NASA is planning on growing habitable structures out of fungus — also called mycotecture — for space colonies on the Moon and then Mars.
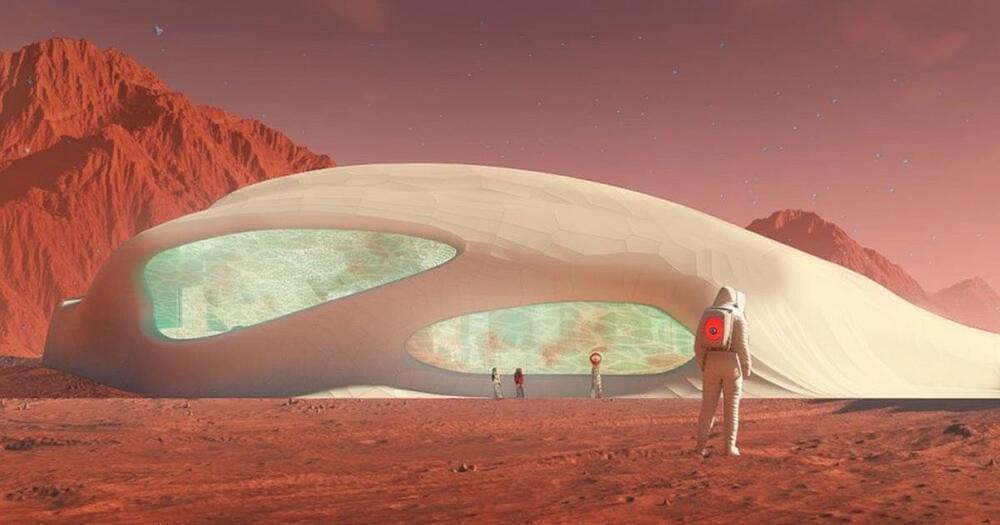
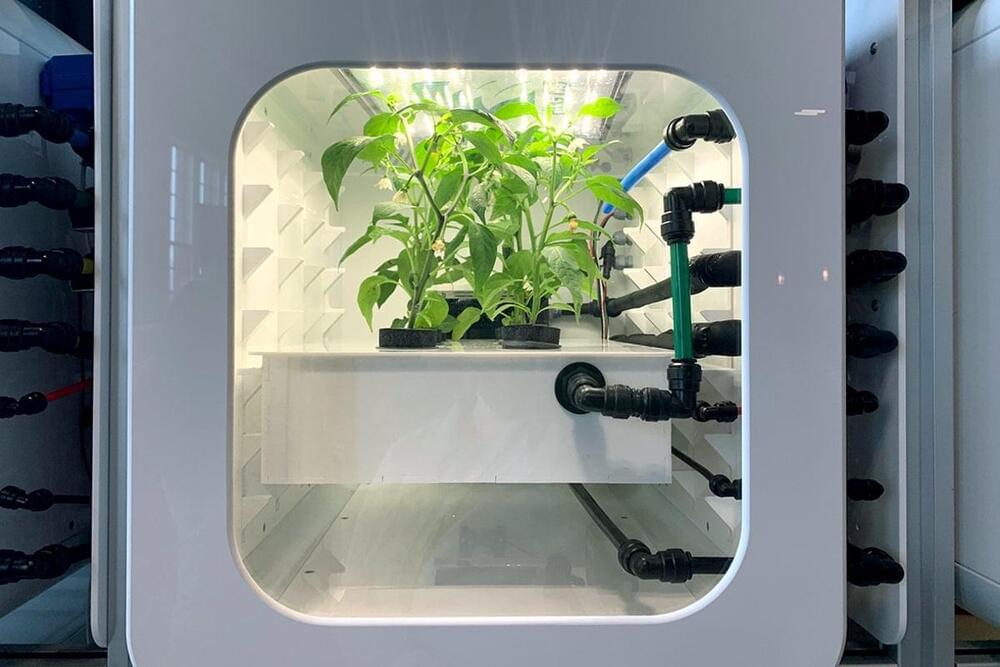



Here’s how the winners of NASA’s Deep Space Food Challenge are making food out of thin air.
