Read about the importance of International Observe the Moon Night and how you can celebrate it on September 14, 2024!
Beginning in 2010, NASA began International Observe the Moon Night based on two events occurring simultaneously in 2009 during the International Year of Astronomy celebration: “We’re at the Moon!”, which was sponsored by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) and the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS) teams, and “National Observe the Moon Night”, which was hosted in the United States.
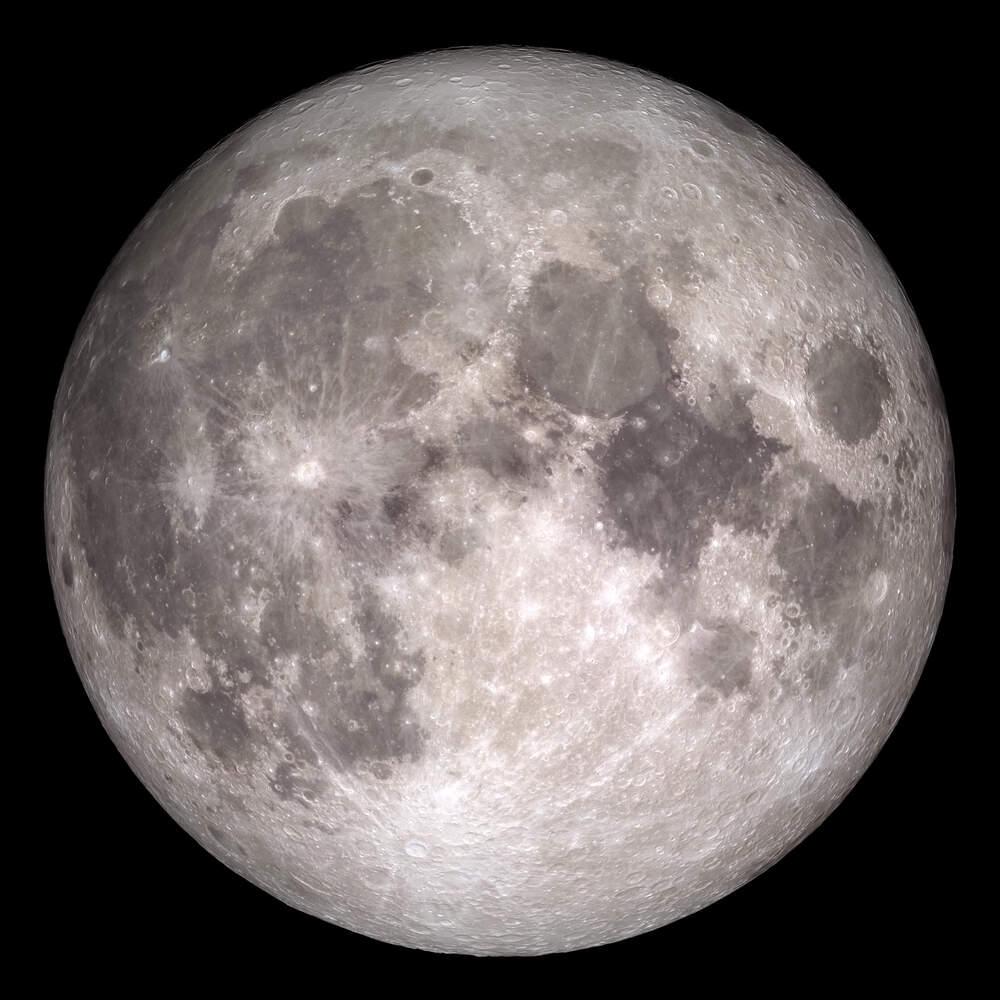
This year’s International Observe the Moon Night is occurring on September 14 with the goal of sharing the incredible science and wonder of the Moon, including its observational and scientific history, why it’s so important to study, and how we’re studying it. For example, evidence has suggested that ancient humans as far back as 20,000 years ago used the Moon as a timekeeping device due to the changing phases of the Moon over the course of a month. Additionally, when observing the Moon with either the naked eye or a telescope, the Moon’s surface exhibits both bright and dark colors, which are the Moon’s lava plains and highlands, respectively.
Regarding its scientific history, the Moon has been studied by astronomers around the world for hundreds of years, with one of the first astronomers to observe the Moon through a telescope and document their findings being Galileo Galilei, finding the Moon’s surface was imperfect and not smooth as had been previously hypothesized. Regarding robotic exploration, the Moon has been explored in-depth beginning with the Soviet Union intentionally crashing the Luna 2 space probe onto the lunar surface on September 14, 1959. This Space Race between the United States and Soviet Union culminated with the United States landing the first man on the Moon in 1969 with Apollo 11.