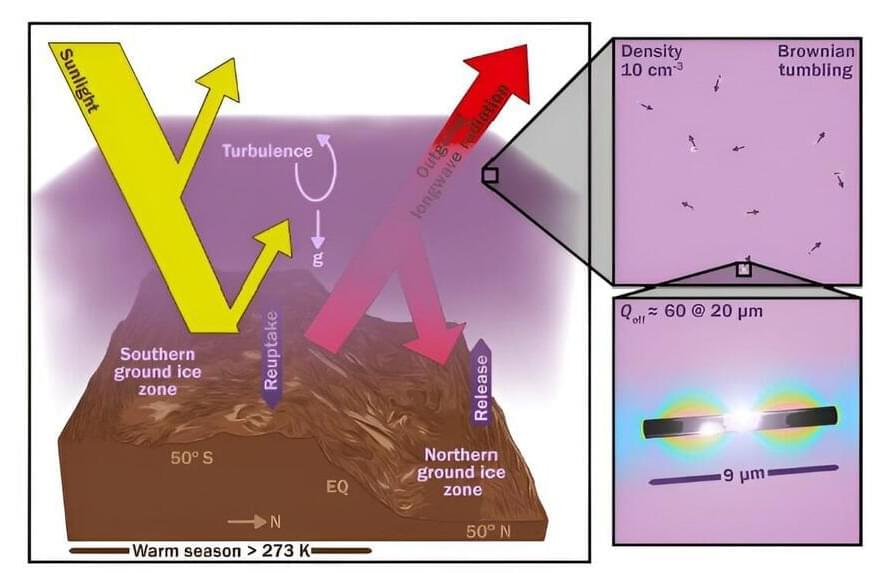
A small team of engineers and geophysicists from Northwestern University, the University of Chicago, and the University of Central Florida has found, via modeling, that creating millions of metal nanorods from material on the Martian surface and then blasting them into the atmosphere would be a more efficient way to heat the planet than generating greenhouse gases. Their paper is published in the journal Science Advances.
Science fiction writers have for many years envisioned a future when Mars is made habitable through terraforming techniques, allowing humans to survive without the need for special buildings and spacesuits. Recently, scientists have begun looking at the possibility, though most project ideas are far less ambitious.
Instead of completely transforming the planet, many are looking at simply warming it up a bit to make it more habitable. Most such ideas have centered on releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere to capture more heat from the sun. Unfortunately, there are few ingredients on the Martian surface that could be used to create and release such gases.