A few weeks ago, I arrived hungry to the Brooklyn Navy Yard in New York City, ready for a unique culinary experience. Finalists of NASA and the Canadian Space Agency’s Deep Space Food Challenge had come from all across the planet to demonstrate how future astronauts might grow their own food. I descended upon a tiny cup of chocolate mousse topped with a raspberry.

“Kepler-51e has an orbit slightly larger than Venus and is just inside the star’s habitable zone, so a lot more could be going on beyond that distance if we take the time to look,” said Dr. Jessica Libby-Roberts.
How many exoplanets are in the cosmos and what can they tell us about planetary formation and evolution? This is what a recent study published in The Astronomical Journal hopes to address as an international team of more than 50 researchers announced the discovery of Kepler-51e, which is the fourth planet residing in the Kepler-51 system. This discovery holds the potential to expand our knowledge of exoplanets, specifically regarding their formation and evolution, as Kepler-51e challenges previous notions about low-density exoplanets, also called “puff planets” or “Super-Puffs”
“Super puff planets are very unusual in that they have very low mass and low density,” said Dr. Jessica Libby-Roberts, who is a Postdoctoral Scholar in the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at Penn State University and second author of the study. “The three previously known planets that orbit the star, Kepler-51, are about the size of Saturn but only a few times the mass of Earth, resulting in a density like cotton candy.”
For the discovery, the researchers used NASA’s powerful James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) using a method called transit timing variations, which are caused by other planets in the system tugging on each other, resulting in very slight changes in their orbits. For example, the team noticed that the third planet in the system, Kepler-51d, transited its star two hours earlier than anticipated, indicating the gravity of an unknown fourth planet was tugging on it.
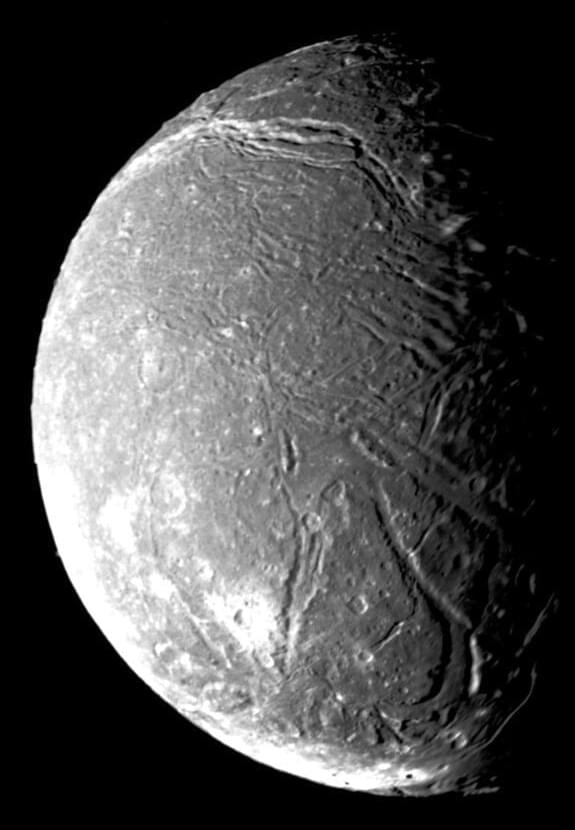

“Discovering liquid water oceans inside the moons of Uranus would transform our thinking about the range of possibilities for where life could exist,” said Dr. Douglas Hemingway.
Do the moons of Uranus have interior liquid oceans like the moons of Jupiter and Saturn? This is what a recent study published in Geophysical Research Letters hopes to address as a pair of researchers investigated the likelihood of five Uranus moons, Miranda, Ariel, Umbriel, Titania, and Oberon possessing interior oceans. This study holds the potential to not only help researchers better understand the compositions of these moons, but also establish a framework for sending a spacecraft to Uranus for the first time since NASA’s Voyager 2 in 1986.
For the study, the researchers used computer models to simulate changes in each moon’s wobble with the goal of estimating the potential amount of liquid water that each moon could be harboring. This technique could be used to detect liquid oceans within these moons, thus increasing the feasibility of a future spacecraft mission to Uranus.
