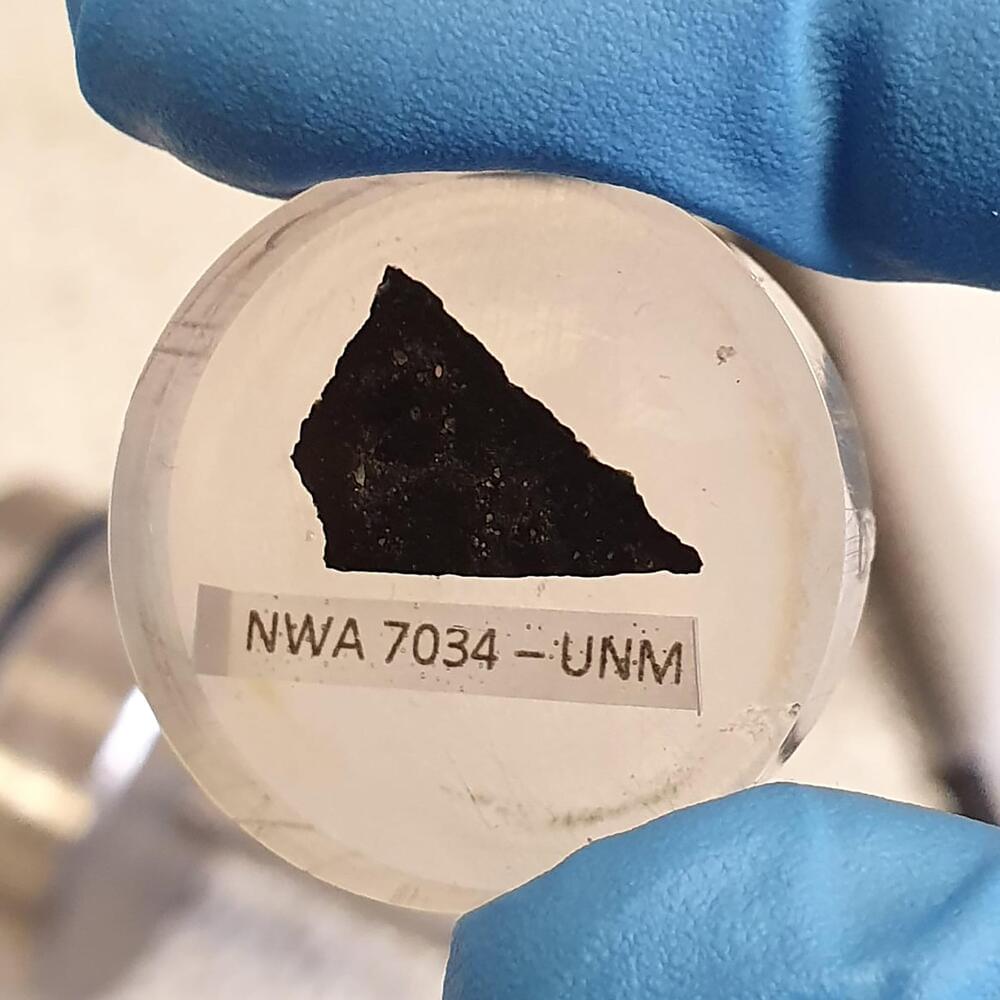
However, Hassabis’ true breakthrough came just a month ago, when he and two colleagues from DeepMind won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their development of AlphaFold, an AI tool capable of predicting the structure of the 200 million known proteins. This achievement would have been nearly impossible without AI, and solidifies Hassabis’ belief that AI is set to become one of the main drivers of scientific progress in the coming years.
Hassabis — the son of a Greek-Cypriot father and a Singaporean mother — reflects on the early days of DeepMind, which he founded in 2010, when “nobody was working on AI.” Over time, machine learning techniques such as deep learning and reinforcement learning began to take shape, providing AI with a significant boost. In 2017, Google scientists introduced a new algorithmic architecture that enabled the development of AGI. “It took several years to figure out how to utilize that type of algorithm and then integrate it in hybrid systems like AlphaFold, which includes other components,” he explains.
“During our first years, we were working in a theoretical space. We focused on games and video games, which were never an end in themselves. It gave us a controlled environment in which to operate and ask questions. But my passion has always been to use AI to accelerate scientific understanding. We managed to scale up to solving a real-world problem, such as protein folding,” recalls the engineer and neuroscientist.