In the end, the researchers found that oceans greater than 40 kilometers (25 miles) thick could be detectable, but ocean thickness less than that could prove difficult to detect without better resolution of the wobble calculations. Using these wobble calculations, the researchers estimate that a wobble of 300 feet could indicate an ocean 100 miles thick with an ice shell of 20 miles, using Ariel as an example.
When it is solicited, the research emphases of E.9 Space Biology: Research Studies will fall under two broad categories: Precision Health and Space Crops.
For Precision Health-focused studies, investigators may propose to use any non-primate animal model system, and any appropriate cell/tissue culture/ microphysiological system/ organoid or microbial models, that are supported by the chosen platform. For Space Crop-focused studies, applicants may propose to use any plant model system, and when appropriate, any microbial or plant and microbial model systems that are supported by the chosen platform.
This opportunity will include five different Project Types: Research Investigations, Early Career Research Investigations, New NASA Investigators, GeneLab Analytical Investigations, and Tissue Sharing Investigations.
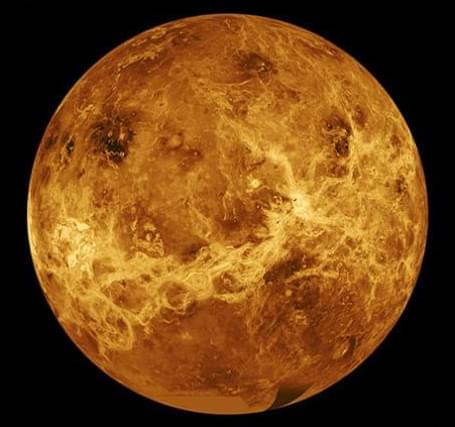


Did Venus have oceans in its ancient past and could they have supported life as we know it, or even as we don’t know it? This is what a recent study published in Nature Astronomy hopes to address as a team of researchers from the University of Cambridge investigated the climate history of Venus and whether it possessed liquid water oceans on its surface deep in its past. This study holds the potential to help scientists better understand past conditions on planetary bodies throughout the solar system and what this could mean for finding evidence of ancient life beyond Earth.
For the study, the researchers used computer models to estimate how fast the Venusian atmosphere is losing water, carbon dioxide, and carbonyl sulphide molecules, all of which are required to be replenished by volcanic gases so atmospheric stability can be maintained. Therefore, by studying how fast these molecules are leaving the atmosphere, scientists can estimate the amount of present and past volcanic activity on Venus, thus determining if Venus once had oceans of liquid water that might have supported life as we know it. In the end, the researchers determined that Venus is far too dry to have ever possessed bodies of liquid oceans on its surface.
“We won’t know for sure whether Venus can or did support life until we send probes at the end of this decade,” said Tereza Constantinou, who is a PhD student at Cambridge’s Institute of Astronomy and lead author of the study. “But given it likely never had oceans, it is hard to imagine Venus ever having supported Earth-like life, which requires liquid water.”
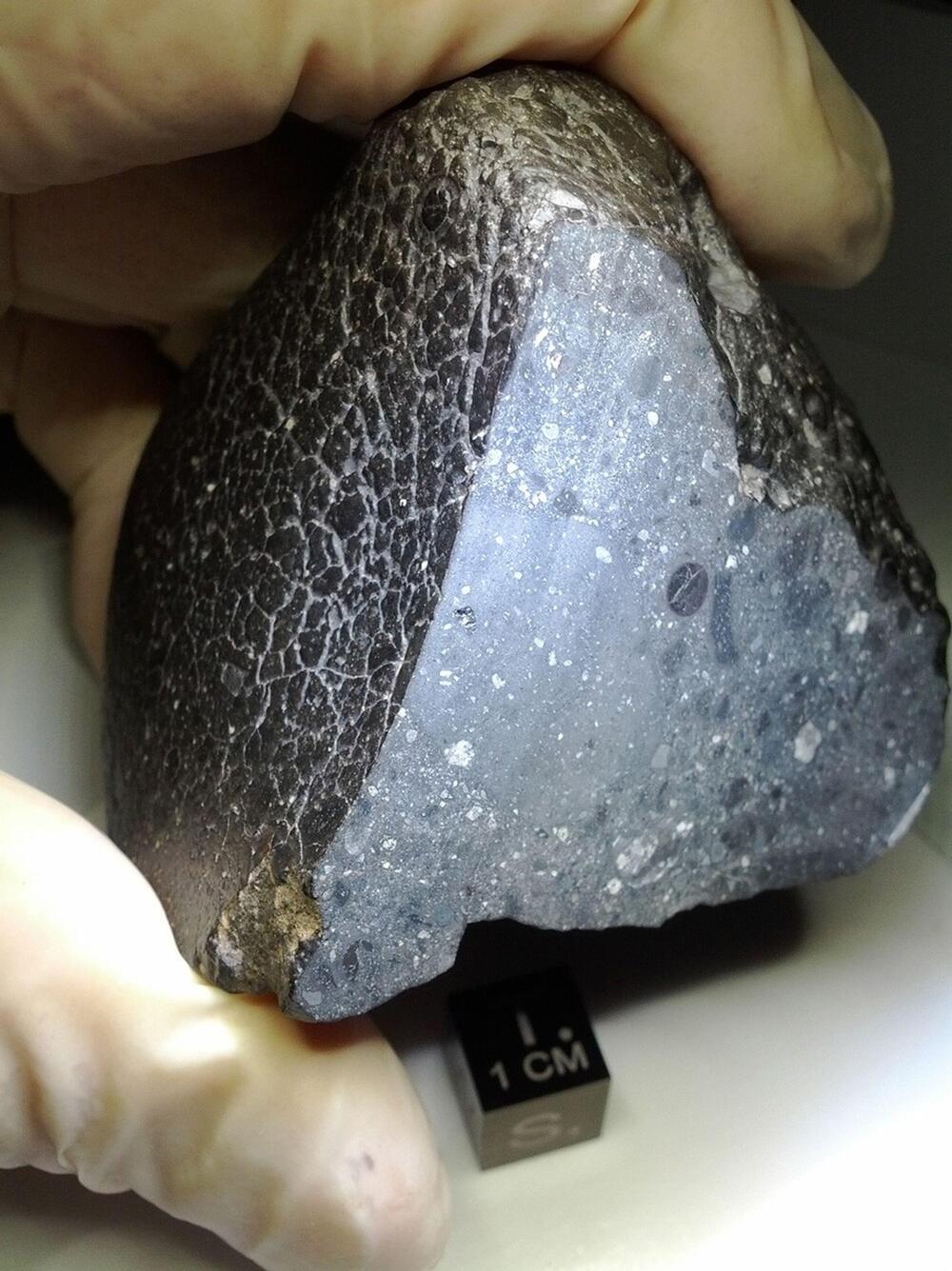

For the study, the researchers conducted microscopy analyses of a zircon grain obtained from Black Beauty, which builds off a 2022 study involving the same zircon grain where researchers found the grain had experienced being “shocked” from a meteorite impact long ago. For this latest study, the researchers found that the zircon grain contained unique evidence regarding past liquid water on the Red Planet.
“We used nano-scale geochemistry to detect elemental evidence of hot water on Mars 4.45 billion years ago,” said Dr. Aaron Cavosie, who is a senior lecturer in the School of Earth and Planetary Sciences at Curtin University and a co-author on the study. “Hydrothermal systems were essential for the development of life on Earth and our findings suggest Mars also had water, a key ingredient for habitable environments, during the earliest history of crust formation. Through nano-scale imaging and spectroscopy, the team identified element patterns in this unique zircon, including iron, aluminum, yttrium and sodium. These elements were added as the zircon formed 4.45 billion years ago, suggesting water was present during early Martian magmatic activity.”
A mysterious object discovered in the main asteroid belt in 2021 was determined to be a main-belt comet by Planetary Science Institute Senior Scientist Henry Hsieh, Scott Sheppard of the Carnegie Institution for Science and Audrey Thirouin of Lowell Observatory.
Main-belt comets are icy objects found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter—rather than the cold outer solar system where icy bodies are typically expected. They sport comet-like features, like tails extending away from the sun or fuzzy clouds as the sun’s heat vaporizes their ice. They were first discovered in 2006 at the University of Hawaii by Hsieh and his then-doctoral advisor, David Jewitt.
Main-belt comets belong to a larger group of solar system objects known as active asteroids, which look like comets, but have asteroid-like orbits in the warm inner solar system. This larger group includes objects whose clouds and tails are made of ejected dust produced after an impact or as they quickly rotate, rather than just those that eject dust due to vaporized ice. Both main-belt comets and active asteroids in general are still relatively rare, but scientists are discovering them at a growing clip.
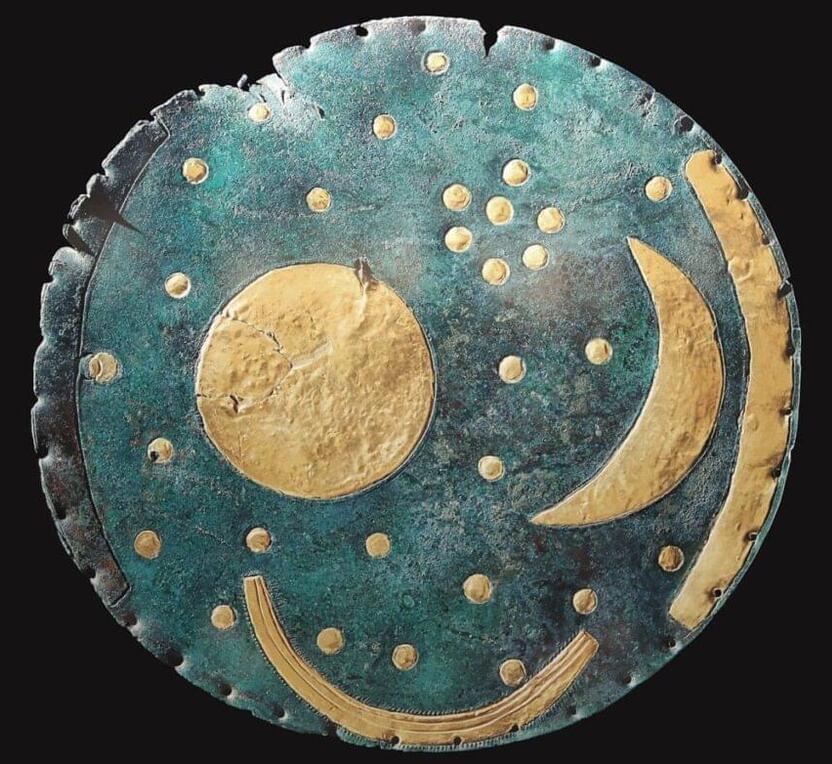

Discovered in 1999 in Germany, the Nebra Sky Disc is the oldest known depiction of the cosmos. A recent examination of the Bronze Age artifact revealed the intricate methods used in its creation, which UNESCO described as “one of the most important archaeological finds of the twentieth century.”
The Nebra Sky Disc is a product of the Únětice culture, which originated in the Bronze Age of Central Europe. It reflects a sophisticated ancient understanding of both metalworking and astronomy and was created sometime between 1800 and 1,600 BCE. Clusters of stars, a sun, and a crescent moon are among the celestial bodies depicted by golden inlays covering the blue-green patina of the Nebra Sky Disc. The angle between the solstices is thought to be indicated by two golden arcs that run along the sides of the disc, one of which is now absent. It is thought that a boat is represented by another arc at the composition’s base. Only a few millimeters thick, the disc has a diameter of around 12 inches.
The Nebra Sky Disc is one of the best-investigated archaeological objects. The origin of the raw materials it is made of is well known The disc is made from copper, tin, and gold—materials whose origins have been traced to Cornwall, England. The rich blue-green patina of the disc’s bronze today results from chemical changes over time. Originally, it would have been a deep bronze hue.